API Methods
Method: login
Returns an authentication token created by Fusion Connect for a new session. Regardless of whether REST or JavaScript is used to access the API, the login method must be the first method called by the user. When REST is used, the session key generated is used as a parameter in every other method type. When JavaScript is used, this session key is stored within the NexusAPI object, and so while other methods do not take it as an explicit parameter, they still require that a successful login request was already made.
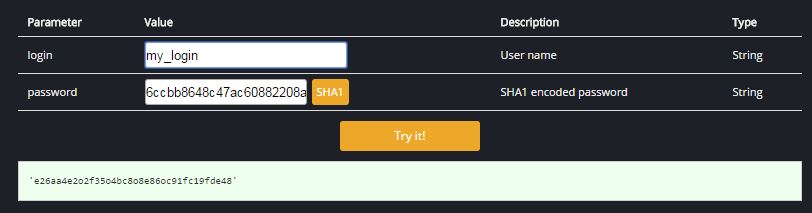
This method NexusAPI.login(login, password) takes in two parameters: "login", which is simply the user name with which the user wishes to log in, and "password", the SHA1 hash of the password associated with that user name. If the login/ password combination is valid, this method will return an authentication token as a string, which will be unique to each session. If the entered login/password combination is not valid, this method will return "No data received".
Successful authentication should look like this:
Method: config
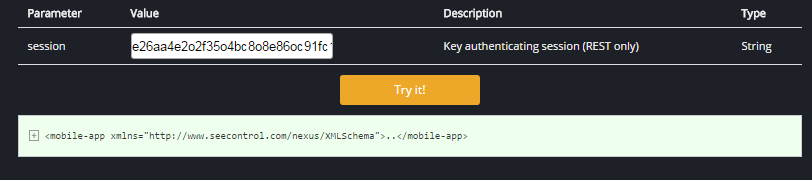
Returns the structure of an application as an XML string. As described on the Broker API section, the Mobile App Menu - defined using the UI of the cloud platform - determines which reports and forms are available over the Broker API. The XML returned in response to a "config" request will list all of these top-level reports and forms, as well as (separately) any forms or reports embedded in those top-level reports. When calling this method using REST, the only necessary parameter is the session key generated by a login request. When calling the config method using JavaScript, it requires that a successful login request has been made prior to calling this method. If the method has been called without the requisite parameter or a prior successful login request, it will return "No data received." An example response to a successful request is as follows:
A successful result should look like this:
<mobile-app xmlns="http://www.server-name.com/nexus/XMLSchema">
<main-pages>
<page xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="output-page-xtype" code="report_1" name="Report 1">
<element code="_rc$0001_value" name="Time"/>
<element code="_rc$0002_value" name="Target Field 1">
<datatype xsi:type="mobile-datatype-text-xtype"/>
</element>
<element code="_rc$0003_value name="Expression Column">
<datatype xsi:type="mobile-datatype-text-xtype"/>
</element>
<criteria code="criterion_1" name="Criterion 1">
<datatype xsi:type="mobile-datatype-text-xtype"/>
</criteria>
<view xsi:type="output-view-table-xtype" title="Table View">
<column xsi:type="output-view-column-generic-xtype" value-reference="_rc$0001_value" label="Activity Time"/>
<column xsi:type="output-view-column-generic-xtype" value-reference="_rc$0002_value" label="Variable Column"/>
<column xsi:type="output-view-column-generic-xtype" value-reference="_rc$0003_value" label="Expression Column"/>
</view>
</page>
<page xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="output-page-xtype" code="report_2" name="Report 2">
<element code="_1234512345123_value name="Gauge Value">
<datatype xsi:type="mobile-datatype-text-xtype"/>
</element>
<view xsi:type="output-view-gauges-xtype" title="Gauge View">
<gauge type="barometer" label="Temperature" value=reference="_1234512345123_value" lower-limit="0" upper-limit="100"/>
</view>
</page>
<page xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="output-page-xtype" code="report_3" name="Report 3">
<view xsi:type="output-view-map-xtype" title="Map View">
<marker label-reference="rml_0001_label" location-reference="rml_0001_location"/>
</view>
</page>
<page xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="input-page-xtype" code="form_1" name="Form 1">
<section name="Section 1">
<field code="field_1" name="Field 1" required="true">
<datatype xsi:type="mobile-datatype-xtype" pattern=""/>
</field>
</section>
</page>
</main-pages>
<enclosed-pages>...</enclosed-pages>
</mobile-app>
The structure of an account as available over the Broker API is dictated by the Mobile App Menu of the account. As described in the Account Menus section, this menu can contain the submit page for individual forms, or the View page for individual reports that have the API designation. Each form or report included on this menu appears in the Config skeleton of the application as an input or output "page" element, respectively; intuitively, forms are used to input data into the system, whereas reports are used to output data from the system.
Each of the pages directly listed on the mobile app menu appears in the "main-pages" XML element. However, reports can contain embedded forms and sub-reports, and it is necessary for the XML skeleton to include their structures as well, so each report or form linked to a main page report appears in the "enclosed-pages" section.
