Retopology Tools for 3ds Max

Use Retopology Tools to automatically optimize the geometry of your high-resolution model to create a clean, quad-based mesh. Useful for removing artifacts and other mesh issues for animation and rigging, these tools can also be used to apply textures and manipulate objects.
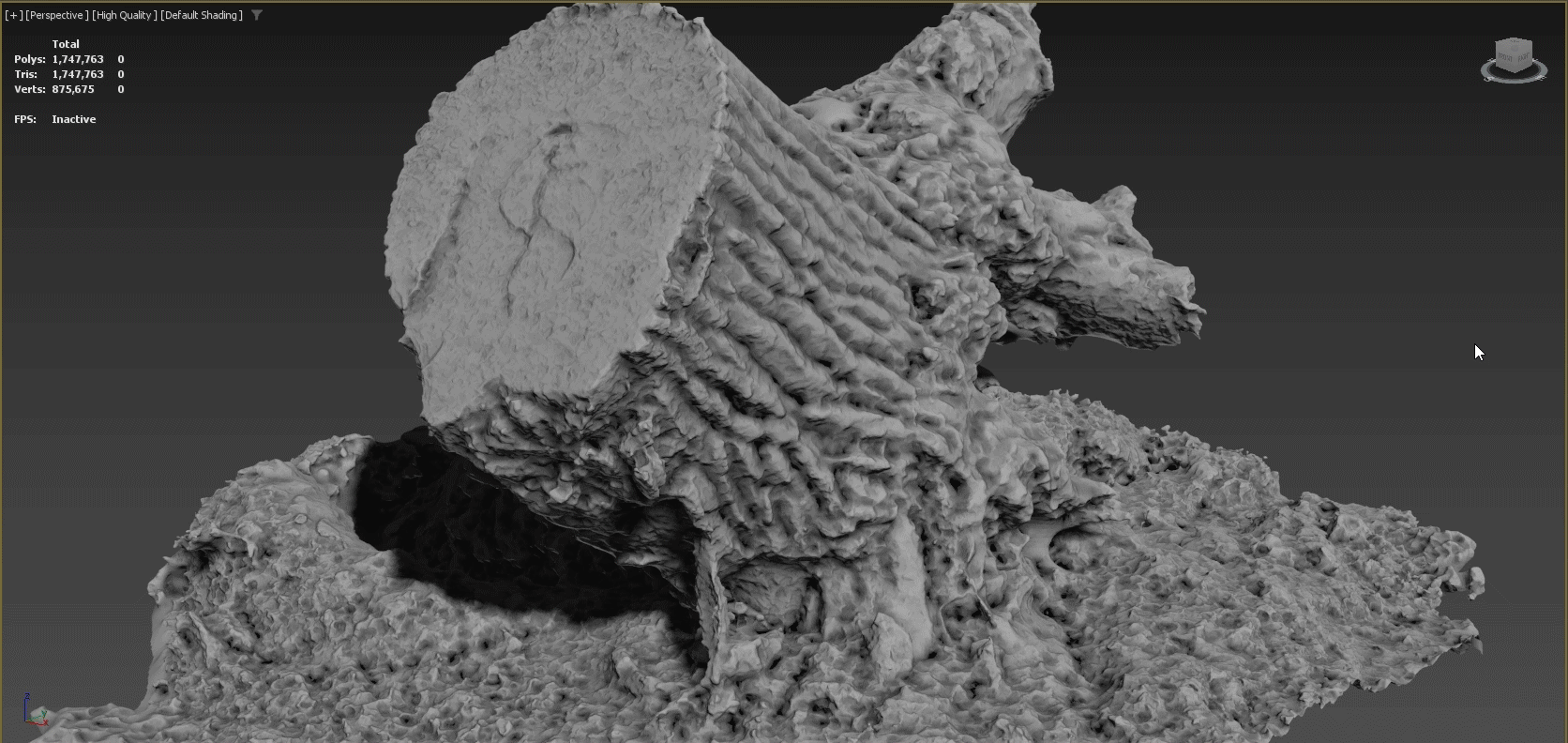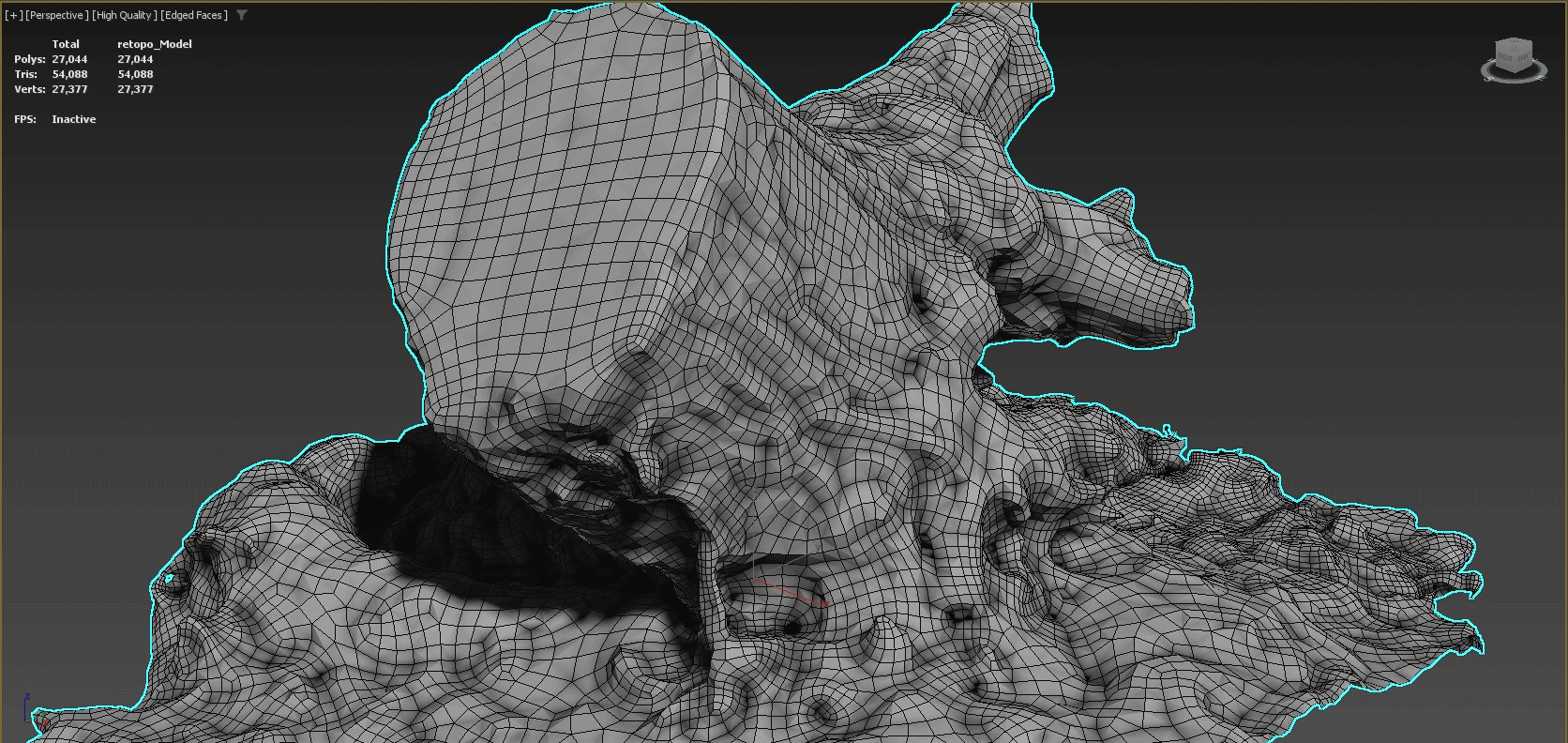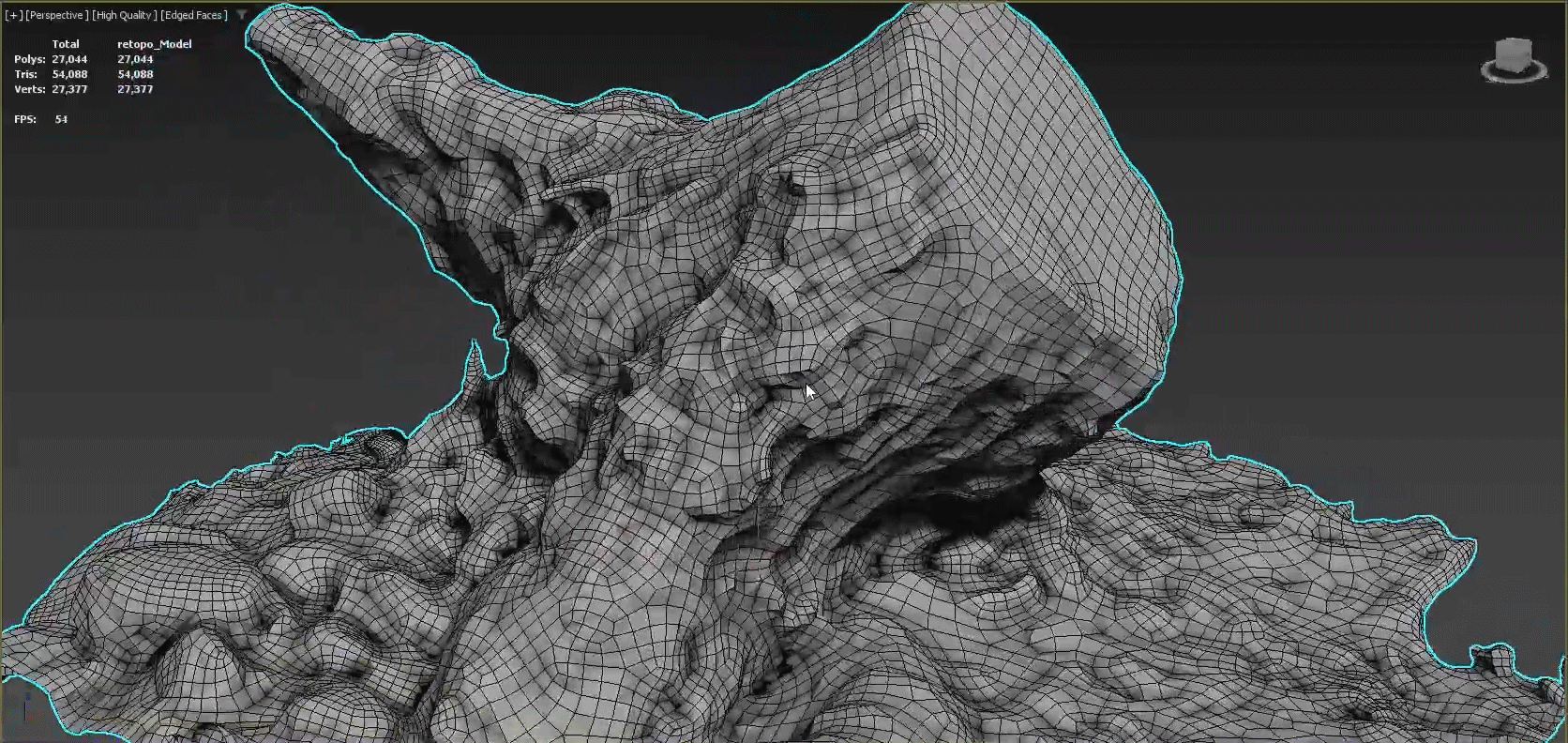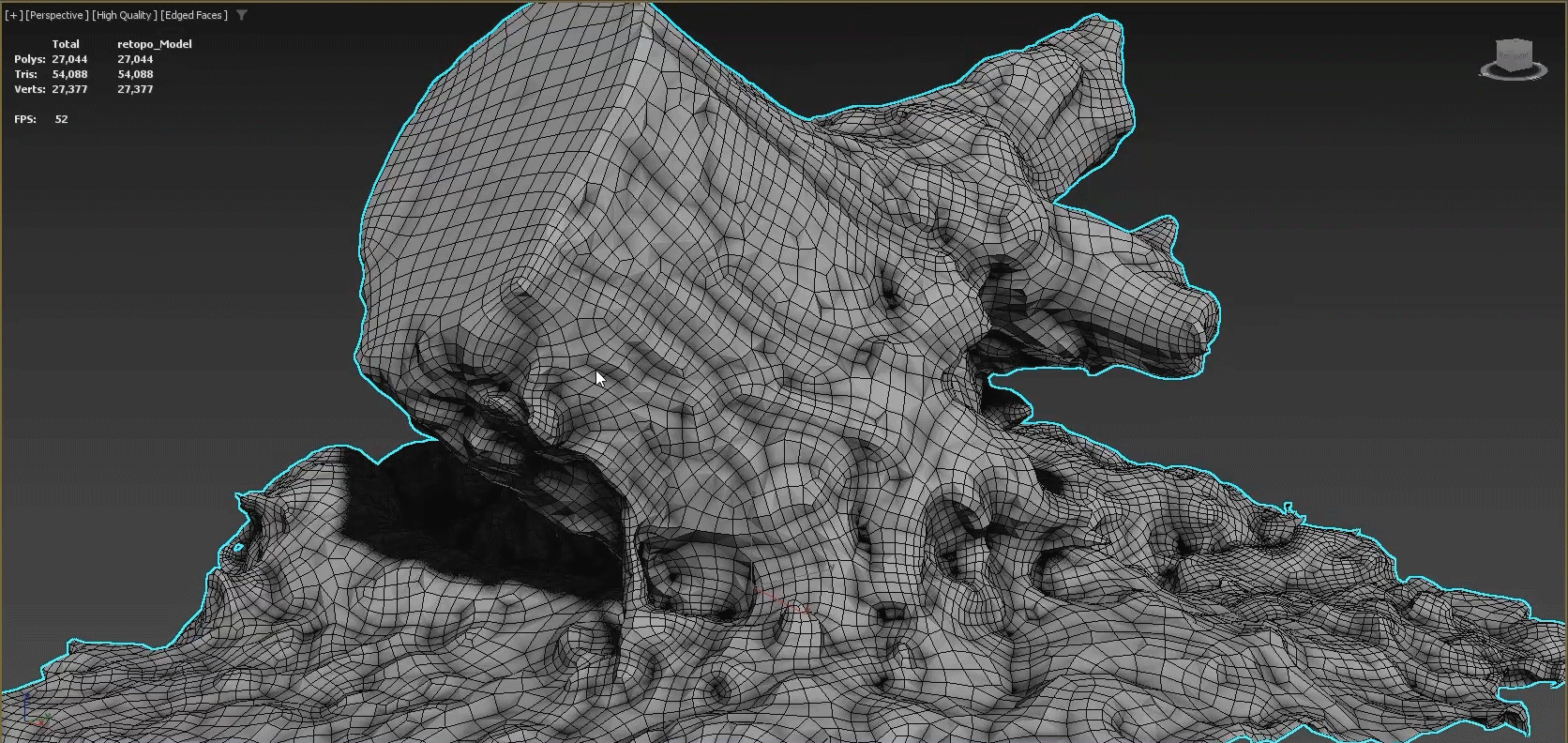
