Incandescent Metal Material tutorial
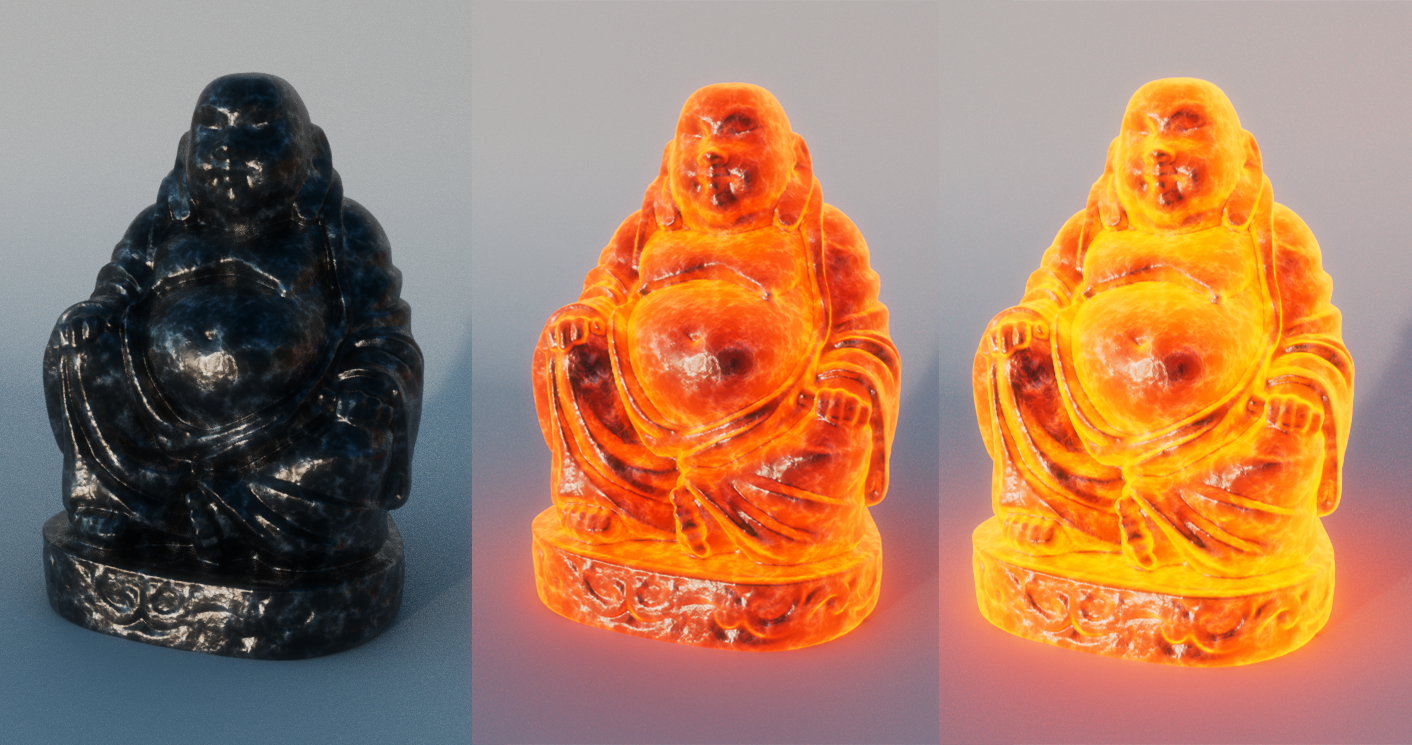

This simple tutorial demonstrates how to create an incandescent metal material. It uses a variety of shaders such as facing_ratio, range, multiply and cell_noise connected to the emission_color of the standard_surface shader. Thanks to Slava Sych for the assistance with this tutorial.
The shader used in this tutorial can be found here.
Standard Surface
Create a standard_surface shader and assign to your model.
- Increase metalness to 1
Cell Noise
Create a cell_noise shader (cell_noise1) and change the following parameters:
pattern : worley2
additive : Enabled
octaves : 4
lacunarity : 1.76
amplitude : 0.72
scale XYZ: 25 25 25 (remember that Scale values depend on the size of your model).