A report skeleton lists each variable or expression used (as "elements"), each criterion, and each view with the API designation. The above code block shows an example of a report with each type of view; note that for the table view, the "Time" field of the selected activity type needs no data type specification, that only generic-type columns are exposed over the API, and that if a column's value is an EL expression instead of a variable, that expression appears as an "element" as well, taking the label of that column as its name.
Elements of a gauges view use a slightly different code format, and all use the name "Gauge Value", as they never need to be differentiated by name. All types of map views list their data series using the "marker" XML element, and do not necessarily include any elements at all.
A form skeleton lists its sections, which include all the fields contained within; if no sections are explicitly defined in the form, the skeleton will include a single nameless section element, containing all the fields of the form. A form field element will list whether it is flagged as required, read-only, or hidden, but not whether it is marked as permanent. Additionally, the data type element of a field will also include the pattern of a text field, which is necessary for users to properly format their input to that field.
Method: get
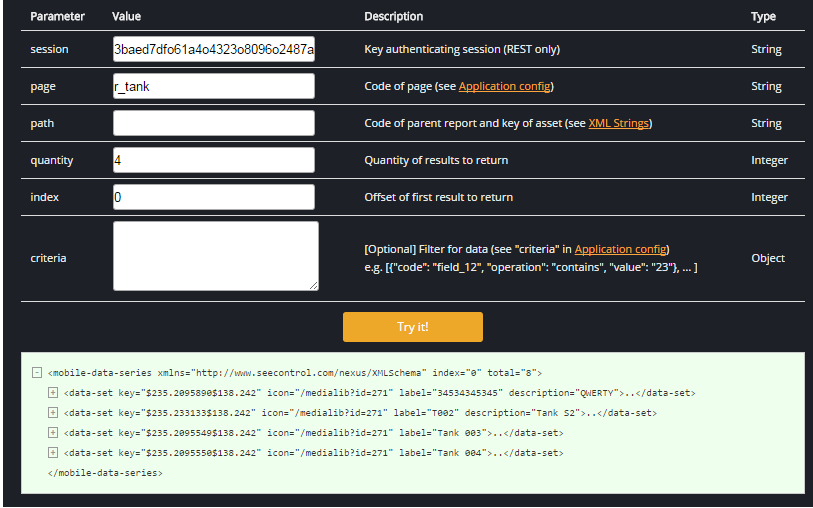
Returns the results of a query defined by the parameters. This method takes in 6 parameters when using REST, and JavaScript uses the last 5:
- "session"- the authentication token returned by a successful "login" request.
- "page"- the "code" attribute of the report you wish to query, out of those listed in the results of the "config" request. The format of the results of a successful "config" request can be found in the Application Config section.
- "path"- an XML string containing information necessary to run a sub-report. This parameter is used only when you wish this method to return the results of a sub-report instead of a report. In that case, the "page" parameter becomes the page code of the sub-report (an enclosed page, not main), and this parameter includes the code of the parent report and the key of the asset about which this sub-report is to be run. The format of this string is detailed below in the XML Strings section.
- "index"- specifies the index of the first query result that should actually be returned. For example, if the query generates 10 results, and an index of 2 is specified, then only results 2 through 9 are returned, and results 0 and 1 are ignored. This parameter defaults to zero, in which case [quantity] number of results starting from the beginning are returned.
- "quantity"- defines the maximum number of results to be returned. For example, if the query generates 10 results, and an index of 2 and a quantity of 4 are specified, then only results 2 through 5 are returned. This parameter defaults to there being no maximum number of results returned.
- "criteria" [optional]- an array containing the criteria that will be used to filter the results of the query. The available criteria for a given page are listed in the results of the "config request", and each of these corresponds to an element of that page. Each criterion has three attributes that you must specify: "code", which is the "code" attribute of the desired criterion as listed in the results of the "config" request; "value", which is the value you wish to compare the corresponding element against; and "operation", the operation to be used in the comparison. An example of a get Method can be found below.

The query results will be returned in the form of a "mobile-data-series" object containing the following: an "index" attribute, which should be identical to the given index parameter; a "total" attribute, which is the number of total results of the query, not the number of results returned, as this can be limited by the "index" and "quantity" parameters; and an array of "mobile-data-set" objects, each representing an entity returned by the query, with "key", "label", "name", and "description" attributes, and containing an array of "mobile-value" objects representing the values of the entity's fields.
