The solid feature tree contains the history of solid operations performed on a solid. Each solid operation is defined as a feature on the solid.
The solid tree is created automatically when you add a solid feature to a solid.
For example:
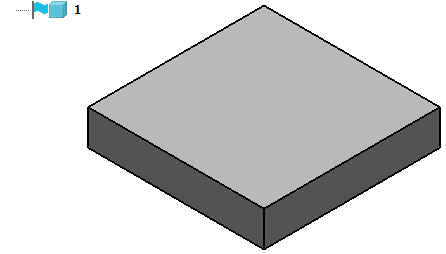
- Create a solid block.
It is automatically added to the solid feature tree. The tree is hidden by default.
- Click Solid Tools tab > State panel > Explorer to display the solid tree in the Explorer window.
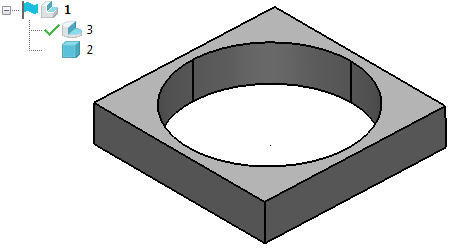
- Add a cut feature to the solid.
The cut feature is displayed in the tree; the block at the bottom of the tree to show that the solid was created from a primitive block.
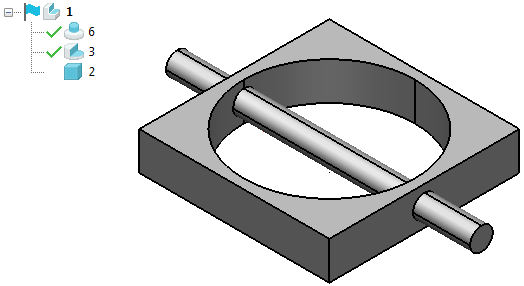
The features are shown in chronological order in the tree. The most recent one applied is shown at the top and the earliest at the bottom.
- Add a Boss to the solid.
The boss feature appears above the cut feature.
The following icons can be displayed in the solid tree:
 - Solid with a history
- Solid with a history
 - General solid without a history
- General solid without a history
 - Active solid
- Active solid
 - Inactive solid
- Inactive solid
 - Extrusion or Extruded solid feature
- Extrusion or Extruded solid feature
 - Solid of revolution or Solid of revolution feature
- Solid of revolution or Solid of revolution feature
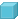 - Block primitive or Block primitive feature
- Block primitive or Block primitive feature
 - Sphere primitive or Sphere primitive feature
- Sphere primitive or Sphere primitive feature
 - Cylinder primitive or Cylinder primitive feature
- Cylinder primitive or Cylinder primitive feature
 - Cone primitive or Cone primitive feature
- Cone primitive or Cone primitive feature
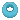 - Torus primitive or Torus primitive feature
- Torus primitive or Torus primitive feature
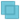 - Add feature
- Add feature
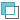 - Subtract feature
- Subtract feature
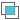 - Intersect feature
- Intersect feature
 - Cut feature
- Cut feature
 - Boss feature
- Boss feature
 - Hole feature
- Hole feature
 - Lightweight hole feature
- Lightweight hole feature
 /
/ - Pocket/Protrusion feature
- Pocket/Protrusion feature
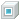 - Hollow feature
- Hollow feature
 - Thicken feature
- Thicken feature
 - Bulge feature
- Bulge feature
 - Fillet feature
- Fillet feature
 - Chamfer feature
- Chamfer feature
 - Rib fillet feature
- Rib fillet feature
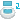 - Wrap feature
- Wrap feature
 - Sculpt feature
- Sculpt feature
 - Suppressed feature
- Suppressed feature
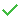 - Unsuppressed feature
- Unsuppressed feature
 - Error suppressed feature
- Error suppressed feature
 - Defer update
- Defer update
 - Group feature
- Group feature
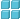 - Pattern feature
- Pattern feature
 - Edited face
- Edited face
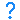 - Unrecognised. This is used to indicate that the feature is not recognised by the version of
PowerShape. It is displayed in the feature tree when you create a model in a future version of
PowerShape that contains a new type of feature and then open that model in an earlier version of the software that cannot recognise the new feature type. When the feature tree is replayed, an
Unrecognised
feature is error-suppressed.
- Unrecognised. This is used to indicate that the feature is not recognised by the version of
PowerShape. It is displayed in the feature tree when you create a model in a future version of
PowerShape that contains a new type of feature and then open that model in an earlier version of the software that cannot recognise the new feature type. When the feature tree is replayed, an
Unrecognised
feature is error-suppressed.
 - Associated features hidden in tree
- Associated features hidden in tree
 - Associated features visible in tree
- Associated features visible in tree