Create AutoLimits Reference
Access
On the Inspect tab, AutoLimits panel, click Dimensional AutoLimits, Area-Perimeter AutoLimits, Physical Properties AutoLimits, or Refresh AutoLimits.
Dimensional AutoLimits
When you use dimensional AutoLimits, your selections refine the AutoLimits type. For instance, if you select a planer model face, and then select another planar model face, the command recognizes that the only valid AutoLimit types are Angle, and minimum distance.
Length 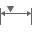
Monitors the length of a selected edge. The measurement can be the result of an accumulation of edges that yield a cumulative length. You can add or subtract the values included in the measurement.
Distance 
Distance monitors the distance between selections. The AutoLimit input is like that of assembly constraints. The measurement can be the result of an accumulation of edges that yield a cumulative length. You can add or subtract the values included in the measurement.
Angle 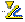
Monitors the angle between selections. The measurement can be the result of an accumulation of selections that yield a cumulative angle. You can add or subtract the values included in the measurement.
Diameter 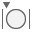
Monitors the diameter of selections, such as a cylinder, cylindrical section, sphere, or spherical section. The measurement can be the result of an accumulation of selections that yield cumulative values. You can add or subtract the values included in the measurement.
Minimum Distance 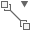
Monitors the minimum distance between selected selections. The measurement can be the result of an accumulation of selections that yield a cumulative length. You can add or subtract the values included in the measurement.
Area-Perimeter AutoLimits
Area 
Monitors the area of a selected face. The measurement can be the result of an accumulation of selections that yield a cumulative area. You can add or subtract the values included in the measurement.
Perimeter 
Monitors the length of edges enclosing a face. The measurement can be the result of an accumulation of selections that yield a cumulative length. You can add or subtract the values included in the measurement.
Physical Properties AutoLimits
Volume 
Monitors the volume of selected input. The measurement can be the result of an accumulation of selections that yield a cumulative volume. You can add or subtract the values included in the measurement
Mass 
Monitors the mass of selected input. The measurement can be the result of an accumulation of selections that yield a cumulative mass. You can add or subtract the values included in the measurement.
AutoLimits Tab
Specifies the objects in a part document that the AutoLimits are attached to.
Selections
Selects an element to monitor in the graphics window from which to obtain the design parameter corresponding to the AutoLimit type.
Radius
Specifies that you want to select a circular or arc edge and monitor its radius value instead of its diameter. Available only when the Diameter AutoLimit is selected and active.
+/-
Specifies how the selected parameter contributes to the total monitored value. You can add or subtract each parameter from the total monitored value. Click the + column to change the arithmetic operator.
Value
Displays the length value of each AutoLimit you select to monitor. When you create another AutoLimit, the value name displays as Length, Distance, Angle, Diameter, Minimum Distance, Area, Perimeter, Volume, or Mass. As you create different AutoLimits, it differs accordingly.
Cumulative
Shows the total value of several AutoLimits selected. It is the result of the plus or minus calculation according to the value list. When you create another AutoLimit, the value name displays as Length, Distance, Angle, Diameter, Minimum Distance, Area, Perimeter, Volume, or Mass. As you create different AutoLimits, it differs accordingly.
Display Precision
Select the level of precision (number of decimal places) you want to specify for your tolerances.
Boundary Tab
Specifies boundaries for the AutoLimits you create in the fields in the Boundaries box.
Lower
Defines the lower value of the boundary range.
LSign
Defines the comparison mathematical operator for the left value of the boundary range. Select the blank to disable the lower value.
Level
Applies a user-defined meaning to various value ranges for the monitored design parameters.
- Green OK (data within normal limits), with a default range of 90-110.
- Yellow Warning (data approaching limit of target range), with a default range of 70-90 or 110-130.
- _Red_Serious Warning (data exceeds target range), with a default range of less than 60 or greater than 140, or 50-70 or 130-150 depending on how you add it.
Upper
Defines the upper value of the boundary range.
USign
Defines the comparison mathematical operator for the upper value of the boundary range.