 Dynamic Section
Dynamic Section
View a cross section of surfaces or meshes by dragging a plane through the model. This tool produces cross-sections in an arbitrary orientation by using a series of parallel planes with a distance between them specified by Step Size.
Unlike the Planar cross sections available from Windows > Editors > Cross Section Editor, dynamic sections update interactively on the geometry as you transform the reference plane.
Access this tool from the Evaluate palette:
Dynamic Sections Control
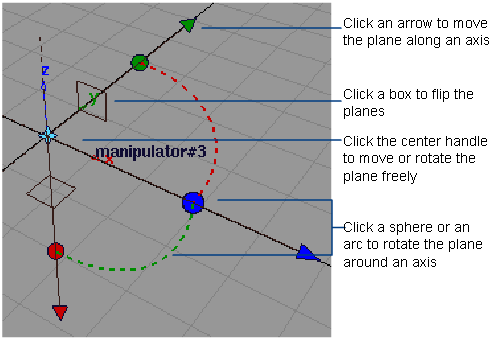
Sections
Number of Planes
The number of cross-section lines to create.
Step Size
The distance between cross-section lines (when Mode is Parallel and Number of Planes is greater than 1).
Curvature Scale
Controls the size of the curvature combs on the cross-section lines.
Curvature Samples
Controls the number of equally-spaced quills that appear on the curvature combs. The default is 50.
Persistent Sections
This flag determines whether the sections will remain after exiting the tool. Supports Query Edit.
Picked Plane
Lists the construction planes in the scene. Select one to use as active clipping plane.
Visual Clip
These options let you visually clip the wireframe and shaded model, leaving the sections visible.
Visual Clip
Check this option to display only the part of the model with the sections (on one side of the sectioning plane).
Flip
Check this option to display only the part of the model that does not have sections. The sections on the invisible part are still displayed.

Clip Offset
This option is only available if Visual Clip is turned on.
When checked on, a second clipping plane appears, and the display of surfaces/meshes is clipped to the location and direction of that second plane as well, leaving only the part of the model between the two planes visible.
The Clip Offset slider specifies the offset distance of the second clipping plane from the first.

Persistent Visual Clip
When selected, the visual clipping planes do not disappear when you exit the tool. With persistent clipping planes, you can print the section display, measure the section, do anything to the section outside the tool.
Section Origin
Translate
These fields specify the position (X,Y,Z) of the sectioning plane’s origin. They let you cut a section at a precise location along one of the main world axes (for example x = 100).
Rotate
These fields specify the rotation angle of the sectioning plane around the world X,Y,Z axes.
Click the Rotation Reset button in the view window to reset all rotations to 0.
Dynamic Section tool workflows
Create and use a dynamic cross section
Pick the surfaces or meshes you want to examine.
A sectioning plane appears, at the geometric center of the object(s). A red cross section appears on the selected objects where the plane intersects them.
Note: At any time you can click additional surfaces or meshes to add to the selection. Clicking an already selected surface or mesh removes it from the selection. (You can use a pick box instead of clicking.)Set the Number of Planes (number of sections) and Step Size (spacing between sections) in the option box.
The cross sections appear as red lines and update on the objects.
Use the manipulator to orient the sectioning plane, or enter specific values in the Translate and Rotate fields in the control window.
Changing these values update the plane manipulator, and vice-versa.
The cross sections update as the plane is moved/rotated.
Note: Using the Translate fields lets you cut a section at a specific location along one of the main world axes (for example X = 100).
Do any of the following:
Use the manipulator to move the sectioning plane through the surfaces.
Select an existing construction plane to use as the base sectioning plane.
Click the Geom button to create free curves from the cross section(s).
Click the Create Planes button to create construction planes corresponding to the sectioning planes.
Click the Curvature On button to show a curvature comb plot on the section(s). To change the scale of the comb plot, adjust the Curvature Scale setting.
Click the Rotation Reset button to reset all the rotations on the sectioning plane to 0, and re-align the sections with the X, Y, and Z axes.
Turn on Visual Clip in the control window, to see only the part of the model in front of the sectioning plane. Turn on Flip to see only the part of the model behind the sectioning plane.
Turn on Visual Clip and Clip Offset to create an additional plane parallel to the sectioning plane, and see only the part of the model between the two planes.
Turn on Persistent Sections in the option box for the sections to remain visible after exiting the tool.
Note: If creating true geometry cross sections with the Geom button, you can use the Sort Sections tool in the Object Edit tool palette to sort out your cross sections into different layers, according to the plane they lie in (X, Y, Z or Other). This grouping is useful for manipulating cross section data.
in the Object Edit tool palette to sort out your cross sections into different layers, according to the plane they lie in (X, Y, Z or Other). This grouping is useful for manipulating cross section data.
How do I use the manipulators?
The manipulators are visible through shaded geometry.
Sectioning Plane
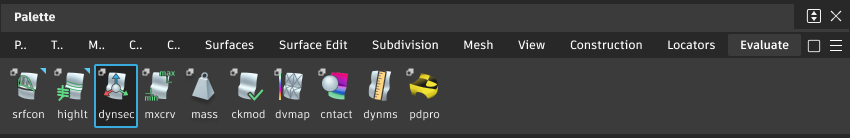
- Drag a handle to move/rotate.
- Click an arrow to change the center handle to the free move handle. Then drag the center handle to move the plane freely.
- Click a sphere or arc to change the center handle to the free rotate handle. Then drag the center handle to rotate the plane freely.
- Click a box (square) to set the plane perpendicular to one of the manipulator axes.
Clip Offset Plane

