A table is a compound object that contains information arranged in rows and columns. Similar to most spreadsheet applications, the rows and columns can be adjusted with grips, and styles can be assigned to the table and to selected cells.
The illustration below shows the grips on a table and a selected cell.
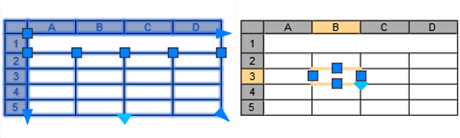
Drawings often include tabular information such as a variety of schedules, parts lists, bills of materials, and price lists. The information itself might be text, graphical blocks, and several types of numeric data. Cells that contain data might be computationally related to other cells or to external information such as a spreadsheet or other extracted data.
Creating tables manually from lines and text can be tedious and modifying them can be time-consuming, but you can easily create a table object simply by specifying the rows and columns from the Table command. You can also create a table object in AutoCAD by referencing a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet.
Table and Cell Styles
Use table styles to store the default settings and definitions for the table and its cells. The settings are similar to what you see in a spreadsheet application. Several cell styles can be saved in a table style. Each cell style stores settings such as text style, height, color, background fill, and cell borders. You can create your own cell styles that you can save in your own table styles. You can also import table styles from other drawings using Autodesk DesignCenter.
Data Links
A data link is information included within an AutoCAD drawing file that establishes a connection to an external source of information, specifically a Microsoft Excel file or a data extraction (.dxe) file.
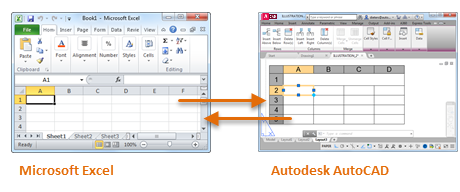
Cells in a table object can be linked to data in specified cells of a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. You can choose whether the link is only in one direction or bidirectional, and where the computations are done.