There are two classes of warnings:
Warnings - This class of warnings indicate a solver event occurred which may need user attention to ensure the quality of the simulation or may alert the user about certain simulation results, like Recoater Interference or Support Structure Failure. These are viewable from the log files.
Critical Warnings - This class of warnings occur when the solver detects a model input or event which is likely to impact the results of the simulation, which may need to be addressed and the simulation re-run. These are viewable from the notifications system and the log files.
How to view warnings
From the Log files:
Click the View Logs button on the
Home or
Results tab, or within the
Job Manager window. There are up to 3 tabs in the view logs button, Thermal, Mechanical, and Recoater Blade Interference. The Thermal and Mechanical tabs will automatically update during the simulation, and by default, scroll to the last line of the log file. To prevent this in order to revisit warnings issued earlier in the simulation, uncheck the
Auto scroll button located at the bottom left of the view logs window.
on the
Home or
Results tab, or within the
Job Manager window. There are up to 3 tabs in the view logs button, Thermal, Mechanical, and Recoater Blade Interference. The Thermal and Mechanical tabs will automatically update during the simulation, and by default, scroll to the last line of the log file. To prevent this in order to revisit warnings issued earlier in the simulation, uncheck the
Auto scroll button located at the bottom left of the view logs window.
Log files will show both Warnings and Critical warnings. Each warning is proceed by a flag and a counter, as follows:
************************ number-warnings## Warning ************************
This informs the user how many total warnings have been recorded for the present simulation.
From the notification system:
Critical warnings will automatically be displayed by the notifications system in the upper right of the program window when they are issued by the solver. Each critical warning will be shown briefly and then the notification will be hidden. To view the notifications again, press the bell icon
 at the upper right of the program window.
at the upper right of the program window.
Below, the common Warnings and Critical Warnings will be described and methods to fix or avoid the more severe warnings will be given.
Warnings
PRM overwrite Warning
PRM file values ... will be overwritten
This warning indicates the current PRM file name chosen already exists in the folder where the PRM generation simulation is being run and that the existing PRM file will be overwritten. To avoid this warning ensure each PRM file is given a unique and identifiable name.
Single STL padding tolerance ignored Warning
*STOL STL padding tolerance is ignored for a single STL.
This warning indicates the *STOL padding tolerance, which helps mesh contact STL files by expanding them by the specified distance, will be ignored for simulations with just 1 STL file.
Loose or rotating elements Warning
disconnected-element-number## Loose or rotating elements removed
This warning indicates the numbered element cannot be solved because it is not connected to the existing part or substrate, or not provided with support structures. The result would be a non-physical floating mass, so the element has been removed from the mesh for analysis.

Disconnected elements
In the figure on the left, you see a complex part. On the right is the solved simulation. Unsupported elements radiating downward have been removed because they could not be built from the bottom up. Rotating the build volume or adding support structures can eliminate these warnings.
Recoater Interference Warning
Recoater clearance = clearance-percentage## % Top z deformed coord: z-max-coordinate## Recoater coord:
This warning indicates build failure could occur due to recoater interference, as the recoater clearance is less than either the recoater tolerance specified by the user in the Solver Settings.
Support Structure Failure Warning
Support structure failure -------------------------------
This warning indicates a support structure element has failed, according to the failure stress specified in the Solver Settings.
Critical Warnings
PRM file missing properties Critical Warnings






These Critical Warnings are issued whenever a part-level simulation is run with a PRM file which is missing one or more necessary material properties. Without these material properties, the results of the simulations using the PRM file will not be valid. It is advised that the PRM file or files be regenerated with all the required material properties. Review the Material Database or custom material file for potential errors.
PRM files mismatching properties Critical Warning

This Critical Warning indicates that two PRM files are used with mismatched material properties. The properties from the first PRM file will be used for all component geometries. It is advised that only PRM files with identical material properties are used.
PRM file version mismatch Critical Warning

