The Drag Plot is a graphical representation of the drag force and drag coefficient as a function of time. When the simulation starts, the drag plot may appear to vary sporadically as the flow develops. As the solution progresses, the flow will either reach a steady-state in which it no longer changes with time or it will often oscillate in a repeating pattern. By watching the Drag Plot as the solution evolves, you can understand how the solution is evolving.
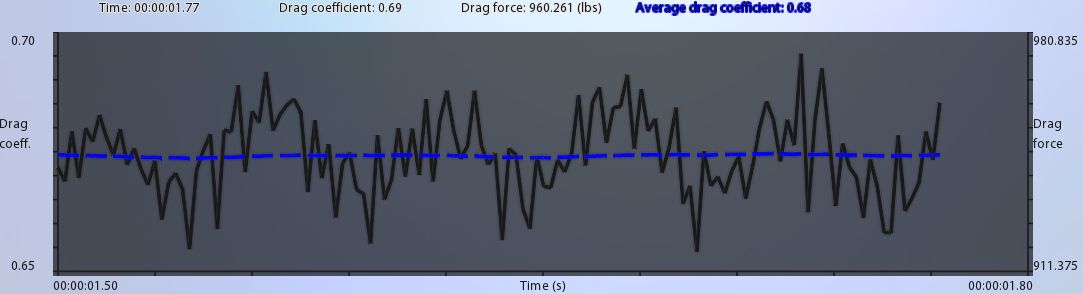
The drag coefficient is a dimensionless quantity that represents the amount of aerodynamic drag of the object. Higher values indicate a greater resistance to the flow, which in turn means that more energy is required to push the object at the required speed. Lower values indicate less wind resistance, which in turn means that less energy is required to propel the object at speed.
The drag force is the amount of force imparted on the model by the wind as it flows into, over, and around the model. Like drag, higher values of force require more energy to propel through the wind at speed. Follow these guidelines to achieve accurate drag force values in your simulations:
- Solve in 3D.
- Ensure the Simulation Resolution is at least 100%, although you may need to use a higher value if your model contains very small details.
- Ensure the wind tunnel is sized according to the recommended guidelines. If the wind tunnel is too small or if the model is closer to one side than another, the drag force results can be artificially affected.