Input and output data from files
As an alternative to inputting and outputting geometries to the host scene, you can input and output files. This is useful, for example, for caching or rendering on a farm. In addition to Bifrost's object format, there are read_* and write_* nodes for several standard formats.
The format to use depends on the type of geometry:
- Use the Bifrost binary object format (.bob) for any type of geometry in Bifrost. However, it can only be read by the Bifrost graph.
- Use Alembic (.abc) for mesh geometry.
- Use OpenVDB (.vdb) for volumes or points.
- Use Field3d (.f3d) for volumes.
- Use PDC (.pdc) for points.
You can also use the file_cache node. This node can read and write .bob, .abc, or .vdb files based on the extension. It also supports tokens in the file path: <project_directory>, <scene_directory>, <scene>, <wedge_index>, <graph>, <node>, and <node_path>. By default, <node_path> returns the full path of the file_cache node, but it can be sliced using the syntax <node_path[from:to]> where from and to are indices of elements, for example:
<node_path[-3:]>: the last 3 indices.<node_path[:3]>: the first 3 indices.<node_path[0:3]>: the specific indices 0—3.
Note that:
- At least one output of the file node must be directly or indirectly connected to the
outputof the top level of the graph. - You can use the output from the
timenode to connect to theframeinput. In some cases, you may need to convert the frame value fromfloattointusingto_int, or convertframe_stepto a frame rate usingone_over. - To include frame numbers in file names, use the token
#. Use multiple characters for frame padding, for example,####for0001,0002, etc. You can also use@instead of#. - When specifying properties to include, you can either list them explicitly or use the wildcard. For example,
*for all properties orpoint_*for all properties beginning with "point_". - You must create directories if they don't exist already.
Writing files using batch execution
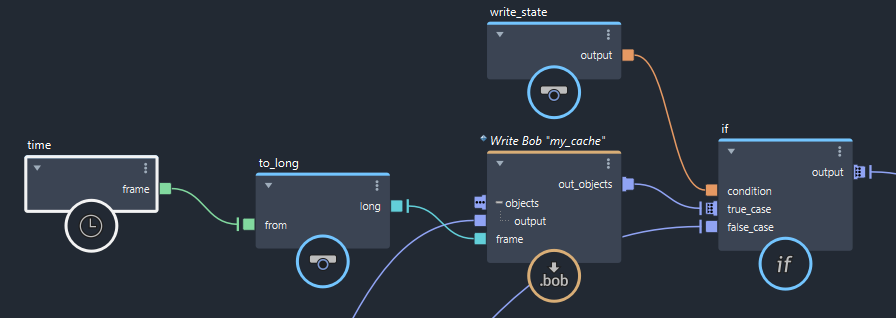
Batch execution lets you write out cache and other files without the risk of accidentally overwriting them. This process uses the write_state global variable, which is managed by Bifrost and set to true during batch execution.
It requires some preparation in your graph:
- If you are using
file_cachenodes, set theirmodeto the new Write State Mode. - If you are using
write_*nodes, useifnodes to execute them only when the output ofwrite_stateis true.
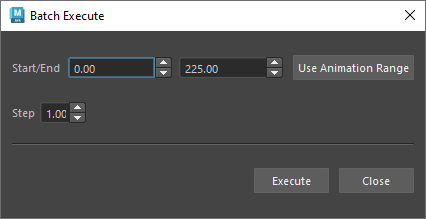
To write files using batch execution:
- Choose Edit > Batch Execute.
- Specify the time range.
- Click Execute. The
write_stateglobal variable is temporarily set totruewhile the files are being written.
You can cancel batch execution in progress by choosing Edit > Cancel Batch Execute.
Note that wedge_cache nodes always write during batch execution so be careful if there are any wedge_cache nodes in your graph.