This Critical Warning is issued when a PRM file is used from an older version of the software which may not be fully compatible with the current version. It is advised that the PRM file be generated again with the most current version of Netfabb Local Simulation.
STL size Critical Warning

This Critical Warning is triggered when any bounding box dimension of the STL is smaller than the base element size. Possible causes are as follows:
- The STL file is too small. Make sure that the units for the STL are correct.
- A coarse mesh size is used. Try refining the mesh size.
STL Cannot be repaired Critical Warning

If a non-manifold STL is attempted to be simulated, the Netfabb Default Repair algorithm is attempted. If this fails, this is the Warning issued. It is advised the user perform an extended or advanced repair in Netfabb, or regenerate the STL from the software of origin.
Zero Laser Line Length Critical Warning

This Critical Warning is issued when a laser line during PRM generation or DED simulations has a length of 0 mm. For PRM generation, certain combinations of interlayer rotation angles and hatch spacing may result in a few such lines, which will have negligible impact upon the resulting PRM. For DED simulations it is suggested the .lsr file be checked over for potential errors in the laser vectors.
Insufficient Memory Critical Warning

This Critical Warning occurs after the meshing step, if the solver estimates that the ensuing simulation will require more RAM than is available on the system. Ensure the workstation meets the
minimum system requirements. To reduce the mesh, if using the Minimal Wall Thickness meshing approach, increase the minimal wall thickness and change to the Fast or Fastest setting. If the Layer Based approach is used, reduce the mesh density by increasing both the Layers per Element and number of Coarsening Generations. For further details consult the
meshing meshing approach help topic.
Plasticity step did not Converge Critical Warning

This Critical Warning is issued when the plasticity algorithm failed to converge. This warning is most often issued during PRM generation or DED simulations. Extremely high energy input and extremely non-linear material properties are the most common causes of poor convergence. Check that the processing conditions used are correct. Plot the material properties to check for typos in the properties. If necessary, add additional relaxation steps to the mechanical analysis.
Multiple Lasers Critical Warning

During DED analysis, if multiple simultaneous heat sources are detected, this Critical Warning is given. Disregard the warning if the system being modeled has multiple lasers, otherwise correct the .lsr file timing to ensure the laser is active at only one location at any time.
More than 20% of the Mesh Removed Critical Warning

When more than 20% of the original parts and support structures fail to mesh, due to loose or rotating elements, this Critical Warning is issued. This commonly occurs when thin-walled components are meshed with too thick of elements. Decrease the minimum wall thickness or decrease the number of layers per element, in
mesh settings. If the part is correctly meshed, i adding additional support structures or changing the orientation of the part or parts may be necessary.
Maximum Iterations Critical Warning

Each time step has a maximum number of times the solver will attempt to reiterate before terminating the simulation, at which point this Critical Warning is reported. This warning is most often issued during PRM generation or DED simulations. Extremely high energy input and extremely non-linear material properties are the most common causes. Check that the processing conditions used are correct. Plot the material properties to check for typos in the properties. If necessary, add additional relaxation steps to the failed analysis.
Structural Plasticity On without Build Plate plasticity properties Critical Warning

If a simulation with the optional Structural Plasticity included, but the build plate does not have plasticity properties assigned to it, this Critical Warning will be shown. Post-process plasticity simulations without assigning these properties will not be valid as the build plate will not be allowed to yield. It is recommended the Build Plate material be updated with plasticity properties and the simulation to be rerun.
Version Mismatch Critical Warnings
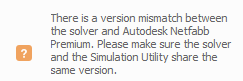
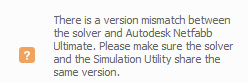

These Critical Warnings are issued whenever there is a mismatch in Version between the installed Autodesk products. It is recommended the user update all installed products to the latest version.
Hard Drive Critical Warnings



These hard drive Critical Warnings indicate a user is running on an encrypted drive, a USB drive, or a Network drive. These drive types have slower write speeds than internal drives and may degrade the solver's performance, increasing computational time significantly. It is recommended that the simulation be restarted on an internal, non-encrypted drive.