The overall length of wiring in a circuit is calculated and displayed as the value for Length in the Properties palette.
The Length is calculated as the sum of the distances along the X, Y, and Z axes.
In the following example, the length is calculated as 12' 11 7/64."
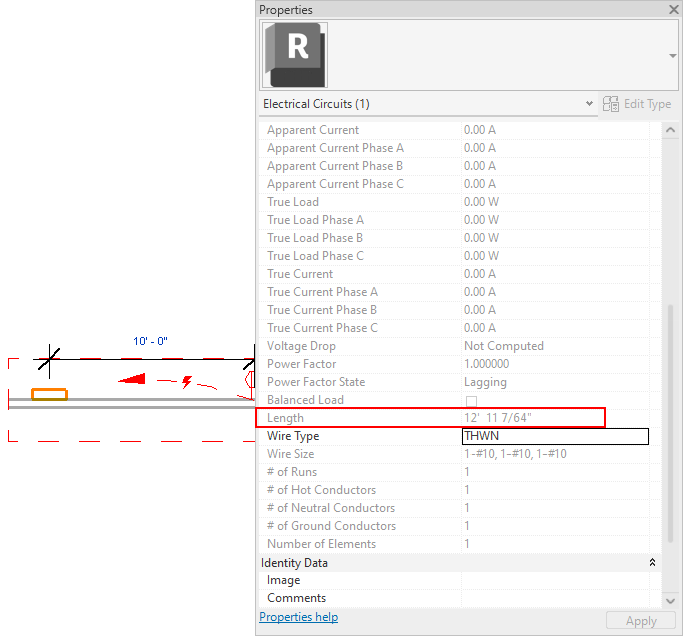
The distance between the receptacle and the panel along the X axis is 10'. However, the panel and the receptacle are at different elevations. The panel is at 4' 0" and the receptacle is at 1' 6", a difference of 2' 6" along the Z axis.
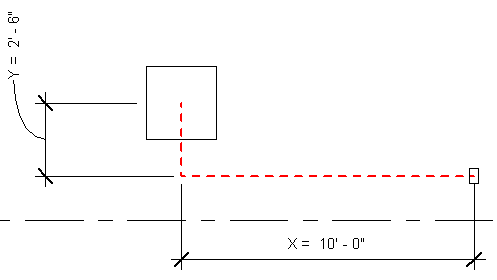
The sum of distances along the X, Y, and Z axes is 12' 6", which is close to the 12' 11 7/64" length value displayed in the circuit instance properties on the Properties palette. The difference can be accounted for as the distance to the connector within the components and the measurements that were extended to the center of each component.
In the previous example, the calculation is straightforward because the geometry of the circuit is aligned parallel to the X, Y, and Z axes. In the following example, the distance between the panel and receptacle is still 10', however, the length is still calculated as the sum of the distances along the X, Y, and Z axes.
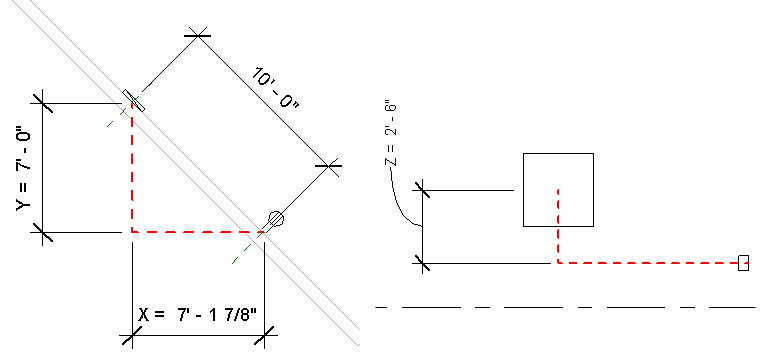
The length is along the X, Y, Z axes is 7' 0" + 7' 1 7/8" + 2' 6" = 16' 7 7/8" and the computed length shown in the circuit properties is 16' 6 13/256".