Revit measures the perimeter of a room at a defined distance above the base level of the room. This distance is the computation height.
It is used to compute the room perimeter, area, and volume. By default, the computation height is 0’ or 0 mm above the base level of the room.
For buildings with vertical walls, the default computation height usually gives accurate results. However, if a building includes sloped walls or other atypical features, you may need to adjust the computation height to achieve more accurate room areas and volumes.
For example, the following drawing shows a section of a room with a sloped wall. The dotted line across the lower part of the room indicates the current computation height. (This line displays when you select the room.) Revit uses the perimeter of the room at the computation height when computing the room area and volume.

Changing the computation height affects the room perimeter, and thus the room area and volume. For example, the following drawing shows the same room, but the computation height has been moved lower (indicated by the dashed line). The room tag shows the changed room area and volume.
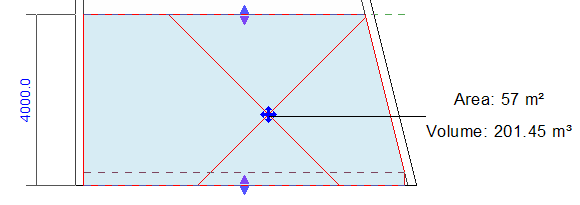
The computation height is defined as a property of a level instance.