 Check Model
Check Model
Checks all, visible, or picked objects for common problems that could prevent data transfer.
Access this tool from the Evaluate palette:

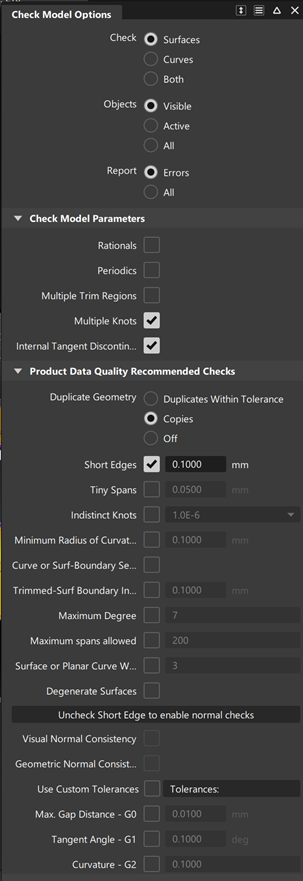
Check Model Options
Check
Check only surfaces, only curves, or both. The default is Surfaces.
Objects
Check all objects, all visible objects, or picked (active) objects. The default is Visible.
Report
Errors – Only show objects that failed one of the checks.
All – Show all objects even if they pass the checks.
The default is Errors.
Check Model Parameters
Rationals
Check for rational geometry.
Periodics
Check for periodic (closed) objects.
Multiple Trim Regions
Use this check to find instances where trims have made a single surface look like separate surfaces, which can confuse some CAD software packages.
Multiple Knots
Check for multi-knots (multiple edit points at the same point in space that may create a sharp corner in a curve or surface).
Internal Tangent Discontinuity
Report objects with internal tangent discontinuities due to multi-knots.
Non-Planar Curves
Check for curves that are not planar. This option only appears when Check is set to Curves or Both.
Product Data Quality Recommended Checks
Duplicate Geometry
Off – No check is done for duplicate or embedded geometry.
Copies – Checks for curves or surfaces that are exact duplicates of each other. Copies have the same CVs, same knots, and same degree. If Report is set to All, the original object is marked “Original” in the Copies column of the Check Model Results window.
Duplicates Within Tolerance – Checks for curves and surfaces that are duplicates of, or embedded into other curves and surfaces, within the tolerance given in the Duplicate Tolerance field.
Duplicate Tolerance
This field appears when Duplicate Geometry is set to Duplicates Within Tolerance. Curves or surfaces that lie within that distance of each other are reported.
Short edges
Check for edges (including trimmed edges) shorter than the distance specified in the text field. This check also finds T-connection situations where the corners of surfaces are close, but not close enough (they are within the topology distance but not within the max gap distance).
Tiny Spans
Check for curves and surfaces whose interior span/isoparm configuration results in the length of a span (or the length of both opposing patch segments for surfaces) being smaller than the distance tolerance specified in the text field.
Indistinct Knots
Check for curves and surfaces whose interior span/isoparm configuration results in knots being closer in parameter value than the tolerance specified in the text field.
Minimum Radius of Curvature
Report surfaces that have a radius of curvature smaller than a user-defined value. The smallest radius found on those surfaces is reported.
Curve or Surf-Boundary Self-Intersect
Report curves, surface boundaries, or trimmed surface boundaries that contain interior self-intersections. A self-intersection refers to the curve or surface boundary intersecting itself at one or more locations that are not both endpoints.
Trimmed-Surf Boundary Intersect
Report trimmed surfaces containing boundaries that intersect other boundaries on the same surface, within the tolerance supplied in the text field.
Maximum Degree
Check for objects with a degree higher than the number specified in the text field.
Maximum Spans
Report curves and surfaces that contain a number of spans exceeding the value specified in the text field.
Surface or Planar Curve Waviness
Report surfaces or planar curves that have more than a user-defined number of inflections (change in curvature sign) over their entire length (or width for surfaces). The maximum number of inflections allowed is entered in the text field (default is 3).
Allowed Inflections Per Span
This field only appears when Surface Curvature Waviness is ON. When turned on, it controls the maximum number of inflections per span allowed for a surface to pass the waviness test, in addition to the overall number of inflection permitted (see previous option). The default is 1.
Degenerate Surfaces
When turned on, your model is checked for the following issues in order of decreasing severity:
- Singular Edge - All CVs on some edge(s) have the same coordinates.
