Intersection points show the relationships between the straights and curve groups in an alignment.
There are two types of intersection points:
Explicit Intersection Points
An explicit intersection point is the point at which two fixed straights meet on a horizontal alignment.
When an alignment is selected, an explicit IP is represented by a  grip. An explicit intersection point can be labeled, moved, deleted, or broken apart.
grip. An explicit intersection point can be labeled, moved, deleted, or broken apart.
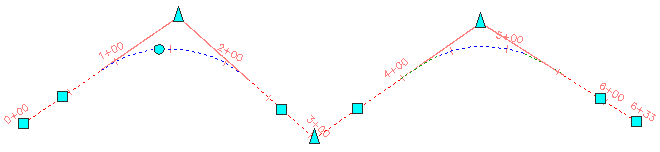
Implied Intersection Points
An implied intersection point is the computed intersection point (IP) at an alignment curve or curve group. An implied IP indicates where straights would meet if they were extended. An implied intersection point can be labeled.
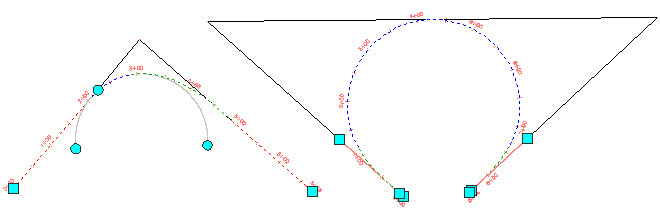
When an alignment is selected, the implied IP of two fixed straights that are joined by a free curve or curve group is represented by a  grip. When the
grip. When the  grip is present, the IP can be solved, which extends the fixed straights to an explicit IP.
grip is present, the IP can be solved, which extends the fixed straights to an explicit IP.
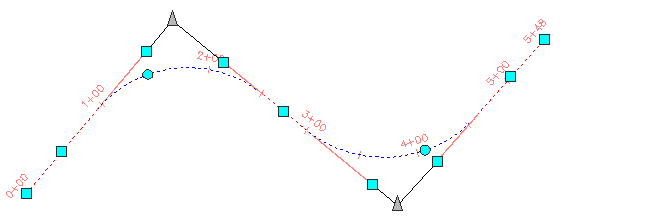
The display of implied IPs is controlled on the Intersection Point Tab (Alignment Properties Dialog Box).