Go to:
Related nodes. Attributes.
This node creates a new poly object for each shell in the inputPoly.
(A shell is a section of the mesh that is not edge-connected to
the rest of the mesh.)
| Node name | Parents | Classification | MFn type | Compatible function sets |
|---|
| polyRetopo | polyModifierWorld | geometry | kReForm | kBase
kNamedObject
kDependencyNode
kReForm |
Related nodes
polySmooth
Attributes (27)
angle, anisotropy, axis, axisOffset, axisPosition, curveInfluenceDirection, curveSingularitySeparation, edgesByAngle, faceUniformity, featureTags, interactiveMode, pivot, pivotX, pivotY, pivotZ, preprocessMesh, preprocessedMesh, preserveHardEdges, shortEdgeTolerance, symmetry, symmetryEdges, targetEdgeDeviation, targetFaceCount, targetFaceCountTolerance, thinTriangleAngleTolerance, topologyRegularity, useFeatureTags
| Long name (short name) | Type | Default | Flags |
|---|
|
angle
(ang)
| angle (double) | 30.0deg |     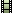 |
|
|
anisotropy
(a)
| double | 0.5 |     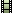 |
|
|
axis
(an)
| enum | 0 |     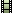 |
|
|
axisOffset
(ao)
| distance (float) | 0.0cm |     |
|
|
axisPosition
(ap)
| enum | 0 |     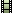 |
|
|
useFeatureTags
(uft)
| bool | 0 |     |
|
|
curveInfluenceDirection
(cid)
| double | 0.01 |     |
|
|
curveSingularitySeparation
(css)
| double | 0.1 |     |
|
|
edgesByAngle
(eba)
| bool | 0 |     |
|
|
featureTags
(ft)
| string | nullptr |     |
|
|
interactiveMode
(imd)
| bool | 0 |     |
|
|
pivot
(p)
| double3 | 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 |      |
|
| pivotX
(px)
| distance (double) | 0.0cm |      | |
|
| pivotY
(py)
| distance (double) | 0.0cm |      | |
|
| pivotZ
(pz)
| distance (double) | 0.0cm |      | |
|
|
preprocessMesh
(pm)
| bool | 1 |     |
|
|
preprocessedMesh
(ppm)
| mesh | nullptr |     |
|
|
preserveHardEdges
(phe)
| bool | 0 |     |
|
|
topologyRegularity
(trg)
| double | 0.5 |      |
|
|
shortEdgeTolerance
(se)
| distance (double) | 0.0001cm |     |
|
|
symmetry
(sym)
| bool | 0 |     |
|
|
symmetryEdges
(sme)
| componentList | nullptr |     |
|
|
targetEdgeDeviation
(ted)
| double | 0.2929 |     |
|
|
targetFaceCount
(tfc)
| integer | 0 |      |
|
|
targetFaceCountTolerance
(tft)
| integer | 10 |      |
|
|
thinTriangleAngleTolerance
(tt)
| angle (double) | 1.0deg |     |
|
|
faceUniformity
(fun)
| double | 0.0 |      |
|