Nonlinear Elastic Fiber
Capture the effects of fiber nonlinear elasticity.
It is generally known that the modulus of fibers can exhibit nonlinear elasticity when subject to large axial strains. When the axial fiber strain is tensile, fibers tend to stiffen. When the axial fiber strain is compressive, fibers tend to soften. You can capture both of these behaviors via the *NONLINEAR FIBER keyword. This keyword must be preceded by the *MATERIAL keyword so that the material of interest is properly identified:
*NONLINEAR FIBER, ETAC=Compressive Knockdown Factor
GAMMA_1T, GAMMA_1CETAC and GAMMA_1C are mutually exclusive options.
For tensile loading, the following equation is used to approximate the nonlinear elastic stiffening of the fiber (and thus the composite):
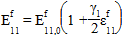
Where:
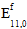 is the original fiber modulus
is the original fiber modulus
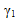 is the nonlinear fiber parameter (GAMMA_1T)
is the nonlinear fiber parameter (GAMMA_1T)
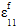 is the axial fiber strain (assumed to be equal to the axial composite strain)
is the axial fiber strain (assumed to be equal to the axial composite strain)
For compressive loading, a simple relationship is used to approximate the modulus softening if ETAC is specified:
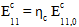
Where:
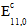 is the original composite modulus
is the original composite modulus
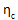 is the composite modulus knockdown factor (ETAC)
is the composite modulus knockdown factor (ETAC)
For compressive loading with GAMMA_1C specified, the following equation is used to approximate the nonlinear elastic softening of the fiber (and thus the composite):
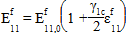
Where:
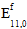 is the original fiber modulus
is the original fiber modulus
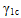 is the nonlinear fiber parameter for compression (GAMMA_1C)
is the nonlinear fiber parameter for compression (GAMMA_1C)
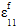 is the axial fiber strain (assumed to be equal to the axial composite strain)
is the axial fiber strain (assumed to be equal to the axial composite strain)
The fiber modulus is considered nonlinear until fiber failure occurs. Once fiber failure occurs, the composite stiffnesses will remain fixed because their influence is negligible and continuing to update the properties would be an inefficient use of computational resources.
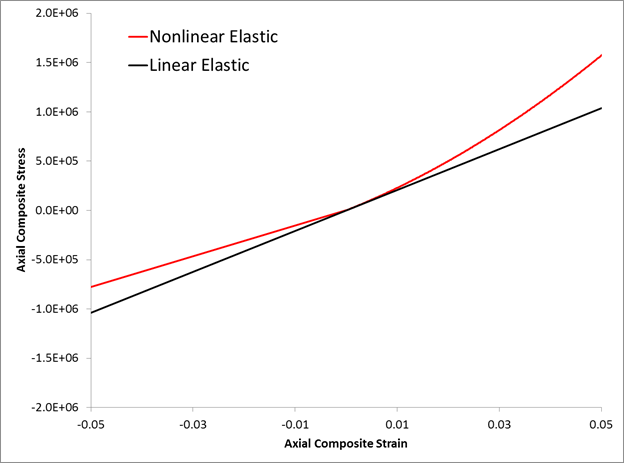
As an example, consider the *NONLINEAR FIBER keyword definition shown below. Given these settings, the material 9002 will be assigned a nonlinear fiber parameter of 21.0 and a composite modulus knockdown factor of 0.75. The image below shows the stress-strain response of this material with the *NONLINEAR FIBER keyword active (nonlinear elastic) and inactive (linear elastic).
*MATERIAL, NAME=9002
*NONLINEAR FIBER, ETAC=0.75
21.0For further information regarding the fiber nonlinearity features, refer to the Theory Manual.