As a result of partitioning, selected objects are divided into the smallest existing objects (subcontours/solids) that comprise the geometry of the input objects. Robot finds all separate common parts (for each object combination) and all logical complements of objects.
An example of a partition operation for 3 cylinders is presented in following image.
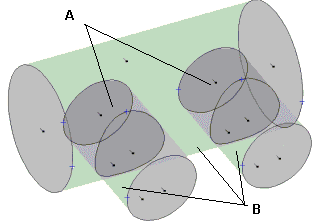
The result of this operation is the generation of 5 objects: 2 objects that are the common parts of the cylinders (A - common parts of the cylinders) and 3 objects that are the complements of the cylinders (B - subtraction operations: smaller cylinders have been subtracted from the larger cylinder and the larger cylinder has been subtracted from smaller cylinders).