This dialog considers mass displacement by an eccentricity in seismic analysis. Open the dialog by clicking Definition of eccentricities in the Modal Analysis Parameters dialog.
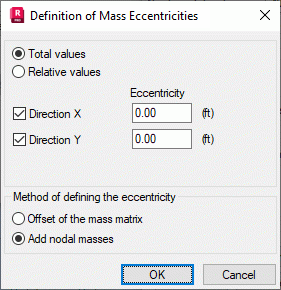
The eccentricity value (mass shift) in the modal analysis can be defined as:
- Total values of eccentricity expressed in a length unit.
- Relative values expressed as percent of the story or the entire building width.
For seismic analyses as specified in codes, it is recommended to consider the mass displacement by an accidental eccentricity e1 which is:
e1j = f * Lj
where:
e1j - An accidental eccentricity of the mass of the j-th story, with respect to its nominal position, is applied in the same direction on all levels.
Lj - A story dimension perpendicular to the direction of a seismic action.
f - A factor; as an example, for the Eurocode8 in accordance with point 3.2, the relative eccentricity value is 5% (0.05).
If stories have not been defined in a structure model, the Eccentricity is calculated based on the global dimensions of the whole model. If stories are defined, a value of the eccentricity is considered for elements belonging to each story separately, on the base of the story dimensions Lx, Ly.
Two methods to define eccentricity are available in the program:
- Offset of the mass matrix: modifies masses matrix elements considering shift of the mass by the indicated distance; only the consistent mass matrix is available for this method
- Add nodal masses considers additional nodal masses which model shift of the mass; all types of mass matrixes are available for this method.
The eccentricity value is defined with appropriate 'plus' or 'minus' sign. The mass is shifted in a minus or plus direction along the global axis X / Y. In order to consider the shift of the mass in X or Y direction to both directions, four cases of modal analysis with an appropriate eccentricity should be defined: X-, X+, Y-, Y+.
In order to carry out the seismic analysis considering the mass eccentricity, after each of the modal analysis cases the independent cases of the seismic analysis should be defined, with the selected excitation directions X,Y,Z. As a result, the definition of many cases of the modal and seismic analysis is necessary. In order to facilitate this process, the program offers the possibility to generate the modal analysis with automatic definition of seismic cases, available in the New case definition dialog.