- Null Span - All CVs which belong to the same NURBS span on the edge are equal.
- Duplicate CVs - Two or more CVs on the edge are colliding.
- Bad Corner - Angle between hull edges at a surface corner is either 0 or 180 degrees.
If more than one of these issues is detected, the most severe one is flagged and reported in the Check Model Results window.
Visual Normal Consistency
Check for surfaces whose normal direction is inconsistent with the visual normal direction of adjacent surfaces.
Geometric Normal Consistency
Check for surfaces whose normal direction is inconsistent with the geometric normal direction of adjacent surfaces.
Use Custom Tolerances
Override the tolerances selected in Construction Presets ( Preferences > Construction Options and perform checks using custom tolerances.
Max Gap Distance - G0
Report objects that exceed a user-defined tolerance for positional continuity between adjacent curves or surfaces.
The tolerance value is given by Maximum Gap Distance in the Tolerances Continuity section of Preferences > Construction Options. Select Use Custom Tolerances to override this value here.
Tangent Angle - G1
Report objects that exceed a user-defined tolerance for tangent continuity between adjacent curves or surfaces.
The tolerance value is given by Continuity Angle in the Tolerances Continuity section of Preferences > Construction Options. Select Use Custom Tolerances to override this value here.
Curvature - G2
Report objects that exceed a user-defined tolerance for curvature continuity between adjacent curves or surfaces.
The curvature deviation is calculated as:
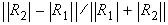
The tolerance value is given by Continuity Curvature in the Tolerances Continuity section of Preferences > Construction Options. Select Use Custom Tolerances to override this value here.
Report Parameters
Topology distance
Used to calculate which surface is adjacent to which surface when a tool needs to know the topology of the model. This is used by the Transformer Rig![]() , Surface Continuity
, Surface Continuity ![]() , and Check Model.
, and Check Model.
Tangent Angle Maximum
Maximum angle allowed between the tangents (or normals) of objects for them to be included in the G1 continuity test.
Curvature Maximum
Maximum curvature deviation allowed between objects for them to be included in the G2 continuity test.
Check Model workflows
Use the Check Model tool to identify possible problems with your model that can affect data transfer to other software packages.
Show a list of modeling problems
Shift-select the Check Model
 tool.
tool.In the Check Model Options window:
Choose whether to check only Surfaces, only Curves or Both.
Choose whether to check All objects, All Visible objects, or the picked (Active) objects.
Choose whether to list only objects with problems (Only Errors) or all objects.
Choose a set of construction tolerances from the Use Construction Preset drop down menu, to use in the model check calculations.
Note: These correspond to the Construction Presets available from Preferences > Construction Options. Select Use Current Tolerances to use whatever preset is already selected in the Construction Options window (indicated by a white arrow).
Choose what types of problems or conditions you want to check for. See Check Model Options for more information on the different checks.
Note: A special section called Product Data Quality contains checks that apply specifically to making a model compliant with the VDA-4955 and SASIG PDQ guidelines, so that it can be better handled by other packages such as NX, Catia, Pro/E, and so on.Click Check.
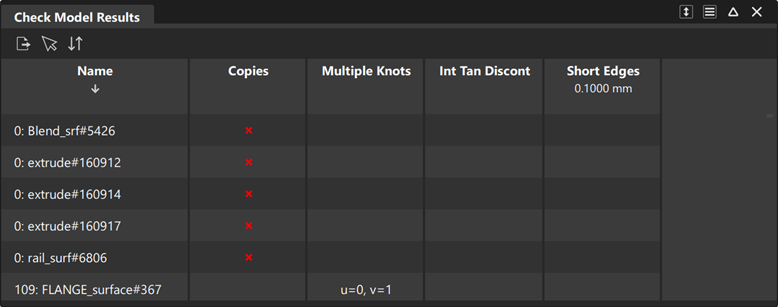
The resulting check data is displayed in a window organized as a table. Geometry that fails a given check will display a mark in the corresponding column.
Check for exact copies
This method is faster than checking for duplicates within a given tolerance.
Set Duplicate Geometry to Copies in the Check Model Settings option window.
Click Check.
The Check Model Results window displays a column titled Copies to help you identify all the copies. If Report is set to All, the original geometry is identified by the word “Original” in the column.
Checking for duplicates within a given tolerance
Set Duplicate Geometry to Duplicate Within Tolerance in the Check Model Settings option window.