A clean 3D topology is key to achieving professional results. When a model's vertices, edges, and faces are better organized, animations will appear much more fluid and rendering will require less memory. Poorly-optimized meshes can also create visual artifacts as well as problems when applying modifiers. Using the Retopology Tools for 3ds Max, you can quickly correct many common problems introduced by a less than optimal mesh.
Retopology Best Practices
The following tools and techniques will help you quickly achieve great results when working with Retopology Tools for 3ds Max.
Poly Count and Shape
The Preprocess Mesh option, introduced in Retopology Tools v1.2, reduces the need to prepare and configure meshes for retopology when using the ReForm algorithm. This is due to the retopology modifier algorithm creating an intermediary triangle-based Remeshed Mesh that is used as a foundation to build the final quad Retopology Mesh.
However, there may be circumstances for artists to choose to retopologize a mesh with ReForm, without using Preprocess Mesh. In this case, a form of best practice is to ensure that the input mesh contains uniform, equally-distributed faces. Here, it is also best to ensure the polygon count of the object is less than 200,000 in order to achieve algorithm results in a reasonable amount of time. A number of modifiers are available that can help optimize the mesh before beginning the operation or if you encounter areas after computing that are still not desirable.
Useful Modifiers
The following modifiers can be applied to your mesh before the Retopology modifier to help achieve the best and fastest results.
