Schematic types define thermal properties for building elements during schematic design.
Subsequent energy analyses then use the corresponding thermal properties, which provide more detailed information than the default conceptual types.
You can select the specific element categories for which you want to use schematic types. Any element categories not overridden with a schematic type will continue to use the default conceptual types. If the Detailed Elements option is enabled, schematic types and conceptual types are overridden by materials-based thermal properties, where defined.
To use thermal properties defined by schematic types
- Click Analyze tab
 Energy Optimization panel
Energy Optimization panel
 (Energy Settings).
(Energy Settings).
- In the Energy Settings dialog, for Other Options, click Edit.
- In the Advanced Energy Settings dialog, for
Schematic Types, click in the
Value column, and click
 .
.
The Schematic Types dialog displays the list of element categories, with the Override checkbox cleared for all categories.
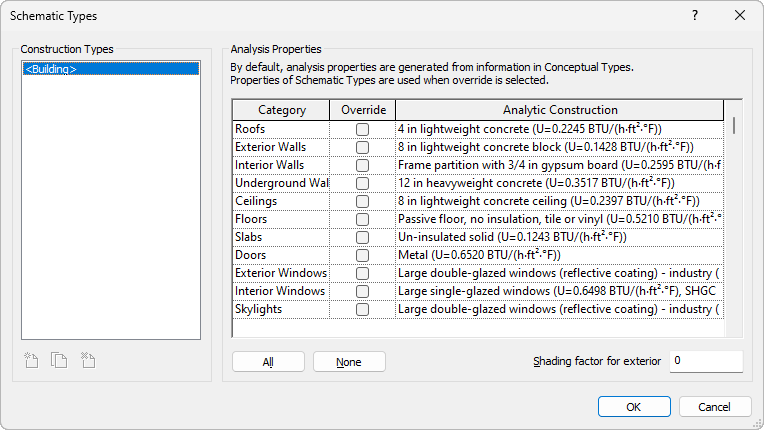
- In the Schematic Types dialog, do the following:
- For a category for which you want to use thermal properties defined by schematic types, select
Override. In the
Analytic Construction column, use the drop-down list to select the desired construction.
Note: To select Override for all categories, click All. To reverse it, click None.
- To continue using thermal properties defined by conceptual types for some categories, clear their Override check boxes.
- Click OK.
- For a category for which you want to use thermal properties defined by schematic types, select
Override. In the
Analytic Construction column, use the drop-down list to select the desired construction.
When you next perform energy analysis, thermal properties for the specified schematic types (analytic constructions) are used for those element categories.
For assumptions on schematic types, download this file.