Adjust the Duplicate Tolerance value. Geometry that is a duplicate of, or embedded into other geometry within this tolerance will be reported.
Click Check.
The Check Model Results window displays two columns titled Embedded In and Tolerance Duplicates to help you identify all the duplicates. The duplicates prefixed by “0” in the Tolerance Duplicates column are considered the originals.
Check continuity between curves or surfaces
Turn on the Max. Gap Distance - G0, Tangent Angle - G1 or Curvature - G2 option in the Check Model Options window.
Note: Tolerances for these continuity checks are found in the Tolerance:Continuity section of Preferences > Construction Options and correspond to the construction preset selected in the Check Model Options window.Note: For the G0 test to be successful, you must also ensure that the Topology Distance tolerance Tolerances:Topology section under Preferences > Construction Options is larger than the Maximum Gap Distance.Click Check.
The Check Model Results window displays columns titled G0, G1 and G2 with marks indicating failure. If geometry fails the G0 test, higher continuity tests for G1 and G2 will not be performed. Similarly, if geometry fails the G1 test, continuity test for G2 will not be performed
In the viewing window, the boundaries that failed the continuity tests are shown as thick yellow lines with a letter identifying the type of discontinuity (P = positional, T = tangent, C = curvature).

What do Report Parameters do?
The report parameters are tolerance values above which certain types of checks will not be executed.
- Tangent Angle Maximum: tangent angle value above which geometry will not be included in the G1 continuity check.
- Curvature Maximum: curvature deviation value above which geometry will not be included in the G2 continuity test.
Check consistency of orientation of surface normals
Turn on the Normal Consistency option in the Check Model Options window. Note: The Topology Distance tolerance is used to determine which surfaces are topologically adjacent and should have their normals checked as a group. It is found in the Tolerances:Topology section of Preferences > Construction Options and corresponds to the construction preset selected in the Check Model Options window.
Click Check.
The Check Model Results window displays a column titled Flipped Normal to help you identify the surfaces with inconsistent normal directions. In the viewing window, the inconsistent normals are shown as white arrows.
Check for maximum degree
This check enables you to identify curves and surfaces that exceed a user-defined degree. The default value for maximum degree is 7.
In the Check Model Settings option window, set the Check option to Surfaces, Curves or Both.
Turn on the Maximum Degree option.
Adjust the value in the text field next to the option selection box. Curves and/or surfaces that have degree larger than this value will be reported.
Click Check.
The Check Model Results window displays a column titled Degree which contains the degree of curves and/or surfaces that failed the test.
Check for minimum radius of curvature
This check enable you to identify surfaces (including trimmed surfaces) that exceed a user-defined curvature radius.
Turn on the Minimum Radius of Curvature option in the Check Model Settings option window.
Adjust the tolerance value in the text field next to the option check box. Surfaces that have a radius of curvature smaller than this value (in any direction) will be reported.
Click Check.
The Check Model Results window displays a column titled Min Radius of Curv which contains the minimum radius found on surfaces that failed the test.
Check for surface or planar curve waviness
This check enables you to identify surfaces or planar curves that have more than a certain number of inflections (change in curvature sign) per span (1 is the default) or over their entire length or width (3 is the default).
Turn on the Surface or Planar Curve Waviness option in the Check Model Settings option window.
Specify your criteria for waviness by changing the value next to the checkbox. This value represents the total number of inflections allowed over the length (or width) of the planar curve or surface for it to pass the test.
If the Allowed Inflections Per Span option is turned on, you can adjust the corresponding value to add an extra waviness criterion. The check will fail if the planar curve or surface has more than the given number of inflections per span, or more than the given number of inflections overall (as specified in step 2).
Click Check.
The Check Model Results window displays a column titled Waviness with marks indicating failure.
Check for short edges
This check enables you to identify curves and surface boundaries that are shorter than a user-defined value. This helps find geometry that may be problematic when used in certain operations, or may not be recognized as valid geometry in downstream CAD systems.
See Prepare a model for import into CAD systems for more information.
In the Check Model Settings option window, set the Check option to Surfaces, Curves or Both.
Verify that the Short Edges option is turned on.
Adjust the value in the text field next to the option selection box. Curves that are shorter than this value and/or surface that have boundaries shorter than this value will be reported.
Click Check.
The Check Model Results window displays a column titled Short Edges which contains the number of short edges on geometry that failed the test.