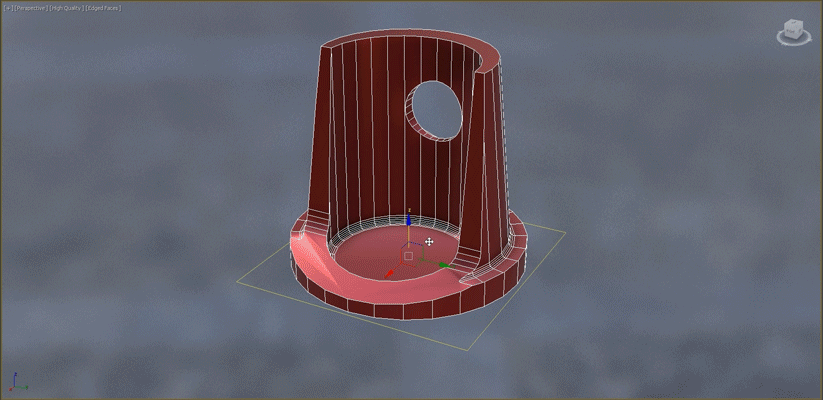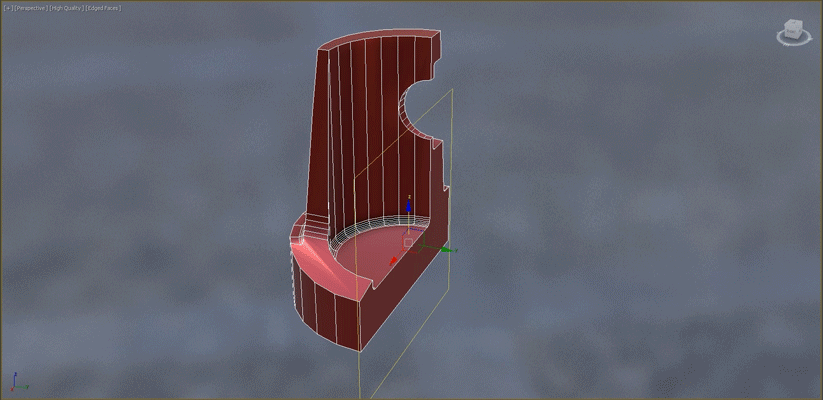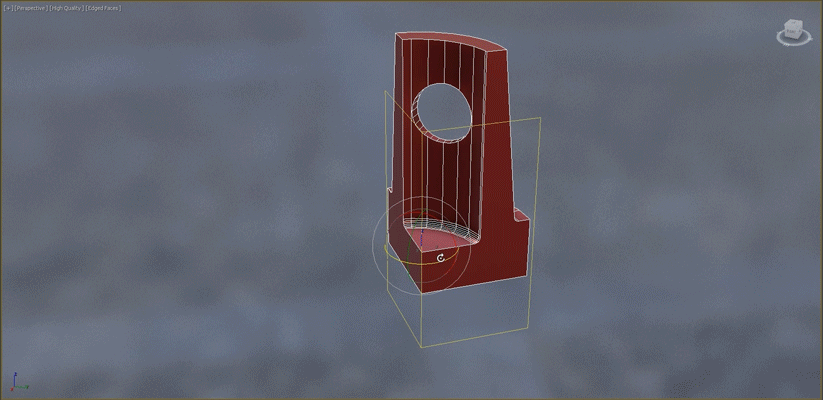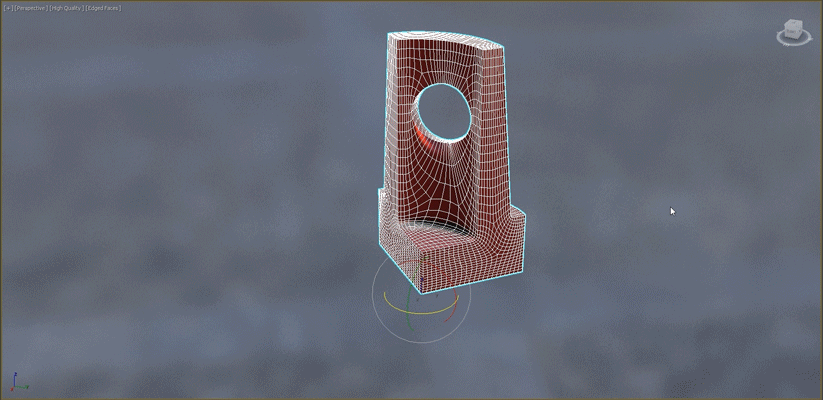
- Slice: When working with symmetrical objects, use the Slice modifier to slice the object in half before beginning the Retopology operation. This will reduce calculation time.
- Smooth: Useful for cleaning the mesh and applying smoothing groups before beginning the Retopology operation.
- ProOptimize: Before computing the retopology, you can use this modifier to reduce the overall poly count.
