Appendix C - MCT State Variables (SVARs)
View a description of all of the solution-dependent MCT state variables.
There are 35 solution-dependent MCT state variables for unidirectional composites and 91 for woven composites (Note that with progressive fatigue analyses there are 31 MCT state variables for unidirectional materials and 94 MCT state variables for woven materials). These solution-dependent state variables are computed or updated by the Helius PFA user programmable feature at each integration point within each finite element. ANSYS will store the converged values of solution-dependent MCT state variables for each substep using the appropriate ANSYS OUTRES command (see Request MCT State Variable Output and Request Output of the MCT State Variables). By default, the naming convention adopted by ANSYS for solution-dependent state variables is SVARi, where i=1, 2, 3… # of state variables. In order to view SVARs greater than 11, power graphics must be turned off using the /GRAPHICS, FULL command. Click here to view the state variables used in Advanced Material Exchange.
The following list describes each of the MCT state variables.
SVAR1
SVAR1 is an integer variable that represents the discrete damage state of the composite material. The range and interpretation of integer values assumed by SVAR1 depend upon the specific set of material nonlinearity features used in the analysis. The following tables provide the interpretation for each allowable integer value of SVAR1 for each possible combination of material nonlinearity features employed by Helius PFA.
Unidirectional Composite Material - nonlinearity deactivated
- Progressive Failure Analysis (activated)
- Pre-Failure Nonlinearity (deactivated)
| Allowable Discrete Values for SVAR1 | Discrete Composite Damage State |
|---|---|
| 1.0 | Undamaged Matrix, Undamaged Fiber |
| 2.0 | Failed Matrix, Undamaged Fiber |
| 3.0 | Failed Matrix, Failed Fiber |
Unidirectional Composite Material - nonlinearity activated
- Progressive Failure Analysis (activated)
- Pre-Failure Nonlinearity (activated)
| Allowable Discrete Values for SVAR1 | Discrete Composite Damage State |
|---|---|
| 1.0 | Undamaged Matrix, Undamaged Fiber |
| 1.25 | Matrix Pre-Failure Degradation Level 1, Undamaged Fiber |
| 1.5 | Matrix Pre-Failure Degradation Level 2, Undamaged Fiber |
| 1.75 | Matrix Pre-Failure Degradation Level 3, Undamaged Fiber |
| 2.0 | Failed Matrix, Undamaged Fiber |
| 3.0 | Failed Matrix, Failed Fiber |
Woven Composite Material - nonlinearity deactivated
- Progressive Failure Analysis (activated)
- Pre-Failure Nonlinearity (deactivated)
- Post-Failure Nonlinearity (not supported)
| Allowable Discrete Values for SVAR1 | Discrete Composite Damage State |
|---|---|
| 1.0 | Undamaged Matrix, Undamaged Fiber |
| 1.4 | Fill Matrix Failure, Undamaged Warp |
| 1.6 | Warp Matrix Failure, Undamaged Fill |
| 2.0 | Matrix Failure in Warp and Fill |
| 2.2 | Fill Fiber and Matrix Failure, Undamaged Warp |
| 2.3 | Warp Fiber and Matrix Failure, Undamaged Fill |
| 2.7 | Fill Fiber and Matrix Failure, Warp Matrix Failure |
| 2.8 | Warp Fiber and Matrix Failure, Fill Matrix Failure |
| 3.0 | Completely Failed |
Woven Composite Material - nonlinearity activated
- Progressive Failure Analysis (activated)
- Pre-Failure Nonlinearity (activated)
- Post-Failure Nonlinearity (not supported)
| Allowable Discrete Values for SVAR1 | Discrete Composite Damage State |
|---|---|
| 1.0 | Undamaged Matrix, Undamaged Fiber |
| 1.057 | Matrix Pre-Failure Degradation Level 1, Undamaged Fiber |
| 1.114 | Matrix Pre-Failure Degradation Level 2, Undamaged Fiber |
| 1.171 | Matrix Pre-Failure Degradation Level 3, Undamaged Fiber |
| 1.229 | Matrix Pre-Failure Degradation Level 4, Undamaged Fiber |
| 1.286 | Matrix Pre-Failure Degradation Level 5, Undamaged Fiber |
| 1.343 | Matrix Pre-Failure Degradation Level 6, Undamaged Fiber |
| 1.4 | Fill Matrix Failure, Undamaged Warp |
| 1.6 | Warp Matrix Failure, Undamaged Fill |