Check for non-planar curves
This check enables you to identify curves that are not planar. In the Check Model Settings option window, set the Check option to Curves or Both.
Turn on the Non-Planar Curves option.
Click Check.
The Check Model Results window displays a column titled Non-Planar Curve with marks indicating failure for the objects listed in the left-hand column.
Check for indistinct knots or tiny spans
This check enables you to identify curves and surfaces whose interior span/isoparm configuration (distance between adjacent isoparametric curves) results in knots being too close (indistinct knots), or in the segment or patch size being too small (tiny spans).
The indistinct knot criterion is violated if two adjacent knots are non-multiple (not exactly equal), but within a user supplied tolerance in the curve or surface parameter space.
The tiny span criterion for the minimal size of NURBS segments is violated if the segment length (or the length of both opposing patch segments for surfaces) is smaller than a user supplied distance tolerance.
Turn on the Indistinct Knots and/or the Tiny Spans option.
Adjust the value in the field next to the option selection box.
Note: For Indistinct Knots, the value is a tolerance in parameter space. For Tiny Spans, the value is a distance expressed in current linear units (for example mm).Click Check.
The Check Model Results window displays columns titled Indistinct Knots and Tiny Spans which contain the number of occurences of indistinct knots and tiny spans respectively, in the geometry that failed the test.
Check for maximum number of spans
This check enables you to identify curves and surfaces that contain a number of spans exceeding a user-defined value.
Turn on the Maximum Spans option.
Adjust the value in the text field next to the option selection box. Curves and surfaces that exceed this number of spans will be reported.
Note: Surfaces will fail the check if the number of spans in either the U or V direction exceeds the given value.Click Check.
The Check Model Results window displays a column titled Spans which contains the number of spans in the geometry that failed the test.
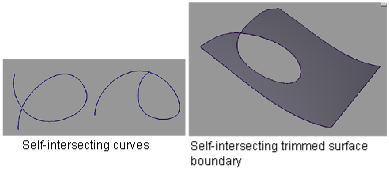
Check for self-intersections
This check enables you to identify curves, surface boundaries, or trimmed surface boundaries that contain interior self-intersections. A self-intersection refers to the curve or surface boundary intersecting itself at one or more locations that are not both endpoints (see pictures below).
Turn on the Curve or Surf-Boundary Self Intersect option.
Click Check.
The Check Model Results window displays a column titled Self-Intersecting with marks indicating failure for the objects listed in the left-hand column.
Check for intersection of trim boundaries
This check enables you to identify trimmed surfaces containing boundaries that intersect other boundaries on the same surface, within a user-defined tolerance (see picture).
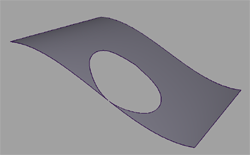
Turn on the Trimmed-Surf Boundary Intersect option.
Adjust the value in the text field next to the option selection box. Boundaries that intersect within this distance will be reported.
Click Check.
The Check Model Results window displays a column titled Trim Bndy Intersect with marks indicating failure for the objects listed in the left-hand column.
View the data in the Check Model Results window
Click the column heading to sort by a column. To reverse the sort, click the column heading again. You can also select the column’s name from the Sort menu.
Hold the
 on a row to highlight the object in the view windows.
on a row to highlight the object in the view windows.Click to select a row, hold
 to select multiple lines.
to select multiple lines.To pick the objects corresponding to the selected rows, open the window’s Pick menu and choose Pick Selected.
To pick all copies, open the window’s Pick menu and choose Pick Copies. This leaves the original copy unselected for each set of duplicates. (This menu item only appears if Copies was turned on in the option window.)
To pick all duplicate objects within tolerance, open the window’s Pick menu and choose Pick Tolerance Duplicates. This leaves one single copy unselected for each set of duplicates. (This menu item only appears if Duplicates Within Tolerance was turned on in the option window.)
To export the data to a text file, open the window’s File menu and choose Export Text.
Note: To import the text file into a spreadsheet program, choose “|” (vertical bar) as the column separator.
Prepare a model for import into CAD systems (ProEngineer Example workflow)
How to use Product Data Quality checks in the Check Model tool ![]() to ensure that your model meets minimum geometric requirements for import into a CAD system.
to ensure that your model meets minimum geometric requirements for import into a CAD system.
