LaRC02 Criterion
The LaRC02 criterion [55] identifies fiber failure and matrix cracking in a unidirectional composite.
Fiber failure is further divided into three possible failure modes:
- Fiber tensile failure
- Fiber compressive failure with matrix compression
- Fiber compressive failure with matrix tension
Matrix cracking is also divided into three possible failure modes:
- Matrix cracking in tension
- Matrix cracking in compression
- Matrix cracking with moderate biaxial compression
If a failure index (FI) equals or exceeds 1.0, failure occurs (fiber or matrix failure).
Common Terms Used in LaRC02
This section presents common terms seen in the LaRC02 failure criteria.
XT = Value of σ11 at longitudinal tensile failure
XC = Value of σ11 at longitudinal compressive failure
YT = Value of σ22 at transverse tensile failure
YC = Value of σ22 at transverse compressive failure
SL = Absolute value of σ12 at longitudinal shear failure
ST = Absolute value of σ23 at transverse shear failure
α0 = Angle of the fracture plane under uniaxial transverse compression (set to 53°)
α = Angle of the fracture plane that maximizes the failure index
G12 = Longitudinal shear moduli
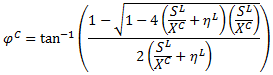
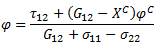
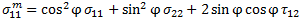
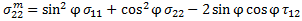
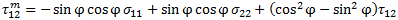
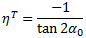
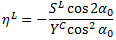
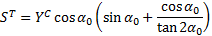
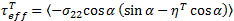
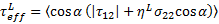
Tensile Fiber Failure
If the longitudinal normal stress (σ11) is positive, the tensile fiber failure mode is used to determine if fiber failure occurs. The tensile fiber failure criterion is
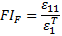
Where ε11 is the current longitudinal strain and 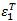 is the longitudinal strain at fiber tensile failure.
is the longitudinal strain at fiber tensile failure.
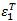 is calculated from axial tensile strength of the composite as
is calculated from axial tensile strength of the composite as
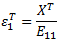
Fiber Compressive Failure with Matrix Compression
There are two fiber compressive failure criterion. The stress state determines which one is used to evaluate fiber failure. Fiber compressive failure is evaluated in a rotated coordinate system. If the transverse normal stress (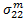 ) is positive, the criterion below is used to evaluate fiber failure.
) is positive, the criterion below is used to evaluate fiber failure.
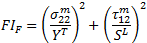
If the transverse normal stress (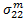 ) is negative, the criterion below is used to evaluate fiber failure
) is negative, the criterion below is used to evaluate fiber failure
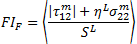
Tensile Matrix Failure
The matrix tensile failure criteria is invoked if the transverse normal stress (σ22) is positive. The tensile matrix failure criterion is
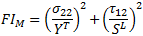
Matrix Compression
There are two matrix compressive failure criterion. The stress state determines which one is used to evaluate matrix failure. If the longitudinal normal stress (σ11) is greater than or equal to the transverse compressive strength (YC), the following criterion is used to evaluate matrix failure
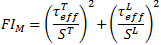
If the longitudinal normal stress (σ11) is less than the transverse compressive strength (YC), the material is considered to be in a moderate biaxial compressive state and the following criterion is used to evaluate matrix failure
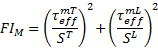
This criterion uses stresses in the rotated coordinate system to calculate the effective stresses.