Interaction with ANSYS
Learn how Helius PFA integrates with ANSYS.
In an ANSYS structural-level finite element analysis of a composite structure, Helius PFA quickly and accurately decomposes the composite average stress/strain field into constituent average stress/strain fields. The constituent average stress states are used by the software to predict damage evolution and material failure for each constituent material (fiber and matrix). Subsequently, it homogenizes the current damaged microstructure to provide an accurate assessment of the current composite average stiffness for use in the structural-level finite element analysis. Helius PFA is designed to provide this enhanced composite modeling capability without significantly increasing the time required to run the analysis. For example, using it in conjunction with a structural-level finite element analysis usually increases the overall solution time by two to three percent (2-3%). This is a very small price to pay for the increased solution accuracy provided.
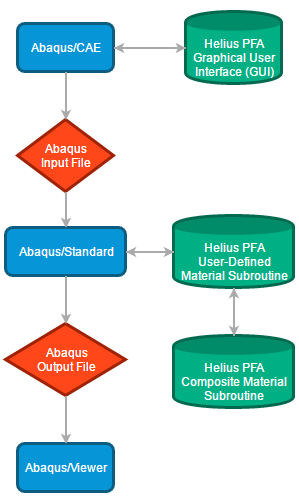
The image below shows a schematic diagram of the individual components of the Helius PFA software and their interaction with the ANSYS software components. Blue rectangles indicate the components of the ANSYS finite element modeling package, red diamonds indicate files containing inputs and outputs, and green ovals indicate the individual components of the software. The Helius PFA Graphical User Interface (GUI) is accessed from within the ANSYS Mechanical APDL and assists you in defining the ANSYS input file commands required during a finite element analysis that uses Helius PFA.
The Helius PFA User Programmable Feature calculates composite constitutive relations and stresses for use within the ANSYS finite element code. It contains all of the MCT constitutive relations for the individual constituent materials (fiber and matrix) and the homogenized composite material. In addition, the User Programmable Feature contains the constituent damage and failure criteria and the algorithms to degrade the stiffnesses of the constituents and the homogenized composite material to reflect the current damaged state of each constituent material. The ANSYS finite element code calls the User Programmable Feature at each Gaussian integration point in the model where constitutive relations or stresses are needed.
In graphic below, the Helius PFA Composite Material Database is used to store all of the material coefficients that are needed to completely define the MCT multiscale material model for various composite materials. Before a particular composite material can be used in a Helius PFA-enhanced finite element model, the composite material must undergo MCT characterization, and its coefficients must be entered into the Composite Material Database. As shown below, the Helius PFA User Programmable Feature opens and reads the Composite Material Database to extract the necessary material coefficients for any composite materials that are used in the finite element model. Note, the material database is not necessary for Helius PFA cohesive materials. Since the number of inputs required to define a cohesive material are much less than a composite, the entire material is defined in the ANSYS input file.
In addition to the software modules depicted above, Helius PFA contains one additional auxiliary program: Composite Material Manager. Composite Material Manager is a stand-alone program that allows you to characterize new composite materials and add them to the Composite Material Library.