The following workflow is ideally suited to prepare the following model for import into ProEngineer:
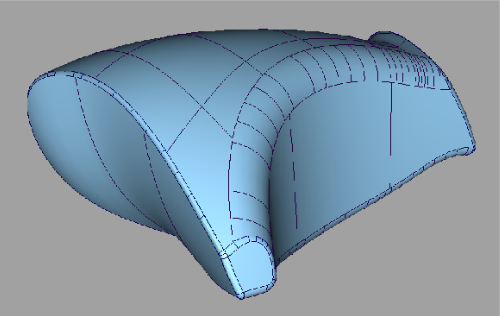
Choose the correct Construction Presets
Choose Pro/ENGINEER from the Use Construction Preset drop down menu.
All the construction tolerances are set to the proper Pro-Engineer values.

The above image shows the Check Model options on the left, and the construction tolerances for ProEngineer on the right.
Check the model for duplicate geometry
This check enables you to find both duplicate and embedded curves and surfaces in your model. Embedded geometry consist of curves and surfaces that duplicate parts of larger objects.
Set Duplicate Geometry to Duplicates Within Tolerance Check Model tool
 option window.
option window.Adjust the tolerance in the Duplicate Tolerance field.
This value represents the maximum distance allowed between two surfaces (or curves) for them to be considered duplicates. It is measured along the geometry’s normal.
Click the Check button.
The spreadsheet window appears, listing the geometry that failed the check on the left-hand side. This geometry is either a duplicate of, or embedded in, the geometry shown in the corresponding columns (labeled Tolerance Duplicates and Embedded In). The names of curves or surfaces that are duplicates of each other are all prefixed by the same number.
Selects a row in the spreadsheet.
The corresponding geometry is highlighted while you press the mouse button. To have the geometry selected permanently, choose Pick > Pick Selected in the spreadsheet menu.
Our example shows one duplicate and one embedded surface.
To select the duplicate, choose Pick > Pick Tolerance Duplicates in the spreadsheet menu.
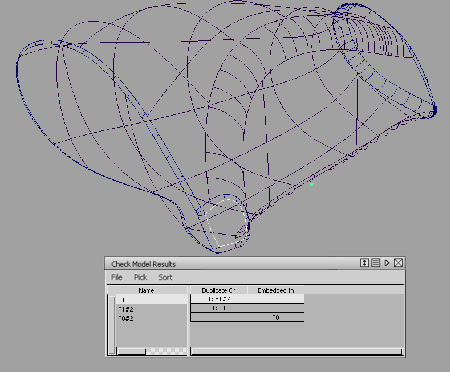
Delete the duplicate and embedded geometry.
Note: If you are not concerned about embedded geometry and only want to find exact duplicates, set Duplicate Geometry to Copies instead. Use Pick > Pick Copies in the spreadsheet menu to select them.
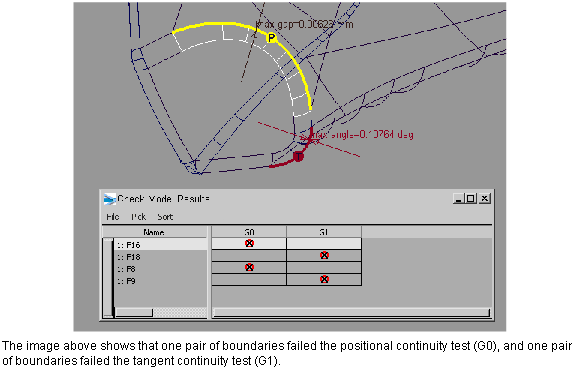
Check the model for continuity between curves and surfaces
Now that the redundant geometry has been removed, we can proceed with the continuity check.
Choose the Tangent Angle - G1 option in the Check Model Options window.
Notice that the check for positional continuity (Max. Gap Distance) was turned on automatically, since geometry must pass the positional continuity test before tangency can be checked. Similarly if the Curvature check was selected, the tangency and positional checks would be turned on automatically.
Note: All three continuity checks use the continuity tolerances from Preferences > Construction Options for the specific construction preset selected in the Check Model Options window.Click the Check button.
The spreadsheet window appears, listing the geometry that failed the checks on the left-hand side. The G0 and G1 columns display a mark showing which continuity check failed.
In the viewing window, discontinuous boundaries are highlighted, and the letters P, T or C indicate the type of discontinuity (Positional, Tangent or Curvature).