If this method is called improperly, it will return an empty "mobile-data-series" object. The below example shows the result of calling the get method on the "Report 1" report (the results of the table view only)
<mobile-data-series xmlns="http://www.server-name.com/nexus/XMLSchema" index="0" total="10">
<data-set key="$123.124512345123.12345" label="Record 1 Label" description="Record 1 Description">
<mobile-value code="_rc$0001_value">
<valueDate>2015-02-17T15:43:00:000Z</valueDate>
</mobile-value>
<mobile-value code="_rc$0002_value">
<valueText>Variable 1 Value</valueText>
</mobile-value>
<mobile-value code="_rc$0003_value">
<valueText>Expression 1 Result</valueText>
</mobile-value>
</data-set>
</mobile-data-series>
Method: load
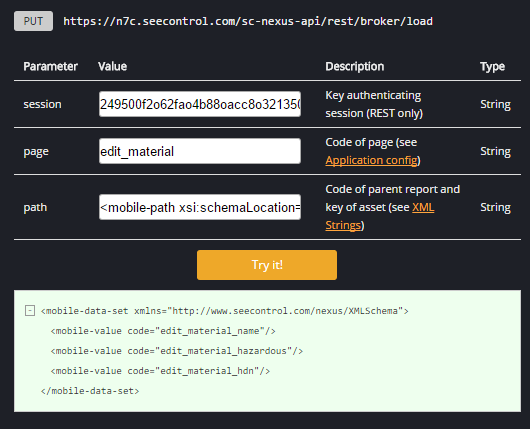
The "load" method loads all the information that populates a form when it is opened. For a form that is itself a main page, this includes all possible options for the drop-down menus on the form, typically referring to selecting the asset to which the form should apply. For a form embedded within another report, the load method returns the values that pre-populate each field; for example, a report listing existing assets can include an "Edit Asset" form to edit the fields of a selected asset, and the load method returns the fields of that asset so they may pre-populate the fields of that form. This method requires two parameters on top of authentication:
- "page"- The "code" attribute of the form you wish to load, either as a main page or as an enclosed page, from those listed in the results of a config request. The format of the results of a successful "config" request can be found in the Application Config section below.
- "path"- Used only when the form you wish to load is embedded within a main page. It is an XML string containing the code of that main page, as well as the key of the asset to which this form pertains.
If this method is called improperly, it will return "Request failed". An example of a get Method can be found below:
Method: submit
The "submit" method is used to submit data to Fusion Connect using a form, embedded or otherwise. It takes three parameters on top of authentication:
- "page"- The "code" attribute of the form you wish to submit, either as a main page or as an enclosed page, from those listed in the results of a config request. The format of the results of a successful "config" request can be found in the Application Config section below.
- "path" - Used only when the form you wish to submit is embedded within a main page. It is an XML string containing the code of that main page, as well as the key of the asset to which this form pertains.
- "data" - An XML string containing the data you wish to submit using the form. Its structure is detailed in the XML Strings section below.
If this method is called improperly, it will return "Request failed". An example of a get Method can be found below.
On the example "path" parameter has a value:
<mobile-path xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.server-name.com/nexus/XMLSchema schema/mobile-app.xsd" xmlns="http://www.server-name.com/nexus/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" page="r_material" key=""/>
and “data” parameter has a value of
<mobile-data-set xmlns="http://www.server-name.com/nexus/XMLSchema"> <mobile-value code="add_material_name"> <valueText>TEST1234</valueText> </mobile-value> </mobile-data-set>
Method: import
The import method is the API version of the Data Import feature, and is used to import CSV data into a form in Fusion Connect.
Forms provide a way for the system to execute logic using information provided by the user. If a user needs to run a form thousands, or millions of times, it is not practical for him or her to manually input information into a form that many times.
Fortunately, the import method allows you to automate the execution of forms for larger amounts of data. You can incorporate data from a single CSV file, with each row containing a set of information you want to input into a form. The system automatically executes a form upon each row of the file.
Parameters
You must provide a profile, a time zone, and the import lines for this method.
@Path("import")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_XML)
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED)
public JAXBElement<MobileResultXtype> importData (@FormParam("session") String sessionId,
@FormParam("profile") String profile, @FormParam("timeZone") String timeZone,
@FormParam("importLines") List<String> importLines)
Import lines encoding example:
Form form = new Form();
form.add("importLines", “Line 1");
form.add("importLines", “Line 2");
form.add("importLines", “Line 3");
service.path(...)...
.post(String.class, form);
}
Method: messages
The messages method returns messages for a given data range, or last {page-size} messages if the date range is omitted. The messages are ordered by message received and time. Optionally, you can also filter messages by device and/or message-type.
###Parameters
- (Optional) date-start
- (Optional) date-end
- (Optional) device
- (Optional) message-type
- (Optional) page-number.
- Default setting is 1.
- (Optional) page-size.
- Default setting is 10. Maximum setting is 1000.
Method: account
The account method is used to create a new account based on an application template.
Parameters
- Account Name
- List of Gateways to enable
- Administrator user credentials (username and password)
- Administrator first and last name.
- Administrator email.
Please note there may be a number of limitations on new account creation as well as associated billing requirements, you should contact Autodesk for more details on usage and pricing.
Method: logout
The logout method invalidates a session key, thereby terminating that session.
When using REST, this method takes one parameter: the session key used for the current session.
When calling this method using JavaScript, no parameters are required, as the fcAPI object stores the session key internally. Once this method has been called, the session key supplied as a parameter can no longer be used for authentication in any other method, and another login call must be made.
If the supplied parameter is not a recognized session key, a logout call will have no effect. Regardless of whether the method call is successful, it will not return anything.