Spaces are required to allow calculating the volumes of the areas that demand heating and cooling. The volume computation for a space is based on its room-bounding components and is calculated as the area of its base multiplied by the height of the space.
In Revit, both area and volume are calculated to wall faces (volumes based on planes other than finish faces will be different when the project is upgraded). The base computation height is specified by the (reference) Level and Base Offset. The default computation height of the base is 0' 0" (0.00 mm) above the reference level of the space. The vertical extent for a space is specified as the Upper Limit and Limit Offset. Spaces have a default vertical extent of 8' 0" (2600 mm) above the base (reference) level.
Volumes and Linked Files
You should verify the upper limits and boundaries of spaces that are automatically created from existing rooms (in a local file or a linked model), and redefine these upper limits where necessary. When working with a linked model, all spaces (and zones) must be in the host file. Volume calculations and heating and cooling loads analyses are not supported if the analyses are based on spaces (and zones) that reside in a linked model.
Areas and Volumes Option
When the Areas and Volumes option is selected in the Areas and Volumes Computations dialog (Architect tab Room & Area panel drop-down
Room & Area panel drop-down Area and Volume Computations), additional room-bounding components may determine the vertical extent for spaces, and affect the volume computations. With Areas and Volumes selected, space boundaries snap to roofs and ceilings. Snapping occurs if Areas and Volumes is selected and the vertical extent of the space intersects one of these room-bounding components. The base and vertical extent properties for a space are not changed by the Areas and Volumes setting.
Area and Volume Computations), additional room-bounding components may determine the vertical extent for spaces, and affect the volume computations. With Areas and Volumes selected, space boundaries snap to roofs and ceilings. Snapping occurs if Areas and Volumes is selected and the vertical extent of the space intersects one of these room-bounding components. The base and vertical extent properties for a space are not changed by the Areas and Volumes setting.
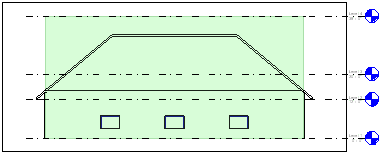
Section View of a Space with Areas and Volumes off.
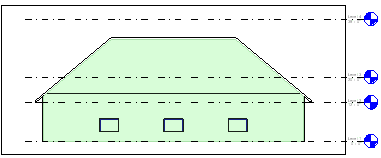
Section View of a Space with Areas and Volumes on.
Revit uses shading to display spaces in plan views and section views.
With the exception of spaces that span multiple levels (shafts and chases), you should specify the upper limit of a space to be up to the next level above the base level of the space. You should select Areas and Volumes (default setting) to allow more accurate volume computations and heating and cooling analysis. If Areas and Volumes is not selected, the space boundary snaps to its vertical extent (and the Volume property for the space displays as Not Computed). Areas and Volumes is selected by default in Revit.