About Deleting and Replacing Faces
About Deleting Faces
Converts a part into a surface, creating delete face feature that you can modify.
The Delete Face command differs from the Delete command (pressing the Delete key).
- Delete Pressing the Delete key removes selected geometry from the part, which you can retrieve only if you immediately use Undo. You cannot use the Delete key to remove individual faces.
- Delete Face command creates a Delete Face feature, and places an icon in the browser hierarchy. The operation automatically converts a part to a surface and replaces the part icon at the top of the browser with a surface icon. Like any other feature, you can use Edit Feature to modify it, and then click Update to incorporate changes.
In the Delete Face command, a window selection contains only one set of body selections. If a surface body and a solid body are defined, you cannot select faces from both at the same time. After you make the initial selection on a body, you can select only surfaces from that same body.
Delete one or more faces to convert a part into a surface. On the resulting surface, apply a decal, and then save the part. Place the part in an assembly where the decal must span across two parts, using assembly constraints to position it.
The following image shows the result of Delete Face when the Heal option is not selected.
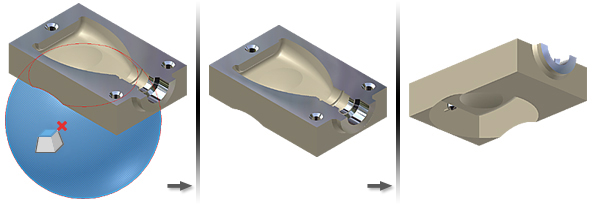
Delete one or more faces, using the Heal option to extend adjacent faces. Gaps between faces, such as when a fillet is deleted, are repaired by extending the adjacent faces until they intersect.
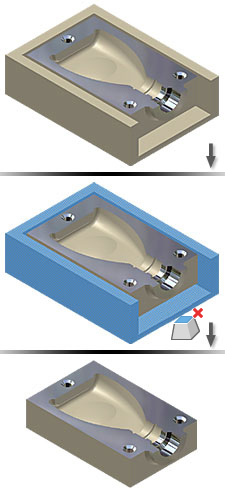
Delete a lump, such as a result of defining a mold base. A lump is a group of faces that may contain some or no void. A part or surface body should have at least one lump. When you model the mold shape and cut the part from the base, a lump remains. Use Delete Face to delete the lump from the cavity.
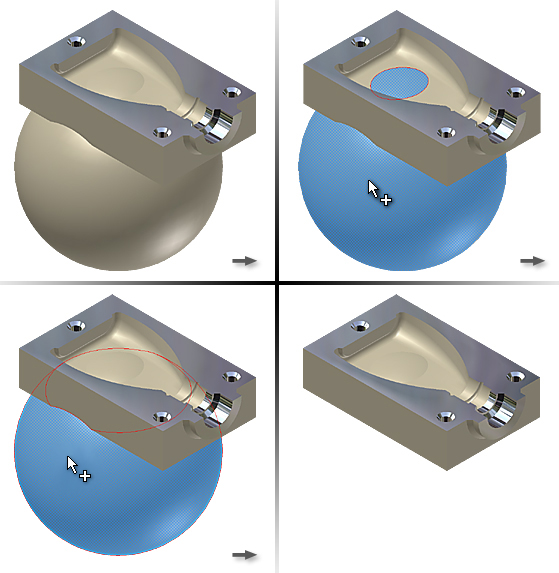
Delete a void to restore mass to the model. A void is a group of faces that define an internal hollow space. Some modeling operations, such as a shell without removing a face, create a hollow inside a model that you later want to remove. Because the void is hidden inside a model, you cycle through selections using the Select Other method to highlight the void to delete.
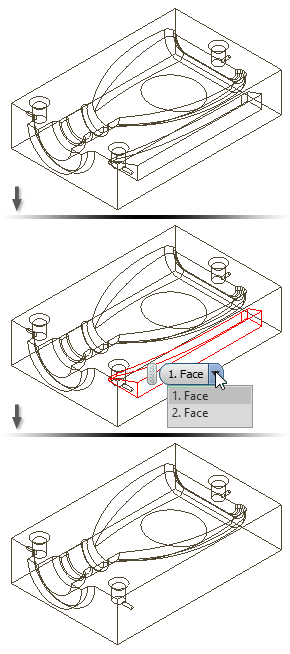
About Replacing Faces
Certain workflows can require you to match a face with a body face, with a sculptured surface, or a work plane.
Use Replace Face to select both the face to replace, and the new face. A Replace Face feature is created. You can edit it with sketch and feature commands.
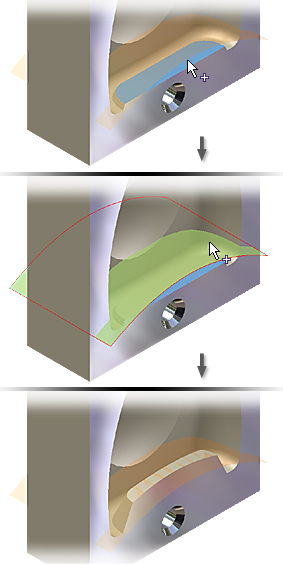
When replacing part faces:
- Solid faces, surfaces, or work planes are selectable as replacement faces.
- The part body must completely intersect the new face. For best results, the new face should be larger than the face being replaced and is trimmed to match the size and shape of the body. The original part face does not expand or contract to match the new face dimensions.
- If importing or combining surfaces, use the Stitch command to stitch surfaces into a quilt.
- You can’t replace faces that are perpendicular to the new face because they do not intersect the new face.
- You can’t copy or paste the replaced face, or use it in a pattern or iFeature by itself. You can include it in these operations when its parent feature is also selected.
- You can create and select one or more work planes to generate a planar replacement face. Work planes behave like selected surfaces, except for extents. Work plane extents are infinite, regardless of the graphical display.
When editing a replaced face feature, changing from a single work plane selection to an alternate single work plane selection preserves dependent features. Dependent features are not preserved when changing between single and multiple selections, or alternate multiple selections.