The parameters of the seismic simplified analysis according to the equivalent lateral force method depend on a seismic code and a method of defining values of the fundamental periods selected in the Seismic Analysis dialog.
- Access
-
- Click
Tools
 Job Preferences
Job Preferences  Design Codes.
Design Codes.
- Go to the Loads section, and then select ASCE 7-22 from the seismic loads menu.
- Click
Analysis
 Analysis Types.
Analysis Types.
The Analysis Types dialog displays.
- Click
New.
The New Case Definition dialog opens.
- Select
Seismic (Equivalent Lateral Force Method), and click
OK.
The Seismic Analysis dialog opens.
- Click
Seismic Analysis Parameters.
The Parameters dialog opens.
- Click
Tools
Dialog elements
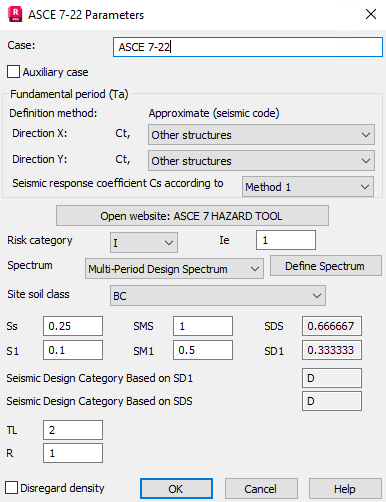
- Fundamental period (Ta)
- The calculation of the fundamental period (Ta) depends on the method selected in the Seismic analysis dialog.
-
-
Approximate method
The fundamental period Ta is calculated according to the ASCE 7-22, equation 12.8-8:
Ta = Ct * hn x
where:
Ct - building period coefficient depending on the type of seismic-force-resisting system that is used ( ASCE 7-22, Table 12.8-2)
x = building period formula exponent depending on the type of seismic-force-resisting system that is used (Table 12.8-2)
h - Structural height (m) as defined in Section 11.2
-
User defined
The fundamental period Ta values are entered manually by the user in each X and Y direction.
-
Precise method
In this method a modal analysis case is created. Fundamental period is calculated for both X and Y directions.
If the option "Periods with maximal mass participation" is off in the Seismic Analysis dialog, then the first mode in direction where are participating masses is taken as fundamental period.
If this option is on, fundamental period is taken from the mode, which fulfill limitations and gives the maximum participating masses in the direction.
Fundamental period Ta calculated according to the approximate method, t he Seismic Response Coefficient Cs is calculated by one of two available methods as defined in ASCE 7-22 Section 12.8.1.1, which can be chosen in the dialog.
The maximal period is calculated according to the formula:
Tmax = Cu * Ta,
where:
Cu - Upper Limit Coefficient (Table 12.8-1),
Ta - Approximative Period
The Seismic Response Coefficient Cs is calculated by one of two available methods as defined in ASCE 7-22 Section 12.8.1.1.
-
Approximate method
- Code parameters
- To complete the seismic analysis according to the rules given in this code, define the following parameters:
-
Risk category
(I, II, III, IV) based on use or occupancy of buildings and structures, classified according to Table 1.5-1
- Ie - Seismic Importance Factor, based on risk category, as specified in Table 1.5-2
- Spectrum
There are four spectra available to choose. Two of them - Multi-Period Design Spectrum and Multi-Period MCER Spectrum - require defining the spectrum in the new dialog window, which can be accessed by clicking the 'Define Spectrum' button located next to it.
It is possible to access official ASCE 7 website: ASCE 7 HAZARD TOOL by clicking the 'Open website: ASCE 7 HAZARD TOOL' button. This page allows to obtain values required for defining the spectrum and coefficient values based on basic data such as location, risk category and site soil class. To transfer the values from the spectrum definition table on the webpage to the definition table in the Robot Structural Analysis, the copy-paste operation can be used.
- Site soil class
(A, B, BC, C, CD, D, DE or E) based on the site soil properties, classified according to Chapter 20 of ASCE 7-22.
-
Spectral response accelerations
as specified in ASCE 7-22 Section 11.4 and in Chapter 22 of ASCE 7-22:
- S1 - Acceleration parameter for 1-second period.
- Ss - Acceleration parameter for short period.
- SMS - is the site adjusted Maximum Considered Earthquake Spectral Response Acceleration Parameter at short periods.
- SM1 - is the site adjusted Maximum Considered Earthquake Spectral Response Acceleration Parameter at a period of 1 s.
- TL - long-period transition period, specified according to Chapter 22 of ASCE 7-22. You can obtain the value of this parameter at https://asce7hazardtool.online/ site, based on location, risk category and site soil class.
- R - response modification coefficient, as specified in ASCE 7-22, Tables 12.2-1, determined by the structure Seismic Force-Resisting System and material.
-
Risk category
- Base shear
- Finally, Base Shear force in the direction of concern is calculated according to the formula of the seismic code ASCE 7-22 Section 12.8:
V = Cs *W
where Cs is t he Seismic Response Coefficient calculated according to ASCE 7-22 Section 12.8.1.1, based on the chosen spectrum type and fundamental period Ta,
and W is the effective seismic weight of the structure. The effective seismic weight of each story is calculated based on the self-weight of the structural elements, as well as added masses and loads converted to masses.
The lateral seismic force distributed to each level is determined from:
Fx = V * wx * hk x / (Σ wi * hki) (eq. 12.8-11 and 12.8-12)
where:
wi and wx - Portion of the total effective seismic weight of the structure (W) located or assigned to level i or x
h - height from base level to appropriate floor level
V - total design lateral force or shear at the base of the structure (kN)
k - exponent depending on the period value:Period k < 0,5 sec
1
0,5 - 2,5 sec
Linear interpolation
> 2,5 sec
2
- Disregard density
- Excludes the density of the structure element (ρ=0) during the estimation of effective seismic weight applied to the stories of the structural model during analysis.
In this case you need to apply added masses or loads conversion to masses as defined in Load Types dialog at Load to Mass Conversion tab.
You can examine all the input parameters and base shear force distribution in the Calculation Notes (open Analysis > Calculation Notes > Simplified/Full Note)