- Subdivide: Retopology works best on meshes containing either quads or uniform triangular polys. If a mesh contains long, thin triangular faces, use the Subdivide modifier to create smaller, more even triangles before beginning any retopology operations.
- Mesh Cleaner: Data imported from other applications or processed through operations such as Boolean can have malformed data that can impede the ability for Retopology to succeed or process quickly. Before applying the Retopology modifier, use Mesh Cleaner check and fix such errors.
- Relax: The ReForm algorithm is tuned to produce a topology output that is as accurate to the input mesh as possible. Due to this, if you are attempting to retopologize a mesh with lots of noise or high frequency data, this can result in a longer retopology operation. To aid the retopology process, applying a Relax Modifier with volume preservation active and a few iterations applied, before the Retopology modifier can help speed up the process. This will reduce the surface noise without hindering the integrity of the input mesh.
- ProOptimize: Before computing the retopology operation, you can use this modifier to reduce the overall poly count. This modifier is not necessary if you are using Pre-Processing in the Retopology Modifier.
- Subdivide: Retopology works best on meshes containing either quads or uniform triangular polys. If a mesh contains long, thin triangular faces, use the Subdivide modifier to create smaller, more even triangles before beginning any retopology operations. This modifier is not necessary if you are using Pre-Processing in the Retopology Modifier.