Range shader (range3)
Create a range shader and connect it to the base_weight of the standard_surface shader. Connect the cell_noise shader to the Input of range3. Change the following parameters:
input_min : 0.249
output_min : 0.3
output_max : 0.7
smoothstep : Enabled
Range shader (range2)
Create another Range shader and change the following parameters:
input_min : 0.3
input_max : 0.7
output_min : 0.1
smoothstep : Enabled
Bump2D
Create a bump2D shader and change the bump_height to 0.02. Connect the range shader (range2) to bump_map in the bump2d shader, and connect the bump2d shader to normal of the standard_surface shader.
Facing Ratio
Create a facing_ratio shader and change the following parameters:
bias : 0.6
gain : 0.48
linear : Enabled
invert : Enabled
Color Correct
- Create a color_correct shader. Change the input color RGBA to: 2.9642 0.5212 0 1
Connect the facing_ratio shader and color_correct shaders to a multiply shader (multiply1).
Range Shader (range4)
Create another range shader and change the following parameters:
input_min : 0.249
input_max : 0.484
output_min : 0.7
output_max : 1
Enable smoothstep
Connect the cell_noise shader (cell_noise1) to the input of the range shader (range4).
Create a multiply shader (multiply2). Connect multiply1 to the Input 1 of multiply2.
Connect the range shader (range4) to input2 of multiply2.
Range shader (range 1)
Create a range shader.
- Change the output_max to 3.
Connect the multiply shader (multiply2) to the input of range shader (range1). This is required for the higher value color intensity values.
Connect the range shader (range1) to the emission_color of the standard_surface shader.
Now it is possible to control the incandescence using the emission_weight (0 to 1). If you require more intensity, increase the output_max value in range shader (range1).
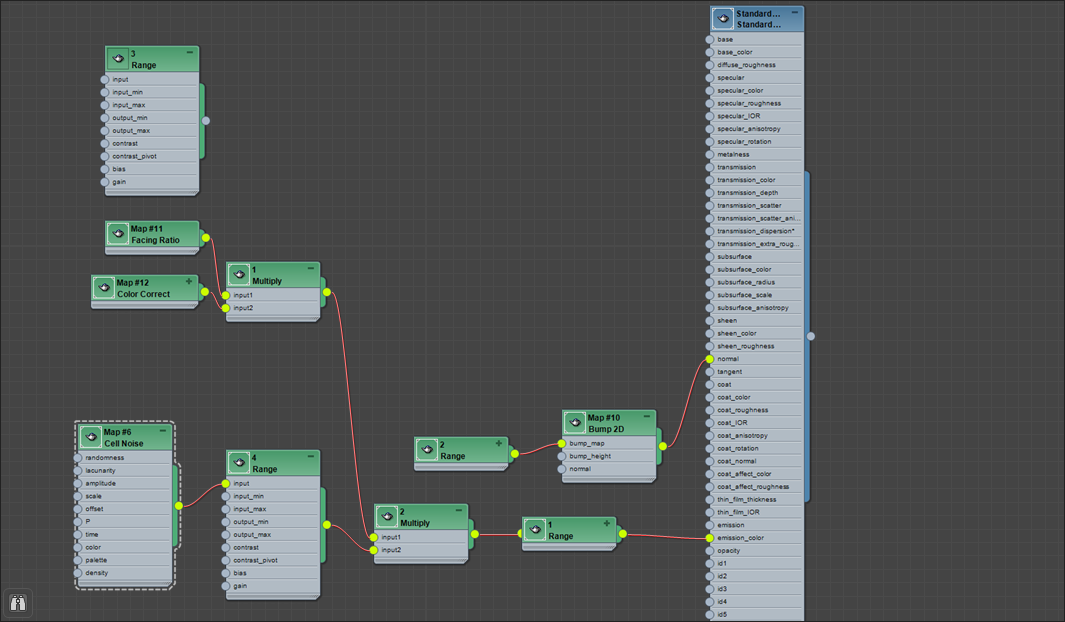
Final shading network