Data Standard and Localization
The dialogs and tabs that come with Data Standard automatically support twelve different languages.
Text strings for these languages are defined in XML files. The files are located here:
C:\ProgramData\Autodesk\<Vault version>\Extensions\DataStandard\<localization folder>
where <language code> is the folder name for a language (e.g., en-US, de-DE, it-IT).
Each language folder contains two files:
- UIStrings.xml–Contains strings that are visible in dialogs, tabs, and menus.
- PropertyTranslations.xml–Contains mapping for Vault properties, from a language independent property name to the real property name in the Vault database.
These files can be extended to support different languages in customized Data Standard dialogs.
How Is the Language Determined?
Vault Client
By default, the language used for the Data Standard UI strings and the property translations is the same as the Vault client that is installed. However, this can be overridden by modifying the DSLanguages.xml file located at:
C:\ProgramData\Autodesk\<Vault version>\Extensions\DataStandard\Vault.
Set the DSLanguages.xml correctly: Change the DB Language manually to the language of the server, for example en-US. Leave the Language Code ID=UI blank: It enables Vault Client to read property labels, messages and headers from the source based on the active language pack (for example, to read values from de-DE\UIString.xml).
<Language_Code ID="DB">en-US</Language_Code>
<Language_Code ID="UI"></Language_Code>Change Category values – UIStrings.xml: Category names in the Category Combobox VDS dialogs aren't displayed when the language of Client is different from the language of the server. Therefore, we recommend changing the Category names in the UIStrings.xml to the Category names that correspond with the language of vault server. See picture below:
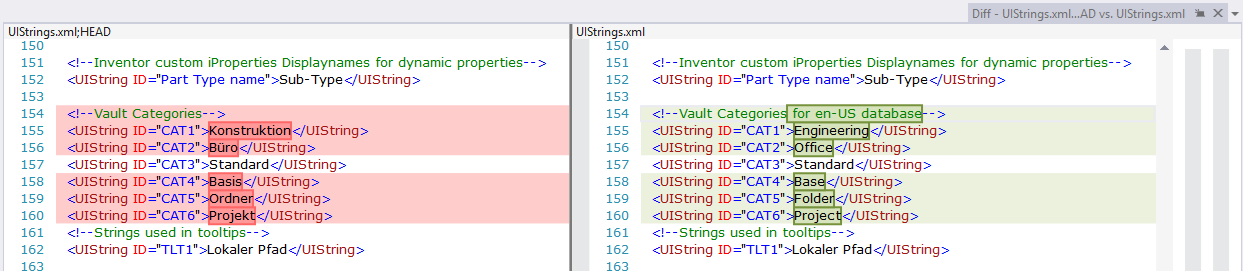
CAD
For Inventor and AutoCAD, the language is determined automatically and cannot be set. Data Standard tries to use the same language that the CAD application uses. If the CAD application uses a language that is not supported by Data Standard, English is used as fallback.
The Vault database language is not relevant for the CAD applications because Data Standard uses mapped properties (Inventor iProperties, AutoCAD DWG properties, and block attributes).
UI Strings
Sample: UIStrings.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<UIStrings LanguageCode="en-US">
<UIString ID="LBL1">Folder</UIString>
<UIString ID="LBL2">Title</UIString>
<UIString ID="LBL3">Description</UIString>
...
</UIStrings>The XML file contains a <UIStrings> element with an attribute LanguageCode to specify the language. The <UIStrings> element is a collection of <UIString> elements. The attribute ID has to be unique. For your own strings, Autodesk recommends that you use a prefix (e.g., ID="MYPREFIX_LBL1"). The value of the element is the text string.
How to Use UI Strings
The UI strings can be used in different Data Standard components by using the following expressions:
XAML Files:
UIString[<ID>]For example,
<Label Content="{Binding UISTring[LBL2]}"/>The above sample looks in the UIStrings.xml (based on the used language) for a
<UIString>element with the ID LBL2 and returns the Title string and displays this as a label in the dialog.PowerShell files:
$UIString["<ID>"]MenuDefinitions.xml File:
$UIString[<ID>]. The MNU file was replaced the with the MenuDefinitions.xml file in VDS 2017.This can be used in variables
Description,Hint,Label, andNavigationTypesof a menu item definition. See MenuDefinitions.xml-File for more information.Labeling in Dynamic Category Properties Grid. By default, the first column in Dynamic Category Grid lists the property name (System Name).