Post Retopology Processes
- Weighted Normals: After generating an output you may want to apply a Weighted Normals (or Smooth) modifier onto your retopology output to generate a new set of explicit normal for the model.
- Symmetry: After using the tools to achieve an optimal topology on a sliced object, restore the other half of the object using the Symmetry modifier.
- Edit Poly/Edit Mesh: The retopology output is based on what the algorithm assumes and infers from your mesh data. Sometimes this results in data that may need small adjustments or quick fixes which can be done by applying Edit Poly or Edit Mesh modifiers. Examples include capping holes, bridging edges, moving vertices, removing extra edge loops.
Generative and Low Poly Models
The Retopology Tools are not only useful for reducing polygon topology, but also to aid in the modeling process, assisting in the generation of clean quad topology, with a consistent spacing of polygon faces that can be further manipulated with an Edit Poly modifier or by collapsing the stack to an Editable Poly object.
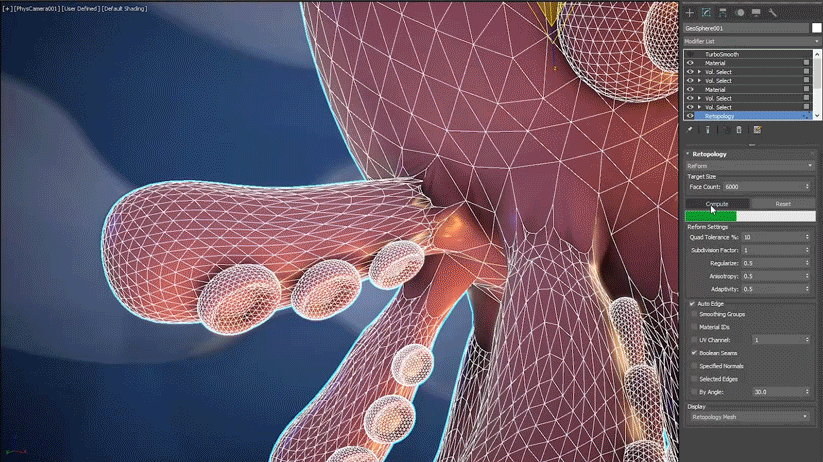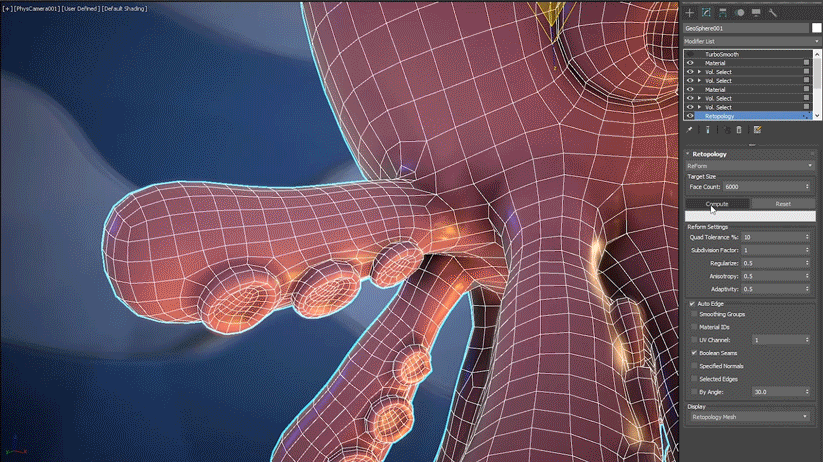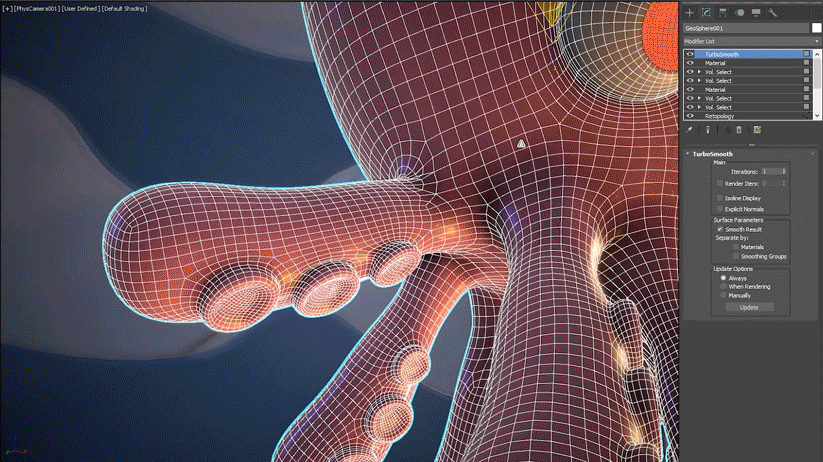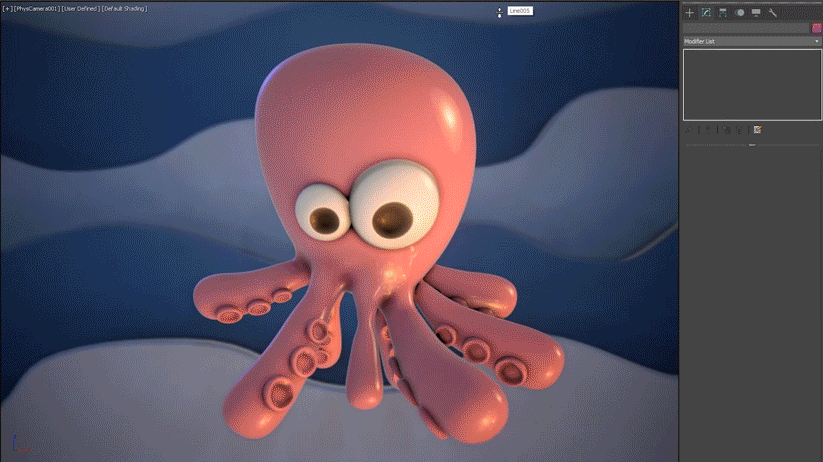
Common workflows with Retopology tools include extruding splines into geometry, cleaning up Boolean operations, and performing Smart Extrude operations. When working with low-poly models that you plan to Boolean together and then retopologize into a clean quad output, it is recommended that you first remesh using the Subdivide modifier or use sub-divisional surfaces to add more form to your model.
