Basic Calculation of Column Buckling
For an axially loaded column, the calculation is in metric or imperial units, depending on the set standard. The ANSI standard uses the imperial units (with appropriate section dimensions).
Calculated parameters
Reduced length
L red = n L
Slenderness ratio
λ = L red / j min
Radius of gyration
![]()
Rankin critical stress
![]()
Rankin’s critical force
F crR = σ R S
Rankin’s maximal force
F maxR = F crR / k S
Rankin’s calculated safety factor
k sR = F crR / F a
Johnson critical stress
![]()
Johnson’s critical force
F crJ = σ J S
Johnson’s maximal force
F maxJ = F crJ / k s
Johnson’s calculated safety factor
k sJ = F cr J / F a
Euler’s critical stress
σ E = π 2 E / λ 2
Euler’s critical force
F crE = σ E S
Euler’s maximal force
F maxE = F crE / k s
Euler’s calculated safety factor
k sE = F crE / F a
Pressure stress
σ p = F a / S
Critical force
F crP = S y S
Maximal force
F maxP = F crP / k s
Calculated safety factor in pressure
k sP = F crP / F a
Strength check
k s ≤ min (k sR , k sJ , k sE , k sP )
Coefficient for end conditions
Factor for reduced (effective) length calculation,whose value depends on the conditions of end support of the column.
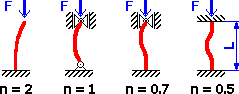
Meaning of used variables