Transient Compressible Flow in a Shocktube
Analysis Characteristics
- Transient Flow
- Two Dimensional Internal flow
- Turbulent
- Compressible
- Non-Adiabatic
Reference
Saad, M.A., “Compressible Fluid Flow, 2nd edition,” Prentice-Hall, New Jersey,1993.
Problem Description
Compressible flow in a shock tube is a classic gas dynamics problem. For ideal flow (no friction), the normal shock relations can be used to determined the shock speed and the conditions downstream of the shock.
For this verification case a shock tube (10 meters long, 0.2 meters diameter) is modeled with an initial static pressure ratio of 3:2. The initial pressure condition simulates the dividing membrane in a real shock tube. Once the membrane is broken, the higher pressure expands into the low pressure air and a normal shock travels down the tube at a supersonic speed. The shock speed is determined by the initial condition pressure ratio across the membrane.
Geometry and Boundary Conditions
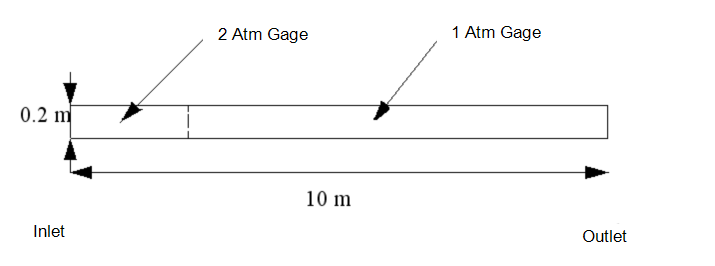
Initial Conditions:
- High Pressure = 44.1 psia, 300K
- Low Pressure = 29.4 psia, 300K
Boundary Conditions:
- Slip walls
- Left edge - 44.1 psia, 300 K
- Right edge - 29.4 psia, 300 K
Results
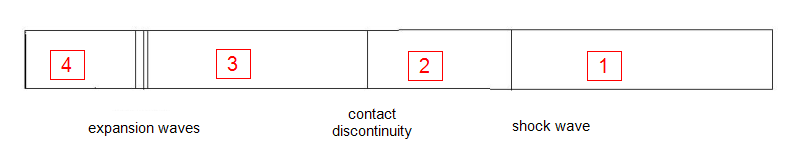
The following figures show the scenarios before the membrane is broken (top) and after it is broken (bottom).

| Ideal Flow (Benchmark) | 2018: Build 20170308 | % Error | 2019: Build 20180130 | % Error | |
| Shock Ma | 1.09 | 1.177 | 7.99 | 1.178 | 8.04 |
| P2 = P3 | 1.464 atm | 1.450 | 0.95 | 1.451 | 0.872 |