Particle Traces
In Autodesk® CFD, you can create particle traces for either massless particles, which follow the flow or for particles with mass. In both cases, a Lagrangian equation is solved to calculate the particle path through the model.
For the massless particles, the equation is:
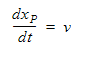
where xp is the particle position vector and v is the local particle velocity.
For massless particles, this local particle velocity is the same as the local fluid velocity.
For particles with mass, a second equation is needed to determine the local particle velocity. We use Newton’s Second Law:
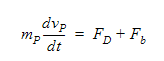
where mp is the particle mass, vp is the particle velocity, Fb is the buoyant force and Fd is the drag force calculated using:
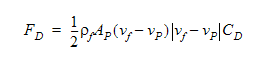
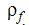 is the fluid density
is the fluid density- Ap is the particle area based on the user input of particle radius
- vf is the fluid velocity vector
- vp is the particle velocity vector
- CD is the drag coefficient, calculated using:
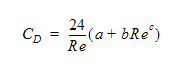
In this equation, a,b and c are user inputs and Re is the fluid Reynolds calculated using:
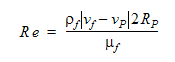
In addition to the definitions above, this equation also uses Rp as the particle radius and 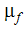 is the fluid viscosity.
is the fluid viscosity.
Finally, the buoyant force is calculated using:
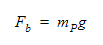
where g is the gravity vector input by the user.