Introduction
The progressive fatigue feature predicts the cycles to failure of a given composite material under a prescribed load history. Within Helius PFA, it is used to aid in progressive fatigue analyses. This is accomplished by damaging the composite material with the minimum cycles to failure and allowing the finite element platform to redistribute loading to the adjacent material. Following this fashion, a composite structure can be analyzed within a finite element platform, and the cycles to failure for the structure can be estimated.
The problem consists of a flat composite plate with a hole in the center subject to fixed boundary conditions on one end and a tensile load on the other end. The plate is made of a unidirectional material. The layup is [0/±45/90]s, and the ply thickness is 0.000127 m which results in a plate thickness of 0.001016 m. The load ratio Smin/Smax is 0.1 and the frequency of loading is 10 Hz. The seed size for the mesh is 0.005 and eight noded isoparametric brick elements with reduced integration are used. The dimensions, boundary conditions, and load are shown below.
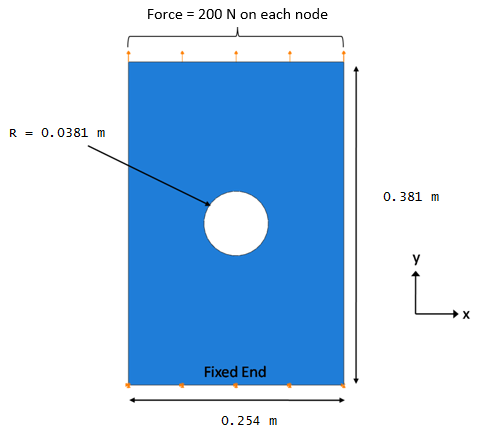
In this tutorial, the model will be created using a combination of the ANSYS Mechanical APDL GUI and input file modifications. Elementary modeling details are omitted. It is assumed you have previous experience in the ANSYS Mechanical APDL environment. Please refer to the ANSYS documentation before completing this tutorial if you are unfamiliar with the ANSYS GUI.
A completed ANSYS input file (Tutorial_4_ANSYS.ans) is available for download here.