Failure Criteria for Unidirectional Composites
Examine the failure criteria for unidirectional composite materials.
For convenience, the constituent failure criteria for unidirectional composites developed earlier (MCT Constituent-Based Failure Criteria) are repeated below.
matrix: 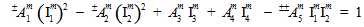
fiber: 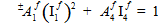
In the constituent failure criteria, the quantities 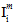 (i=1,2,3,4) and
(i=1,2,3,4) and 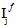 (j=1,4) are the transversely isotropic, constituent average stress invariants computed using the MCT decomposition.
(j=1,4) are the transversely isotropic, constituent average stress invariants computed using the MCT decomposition.
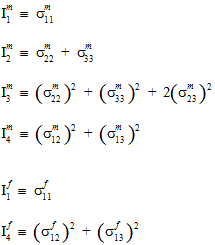
The quantities 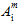 (i=1,2,3,4) and
(i=1,2,3,4) and 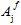 (j=1,4) are adjustable coefficients that must be determined based on measured strengths of the composite material. The ± symbol that precedes some of the quantities
(j=1,4) are adjustable coefficients that must be determined based on measured strengths of the composite material. The ± symbol that precedes some of the quantities 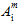 and
and 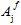 indicates the numerical value of these coefficients is dependent upon whether the corresponding constituent stresses are tensile or compressive. Consequently, 13 constituent failure coefficients must be determined using measured composite strengths.
indicates the numerical value of these coefficients is dependent upon whether the corresponding constituent stresses are tensile or compressive. Consequently, 13 constituent failure coefficients must be determined using measured composite strengths.
From a mathematical point of view, a rigorous determination of the 13 constituent failure coefficients requires 13 independent strength measurements. However, the approach adopted here is based on the belief that available strength data for the composite material is likely limited to the following six industry-standard strength tests.
+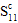 : longitudinal tensile strength (in the fiber direction)
: longitudinal tensile strength (in the fiber direction)
-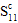 : longitudinal compressive strength (in the fiber direction)
: longitudinal compressive strength (in the fiber direction)
+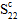 = +
= +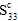 : transverse tensile strength (perpendicular to the fibers)
: transverse tensile strength (perpendicular to the fibers)
-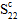 = -
= -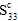 : transverse compressive strength (perpendicular to the fibers)
: transverse compressive strength (perpendicular to the fibers)
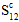 =
= 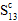 : longitudinal shear strength
: longitudinal shear strength
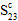 : transverse shear strength
: transverse shear strength
A set of well grounded assumptions is used to determine the remaining composite strength measurements. After studying a large volume of measured biaxial strength data for a wide variety of composite materials, Autodesk has developed highly successful empirical relationships utilizing industry standard strength measurements to approximate composite strengths under various biaxial load states.