Click the plane or the arrow (they turn white) and drag to change the offset distance.
Note: When the sectioning plane is moved or rotated, the offset plane is moved or rotated along with it, so that both planes always remain parallel and separated by the same distance.
Define two visual clipping planes
You can define a secondary visual clipping plane parallel to, and at a given distance from, the primary clipping plane. Only the part of the model between the two clipping planes is displayed.
This secondary plane is always driven by the location and direction of the primary plane.
Select surfaces or meshes
Shift-select the Dynamic Section tool icon to open the control window.
Adjust position and orientation of the sectioning plane.

Turn on the Visual Clip option.
The display of surfaces/meshes is clipped to the location and direction of the current plane.

Turn on the Clip Offset option.
An offset plane appears, and the display of surfaces/meshes is clipped to the location and direction of that second plane as well, leaving only the part of the model between the two planes visible.
Use the Clip Offset slider, or click and drag the offset plane manipulator, to adjust the offset distance of the second clipping plane from the first.
The clipped area updates.
Both the slider value in the option window and the offset plane manipulator on the model update to reflect each other.
Note: To position the offset plane manipulator through keyboard input or snapping, first select it by clicking it without dragging. The manipulator turns white when selected.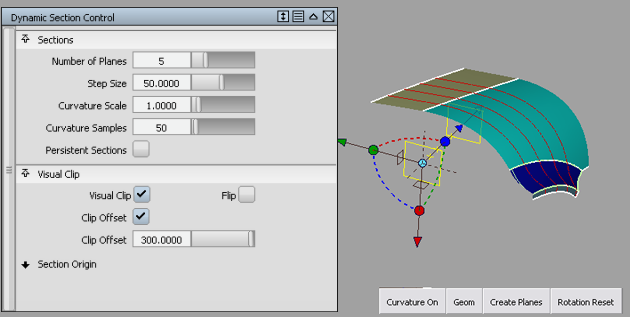
Cut a section at a specific location along one of the main axes
Choose the orientation of the sectioning plane by clicking on one of the three square icons on the manipulator.

Enter the X, Y, or Z location of the plane in the appropriate Translate field.
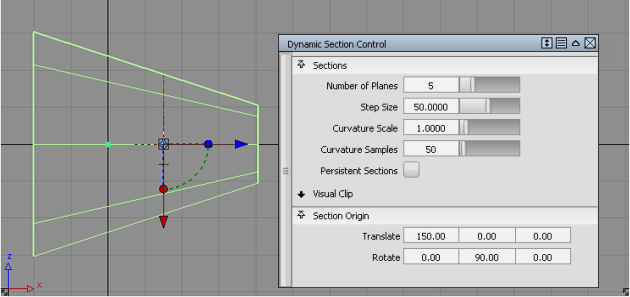
A discreet section cut at x = 150.0
Remove persistent sections
If the Persistent Sections option was turned on, the sections will remain after exiting the tool.
Use the Clear button in the Cross Section Control tab of the Control Panel to remove them.
Related pages
- Cross Section Editor
- Cross section workflows