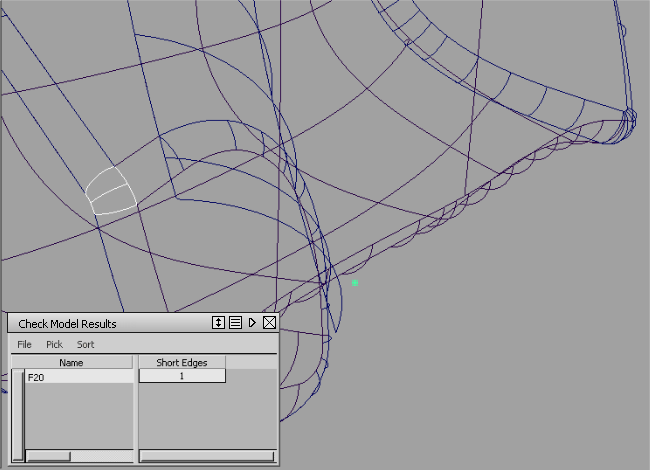
Check the model for short edges
This check identifies surfaces with short edges. Short edges are surface boundaries that are legal in Alias, but may be problematic if used in certain operations, or illegal in other systems into which the model will be imported.
For example, the Offset tool could reduce a 0.1 mm boundary to 0.0 mm, thereby creating a degenerate surface not valid to be passed down to other systems.
As well, if a surface boundary is 0.01 mm in length and you are sending it to a CAD system where the tolerance for coincident points is 0.02 mm, then this surface will not be a legal entity in the CAD system.
To identify short edges:
Choose the Short Edges option in the Check Model Options window.
Adjust the tolerance in the adjoining text field.
This value represents the minimum length that a surface boundary must have to pass the check. All shorter edges will be reported.
Click the Check button.
The spreadsheet window appears, listing the geometry that failed the check on the left-hand side, and the number of short edges in the Short Edges column.
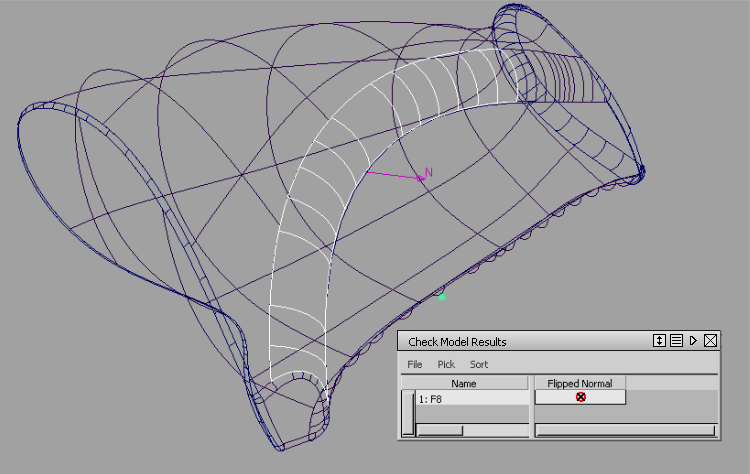
Check the model for uniformity of surface normals
The Normal Consistency check looks for geometry whose normal direction is different from the direction of the majority of the surfaces in the topology being checked. A topology is a group of surfaces whose boundaries are within the Topology Distance shown in Preferences > Construction Options for the construction preset selected in the Check Model tool (Pro/ENGINEER in this case). These surfaces are considered to be adjacent to each other.
To find inconsistent normals:
Shift+ click the Check Model tool icon
 .
.The Check Model Options window appears.
Click the Check button.
The spreadsheet window appears, listing the geometry that failed the check on the left-hand side, with a mark in the Flipped Normal column.
In the viewing window, inconsistent normals are shown as arrows with the letter “N”. In our example, one such surface has been identified.
Click the surface name in the spreadsheet to see it more clearly.
 Tip: Check Model only identifies normal inconsistencies of individual surfaces. To get a complete picture of all the topologies in this model, use Surface Edit > Orientation > Unify Surface Orientation. To reverse normals, use Surface Edit > Orientation > Set Surface Orientation or Surface Edit > Orientation > Reverse Surface Orientation.
Tip: Check Model only identifies normal inconsistencies of individual surfaces. To get a complete picture of all the topologies in this model, use Surface Edit > Orientation > Unify Surface Orientation. To reverse normals, use Surface Edit > Orientation > Set Surface Orientation or Surface Edit > Orientation > Reverse Surface Orientation.