Moist Gas or Humidity Calculations
As noted earlier, the energy equation for moist gas flows is written in terms of temperature with a variable specific heat:
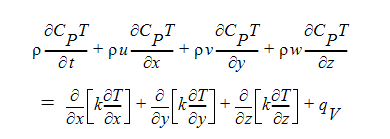
To track the moisture in the fluid, an additional partial differential equation is solved for a scalar quantity which represents the mass fraction of the moisture (in either liquid or vapor phases):
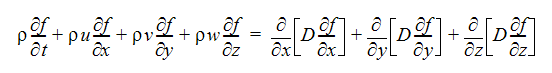
From the solution of these 2 equations and the thermodynamic tables, the quality (vapor fraction) of the moisture can be calculated. With the quality and the mass fraction of the moisture, the mass or mixture fraction of the condensed water can be calculated. This mixture fraction is output for moist gas calculations along with the relative humidity at every node in the solution domain.
The properties of the moist fluid are calculated assuming a homogenous mixture. For example, the density can be calculated as:
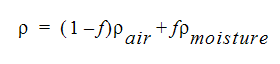
where the moisture density is calculated from the thermodynamic tables using the calculated enthalpy.