Select the Reactions tab in the Nodal Value Selection dialog to select nodal values for reactions for presentation.
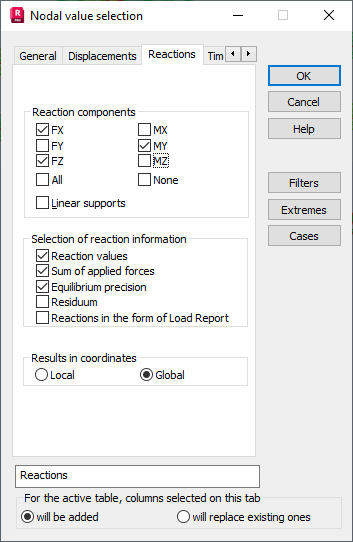
You can select the folowing force components for presentation.
- FX, FY, FZ - If selected, they add table columns to display reaction forces obtained during the structure analysis (X-axis direction, Y-axis direction or Z-axis direction, respectively).
- MX, MY, MZ - If selected, they add table columns to display reaction moments obtained during the structure analysis (X-axis direction, Y-axis direction or Z-axis direction, respectively).
It is also possible to display values of linear reactions for supports defined as linear on edges. These are displayed at nodes belonging to the linear support on the edge. At the remaining support nodes the value will be shown as N/A. Values of linear reactions are calculated as a value of the nodal reaction divided by half the length of sides of the elements adjoining the node. A linear reaction unit is force or moment per length unit.
You can specify the following parameters in the Selection of Reaction Information field.
- Reaction values - displays in the table selected force components in the supported nodes. When inactive, the parameters from the Selection of Reaction Information field (instead of force component values) are presented in the table.
- Sum of applied forces
Sum of applied forces
The following rows will be added to a table.
- Sum of val. - An arithmetic sum of values of forces and moments for a given direction for the currently-filtered nodes.
- Sum of reac. - A sum of values of forces and reaction moments for a given direction for all support nodes (considering the elastic ground reaction).
- Sum of forc. - A sum of values of forces and moments from external loads for a given direction.
The sum of forces is specified for each direction of the global coordinate system.
The sum of moments (for the sum of reactions and the sum of forces) is determined with respect to the point with coordinates (0,0,0). The moments and forces operating at appropriate distances (arms) are taken into account, and recalculated with respect to coordinate point 0,0,0.
In quadratic combinations for cases of the seismic or spectral analysis, the sum of reactions and the sum of forces are calculated by adding the values of the respective sum of values and the sum of forces for individual vibration modes.
- Equilibrium precision - adds a table column to display the equilibrium precision value of the structure. This describes the global equilibrium of applied forces and reactions obtained during structure analysis.
- Residuum - adds a table column to display the parameter which represents the sum of external forces and reactions in the supported nodes for each load case.
- Reactions in the form of Load Report option - allows presenting the reactions in the form that is used in the Robot Load Report.
Precision Value 1
For each node in a structure, the maximum values of force F and moment M, as well as residual forces F (RF) and residual moments M (RM) are calculated. The value RF/max F and RM/max M is calculated for each node. The value of precision is equal to the greater of the quotients.
Precision Value 2
Residual forces F (RF in support nodes) and residual moments (RM in support nodes) are calculated. Then, for each node, |RF| / |Reaction F| and |RM| / |Reaction M| are calculated; The value of precision is equal to the greatest among the calculated values. In this case F, RF, M and RM are vectors.
The value of precision is calculated in a slightly different manner for combinations of load cases. For example, a combination of 1000 load cases with the precision equal to 0.001 for each case will have the precision equal to 1.0.
You can select either local or global coordinate systems in which the obtained reaction values will be presented.