Sets display options for the Legacy Direct3D display driver.
Interface
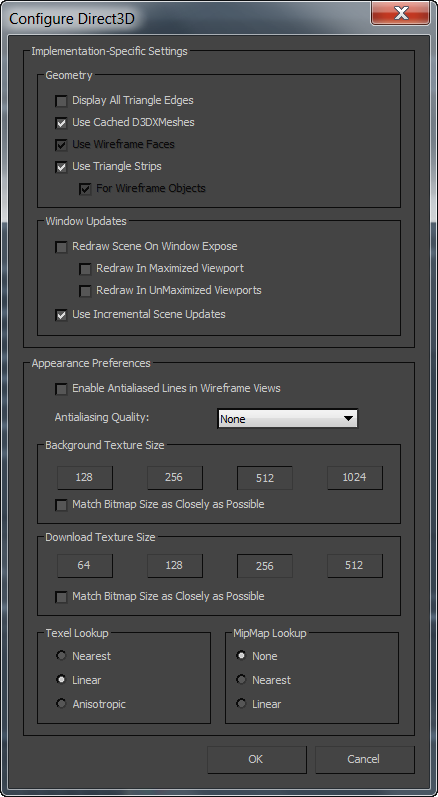
Implementation-Specific Settings group
Geometry group
- Display All Triangle Edges
- When on, all triangle edges are displayed in shaded viewports. When off, triangle edges are not displayed. Default=on.
Turning off this option can improve viewport appearance, but at a cost of display performance.
- Use Cached D3DXMeshes
- When on, enables 3ds Max to use custom driver code to render smoothly shaded objects. Typically this is much faster than using standard Direct3D code, but has an effect only when the driver has hardware-specific custom code. Default=on.
- Use Wireframe Faces
- When on, makes wireframe display accessible to hardware acceleration. Default=on.
This option is intended to allow display-card manufacturers to accelerate 3ds Max wireframe displays in a way that is specific to the underlying display hardware. Check with your display-card manufacturer to see if enabling this option will yield faster wireframe rendering with your display card.
- Use Triangle Strips
- Strips all geometric data out before sending it to the driver. In some cases, such as when topology is constantly changed, the time taken to strip the geometry can cause a slowdown instead. In such cases, turn off this option. Otherwise, leave it on for speed. Default=on.
This option has one subordinate option:
For Wireframe Objects When on, uses triangle strips for wireframe objects. Default=off.
Window Updates group
- Redraw Scene On Window Expose
- Redraws the whole scene when a dialog over the viewports is moved, resulting in smoother dragging of dialogs such as the Material Editor or Track View. However, redrawing takes some time. Default=on.
If the display becomes messy or "corrupted," turn this option on and then redraw viewports by choosing Views
 Redraw All Views (the default keyboard shortcut for this is the
` (accent grave) key, on the left side of the
1 key).
Redraw All Views (the default keyboard shortcut for this is the
` (accent grave) key, on the left side of the
1 key).
This option has two subordinate options. How you should set them depends on how the display card handles its back buffer, which is used for refreshing the screen. Turn on one or the other, as appropriate.
Redraw In Maximized Viewport If, after updating the screen, the display card destroys the back buffer only when there's a single viewport, turn on this sub-option. The Direct3D driver redraws the scene when a single viewport is visible, but doesn't have to redraw when multiple viewports are visible. Default=off.
Redraw In UnMaximized Viewports If, after updating the screen, the display card destroys the back buffer when multiple viewports are visible, turn on this sub-option. Default=off.
- Allow Dual Plane Support
- Uses the front/back plane system when redrawing the viewport. The selected object is manipulated in the front plane and is redrawn, while other objects remain on the back plane and are not redrawn. This default setting provides the fastest redraws under normal circumstances. If your assigned display driver doesn't support dual planes, this option is not available.
Turn off this setting to improve redraw speed if you are rotating the whole scene or moving a camera through the scene (usually situations in which the whole viewport needs to be redrawn anyway).
- Use Incremental Scene Updates
- Redraws only those scene objects that have changed, or that intersect a region changed by another moving object. When off, the entire scene is redrawn for each new frame. Default=on.
If the display becomes messy or "corrupted" as a result of incremental updates, turn this option off and then redraw viewports by choosing Views
 Redraw All Views (the default keyboard shortcut for this is
1 on the numeric keypad).
Redraw All Views (the default keyboard shortcut for this is
1 on the numeric keypad).
Appearance Preferences group
- Enable Antialiased Lines in Wireframe Views
- When on, draws lines slightly thicker and much smoother. This is best used for wireframe-only views, especially if you're making a preview of wireframe objects. Default=off.
- Antialiasing
- Sets a level of antialiasing to use for viewports. The higher the number of samples, the smoother lines and edges in viewports will appear. (This setting is independent of the Antialiased Lines In Wireframe Views setting.)
- None (The default.) Don’t use antialiasing.
- 2 Samples
- 4 Samples
- 8 Samples The high number of samples is determined by the graphics card: This list can vary, depending on the card your system uses.
If you change the Antialiasing level, the change takes place immediately, without your having to restart 3ds Max.
- Background Texture Size
-
128, 256, 512, 1024 Unlike the software display driver, which uses bitmaps to display viewport backgrounds directly, the Direct3D driver uses a texture-mapped background rectangle. This allows for smoother zooms and pans in orthographic views and can take less memory than the direct bitmap method. However, background bitmap resolution can be lost. Increase the resolution if you're using a maximized viewport to digitize.
Match Bitmap Size as Closely as Possible Displays background at full resolution. This allows the viewport to behave like the Rendered Frame Window, in regards to zoom and pan. Default=off.
- Download Texture Size
-
64, 128, 256, 512 Lets you choose the size of the texture map that's downloaded to the driver for texture-mapped scene objects. Larger maps look better, but use more display card memory. Default=256.
Note: When Match Bitmap Size As Closely as Possible is on, these buttons are overridden, however they are still available. The value is still used when procedural textures are converted to bitmaps for viewport texture display.Match Bitmap Size as Closely as Possible To allow the viewport to show actual texture resolutions, bitmaps are individually resized before they are downloaded to the driver. This means that small bitmaps don’t get overexpanded and large bitmaps retain their resolution (but potentially use a lot more video RAM).
Note: Bitmaps can be no larger than 4000 x 4000 pixels (or they will be scaled down to this size) and no smaller than 32 x 32 (or they will be scaled up to this size). Default=off. - Texel Lookup
-
Specifies whether to use the nearest pixel, to linearly interpolate the pixel value from the four closest texels, or to use anisotropic filtering. Using the nearest pixel is faster, but using texels produces a higher-quality display. The Anisotropic filter compensates for the distortion caused by the difference in angle between the texture polygon and the plane of the screen. Default=Nearest.
- MipMap Lookup
-
Specifies whether to use one version of the texture map (None) or to interpolate between a pyramid of progressively smaller maps. With Nearest chosen, the texel lookup is done on the map level nearest the ideal one, and with Linear, the texel values from the two closest map levels are interpolated. Default=None.
Note: When both Texel and MipMap lookup are set to Linear, a true trilinear weighting of 8 texel values is used for a single pixel display. This is very accurate and helps eliminate aliasing, but it is time consuming if the texture-mapping hardware is not accelerated.