- Note that for Vault Client Data Standard the label is pulled from the
$UIString[<ID>]which has a mapping to the ‘system-name’. To review the system name of a user-defined property, add the “system-name” column “System to the grid in: Vault Administration > Behaviors > Properties > Create/Edit Property. - For Data Standard for inventor and AutoCAD the label is pulled from the
$UIString[<ID>]which has a mapping to a custom 'iProperty (Inventor) or a custom File Property' (AutoCAD) or a block attribute name (AutoCAD). A localized designation enables a dynamic override of the label.
- Note that for Vault Client Data Standard the label is pulled from the
UIString Example:
<UIString ID ="7b6a617f-bf95-426f-a2fl-b4d0e9eec0a3">Zeichnungs-Titel</UIString>Result in the Dynamic Category Grid for en-US, for client started in de-DE:
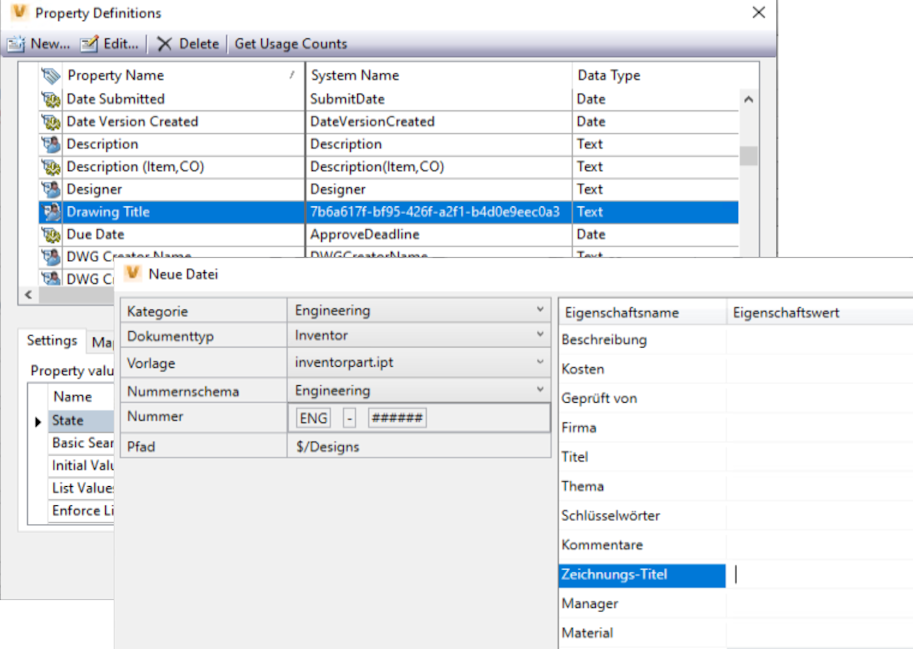
Property Translations
Sample: PropertyTranslations.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<PropertyTranslations LanguageCode="en-US">
<PropertyTranslation Name="NAME">Name</PropertyTranslation>
<PropertyTranslation Name="TITLE">Title</PropertyTranslation>
<PropertyTranslation Name="DESCRIPTION">Description</PropertyTranslation>
...
</PropertyTranslations>The XML file contains a <PropertyTranslations> element with an attribute LanguageCode to specify the language. The <PropertyTranslations> element is a collection of <PropertyTranslation> elements. The attribute Name has to be unique. The value of the element is the display name of the Vault property.
How to Use Property Translations
In XAML and in PowerShell files, Vault properties can be accessed by Prop[<property name>] expressions. Instead of using a fixed property name, the following syntax can be used:
XAML Files:
<TextBox Text="{Binding Prop[_XLTN_<Name>].Value}"For example:
<TextBox Text="{Binding Prop[_XLTN_DESCRIPTION].Value}"/>The
prefix_XLTN_in the above sample looks in the PropertyTranslations.xml for a<PropertyTranslation>element with the name DESCRIPTION and replaces the complete expression_XLTN_DESCRIPTIONwith the value Description. The content of the text box is then bound to the Vault property Description.PowerShell file:
$Prop["_XLTN_<Name>"].Value