| 2.0 | Matrix Failure in Warp and Fill |
| 2.2 | Fill Fiber and Matrix Failure, Undamaged Warp |
| 2.3 | Warp Fiber and Matrix Failure, Undamaged Fill |
| 2.7 | Fill Fiber and Matrix Failure, Warp Matrix Failure |
| 2.8 | Warp Fiber and Matrix Failure, Fill Matrix Failure |
| 3.0 | Completely Failed |
Unidirectional Composites - Static Analyses
For unidirectional composite materials, state variables SVAR2, SVAR3, ..., SVAR35 have the following interpretations for static progressive failure analyses:
- SVAR2
- SVAR2 is a continuous real variable ranging from 0.0 to 1.0, indicating the fraction of the matrix failure criterion that has been satisfied. For example, SVAR2 = 0.0 implies that the matrix stress level is zero, while SVAR2 = 1.0 implies that the matrix stress has reached failure level. Numerically, SVAR2 is computed as
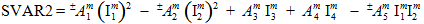
which is recognized as the left hand side of the matrix failure criterion (see the MCT Constituent-Based Failure Criteria section of the Theory Manual).
- SVAR3
- SVAR3 is a continuous real variable ranging from 0.0 to 1.0, indicating the fraction of the fiber failure criterion that has been satisfied. For example, SVAR3 = 0.0 implies that the fiber stress level is zero, while SVAR3 = 1.0 implies that the fiber stress has reached failure level. Numerically, SVAR3 is computed as
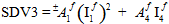
which is recognized as the left hand side of the fiber failure criterion (see the MCT Constituent-Based Failure Criteria section of the Theory Manual).
- SVAR4
- SVAR5
- SVAR5 is the fourth term in the matrix failure criterion and is used in the pre-failure nonlinearity feature (see the Theory Manual).
- SVAR6 - SVAR11
For the case of unidirectional composites, the remaining MCT state variables store the individual components of the matrix average stress and strain states and the fiber average stress and strain states.

Unidirectional Composites - Progressive Fatigue Analyses
For unidirectional composite materials, state variables SVAR2, SVAR3, ..., SVAR35 have the following interpretations for progressive fatigue analyses:
For the case of a progressive fatigue analysis with unidirectional materials, SVAR8 through SVAR31 store the individual components of the matrix average stress and strain states and the fiber average stress and strain states (equivalent to SVAR12 through SVAR35 for static analyses).
Woven Composites - Static Analyses
For woven composite materials, state variables SVAR2, SVAR3, ..., SVAR90 have the following interpretations for static progressive failure analyses:
- SVAR2
- SVAR3
- SVAR4
- SVAR5
- SVAR6
- SVAR7
- SVAR7 is the second term in the MCT matrix failure criterion for woven composites and is used in the pre-failure nonlinearity feature. SVAR7 is unused if pre-failure nonlinearity is turned off.
For the case of woven composites, the remaining MCT state variables store the individual components of the average stress and strain states in the various superconstituents and constituents (e.g., fill = fill tow superconstituent, warp = warp tow superconstituent, matrix-pocket = matrix constituent of the intertow matrix pockets, fill-matrix = the matrix constituent of the fill tow, warp-matrix = the matrix constituent of the warp tow, fill-fiber = the fiber constituent of the fill tow, warp-fiber = the fiber constituent of the warp tow).

Woven Composites - Progressive Fatigue Analyses
For woven composite materials, state variables SVAR2, SVAR3, ..., SVAR91 have the following interpretations for progressive fatigue analyses:
For the case of a progressive fatigue analysis with woven materials, SVAR11 through SVAR94 are used to store the individual components of the average stress and strain states in the various superconstituents and constituents (equivalent to SVAR8 through SVAR91 for static analyses).
In order to view SVARs greater than 11, power graphics must be turned off using the /GRAPHICS, FULL command.