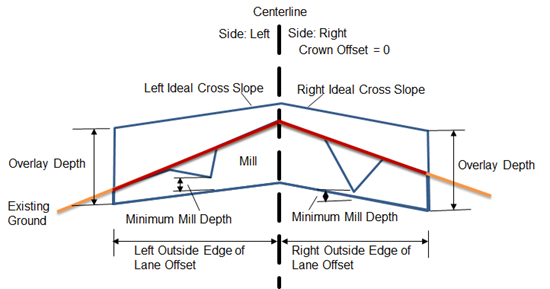
This subassembly adds an overlay layer on top of an existing crowned roadway with a milling layer added as required.
Attachment
The attachment point is the crown point of the overlay layer with finished ground cross slope.
Input Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crown Offset | Positive or negative offset of the crown point. | Numeric | 0.000m (0.000 ft) |
| Crown Use Profile Options | Select to tie the inside edge of the overlay crown point to a profile, or adjust crown point elevation to meet minimum mill depth. | User defined | Minimum Mill Depth |
| Design Lane Width same as Existing Lane Width |
|
User defined | No |
| Inside Edge of Existing Left Lane | This is the start point for calculating existing ground slope for the left lane. | Numeric | 0.000m (0.000 ft) |
| Inside Edge of Existing Right Lane | This is the start point for calculating existing ground slope for the right lane. | Numeric | 0.000m (0.000 ft) |
| Outside Edge of Existing Left Lane | This is the end point for calculating existing ground slope for the left lane. | Numeric | 12.000m (12.00 ft) |
| Outside Edge of Existing Right Lane | This is the end point for calculating existing ground slope for the right lane. | Numeric | 12.000m (-12.000 ft) |
| Overlay Depth | Depth of the overlay layer. | Numeric, positive | 0.600m (0.600 ft) |
| Right and Left Overlay Slope Options | Specifies right and left overlay slope options.
Tip: Flapping is a term used to describe how the corrected cross slope for an overlay in a rehab subassembly is calculated. Flapping outcomes are different, relative to the slope tolerance and the slope difference between existing ground cross slope and ideal cross slope. If the slope difference is less than the slope tolerance for the subassembly, then the use case is considered "within tolerance". If the slope difference is greater than the slope tolerance for the subassembly, then the use case is considered "outside of tolerance."
Note: Slope tolerance is an absolute value. Therefore, for either a slope difference of 0.4% or -0.4%, both have an absolute value of 0.4%. If the slope tolerance is 0.5%, the 0.4% absolute slope difference would be considered within tolerance.
|
User defined | User Defined Without Flapping |
| Left Ideal Cross Slope | Specifies user defined left ideal cross slope. | Numeric, negative | -2.00% |
| Left Minimum Mill Depth | The minimum mill depth between the bottom of the milling layer to the bottom of the existing ground layer on the left side. | Numeric, positive | 0.300m (0.300 ft) |
| Left Slope Tolerance | Tolerance for varying the left overlay slope. | Numeric | 0.50% |
| Right Ideal Cross Slope | Specifies user defined right ideal cross slope. | Numeric, negative | -2.00% |
| Right Minimum Mill Depth | The minimum mill depth between the bottom of the milling layer to the bottom of the existing ground layer on the right side. | Numeric, positive | 0.300m (0.300 ft) |
| Right Slope Tolerance | Tolerance for varying the left overlay slope. | Numeric | 0.50% |
| Left Lane Width | The left lane width, determined by the offset of the outside edge of the left lane from the inside edge of left lane. | Numeric, negative | -12.000m (-12.000 ft) |
| Right Lane Width | The right lane width, determined by the offset of the outside edge of the right lane from the inside edge of right lane. | Numeric, positive | 12.000m (12.000 ft) |
Output Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left Corrected Cross Slope | This is the adjusted cross slope for the left side of the road, which has been optimized to match, as closely as possible, the rehab subassembly parameters you specified. | Numeric | -2.00% |
| Right Corrected Cross Slope | This is the adjusted cross slope for the right side of the road, which has been optimized to match, as closely as possible, the rehab subassembly parameters you specified. | Numeric | -2.00% |
| Left Existing Ground Slope | The cross slope (%) of the existing ground profile for the left lane, calculated from the inside edge of the left lane to the outside edge of the left lane. | Numeric | percentage |
| Right Existing Ground Slope | The cross slope (%) of the existing ground profile for the right side of the road, calculated from the inside edge of the right lane to the outside edge of the right lane. | Numeric | percentage |
Target Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Required? |
|---|---|---|
| Target Surface | Name of the surface defining the existing roadway | Yes |
| Crown Offset Target | Name of the object defining the offset of the crown point. The following object types can be used as targets for specifying this offset: alignments, polylines, feature lines, or survey figures. | No |
| Left Lane Width Target | Name of the object defining the offset of the outside edge of left lane. The following object types can be used as targets for specifying this offset: alignments, polylines, feature lines, or survey figures. | No |
| Right Lane Width Target | Name of the object defining the offset of the outside edge of right lane. The following object types can be used as targets for specifying this offset: alignments, polylines, feature lines, or survey figures. | No |
| Left Inside Edge of Existing Lane Offset Target | Name of the object defining the left inside sample point offset will be used to calculate the existing surface slope. The following object types can be used as targets for specifying this offset: alignments, polylines, feature lines, or survey figures. | No |
| Left Outside Edge of Existing Lane Offset Target | Name of the object defining the left outside sample point offset will be used to calculate the existing surface slope. The following object types can be used as targets for specifying this offset: alignments, polylines, feature lines, or survey figures. | No |
| Right Inside Edge of Existing Lane Offset Target | Name of the object defining the right inside sample point offset will be used to calculate the existing surface slope. The following object types can be used as targets for specifying this offset: alignments, polylines, feature lines, or survey figures. | No |
| Right Outside Edge of Existing Lane Offset Target | Name of the object defining the right outside sample point offset will be used to calculate the existing surface slope. The following object types can be used as targets for specifying this offset: alignments, polylines, feature lines, or survey figures. | No |
Behavior
This subassembly assumes that no leveling layer is added.
Point, Link, and Shape Codes
| Point, Link, or Shape | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | Crown | Crown point for top of overlay |
| P2, P3 | EOV | Overlay edges on finished grade for the left and right side of the road |
| P4 | Crown_Overlay | Crown point for bottom of mill |
| P5, P6 | EOV_Overlay | Edges of bottom of mill for the left and right side of the road |
| P7, P8 | EOV_Milling | Edges of top of mill for the left and right side of the road |
| P9 | Crown_offset | Offset of the crown point from attachment point. |
| L1, L2 | Top, Pave | Top of overlay for left and right side of road |
| L3, L4, L5, L6 | Overlay | Links for the overlay layer. |
| L7, L8 | Mill | Mill links (height) for left and right side of road |
| S1 | Overlay | Area between the top and bottom of overlay |
| S2 | Mill | Area between the top and bottom of mill |
Coding Diagram