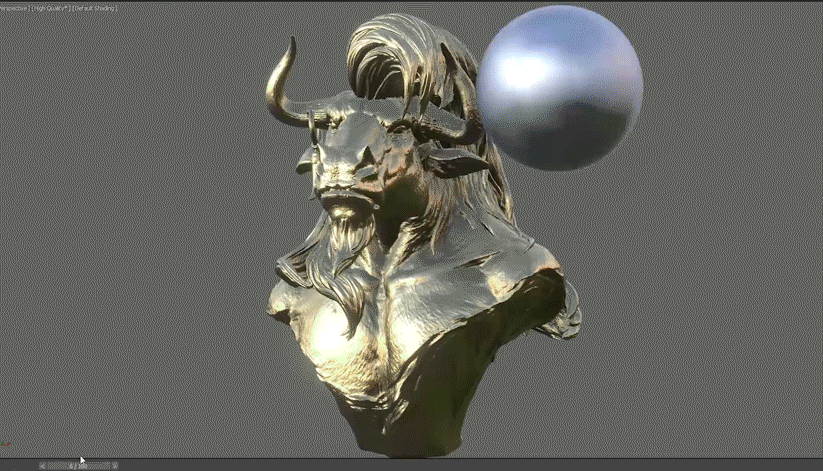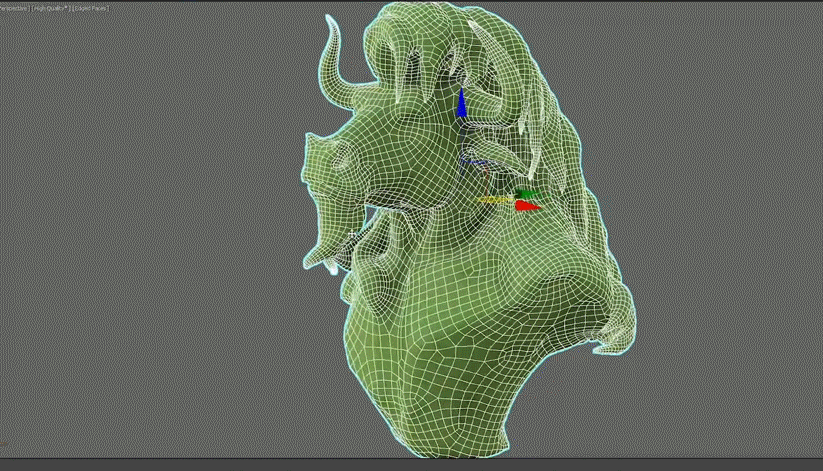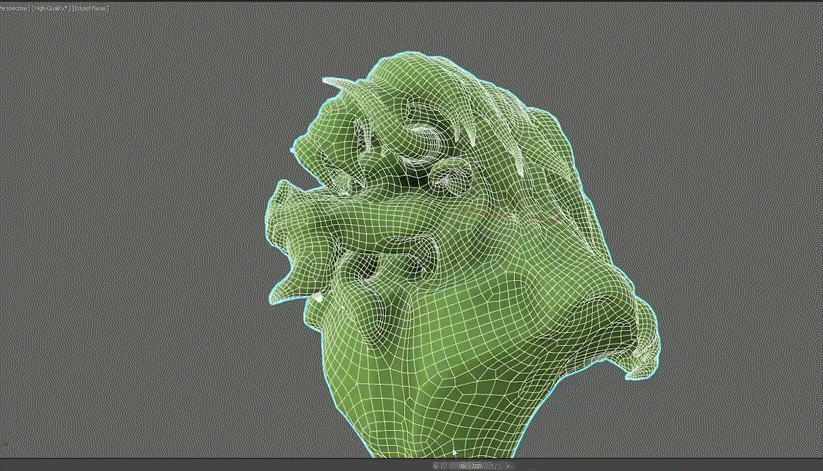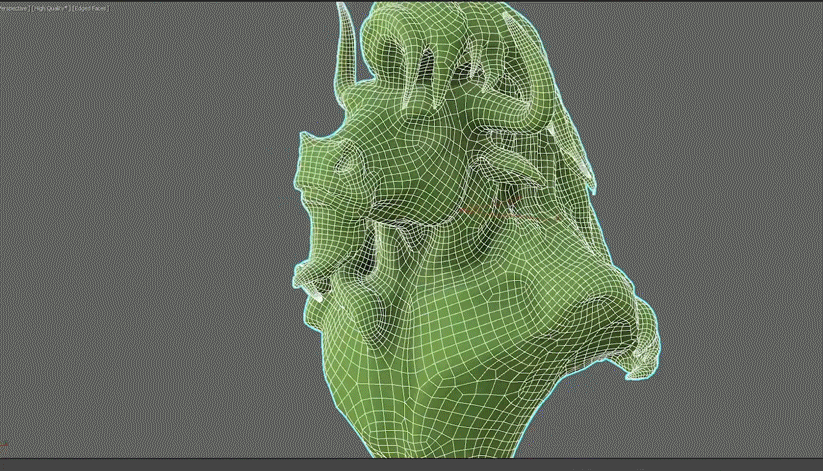
You can also create a proxy mesh that can be utilized in simulations within 3ds Max, due to the highly accurate retopology output generated.
Reference Topics
- Edit Poly Modifier
- ProOptimizer Modifier
- Relax Modifier
- Slice Modifier
- Smooth Modifier
- Subdivide Modifier (Object Space)
- Symmetry Modifier