Component Sources reference (nesting)
This feature is part of an extension. Extensions are a flexible way to access additional capabilities in Fusion. Learn more.
This reference topic describes the controls on the right side of the Component Sources dialog that are used for setting global nesting defaults for these components. These defaults can be overridden in Process Material Library and Nest Study settings.
Click Manufacture > Fabrication > Milling > Sources > Component Sources.
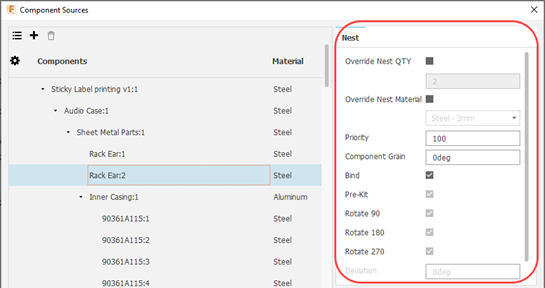
Override Nest QTY: Sets the number of instances of the selected component to include in the nest. This overrides the quantity of the components that came from the nest preparation.
Override Nest Material: Assigns a different material to the component instead of the default one. The materials that appear in this list are from the Process Material library.
Priority: The order in which nesting places the parts on the sheet. Fusion Nesting uses this first, then part size. A part with a lower priority number nests before a part with a higher value, regardless of efficiency.
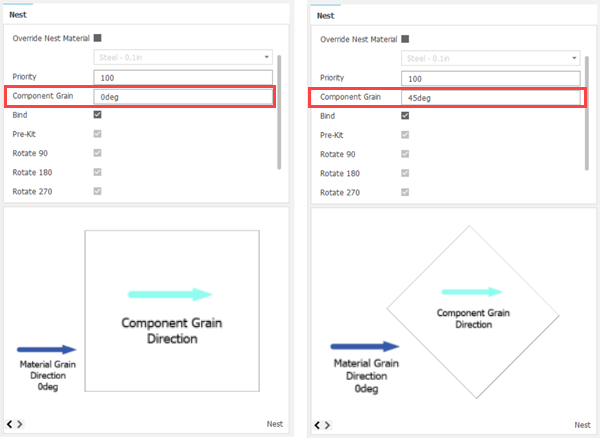
Component Grain: Specifies the direction of the grain on the component for materials such as wood. This affects how the component is oriented on the sheet. The orientation is such that the grain on the component aligns with the grain on the sheet.
You can also preview the orientation of the component on the sheet. The image below shows the difference between using a Component Grain of 0 degrees (left) and using a Component Grain of 45 degrees (right).
Bind: Bind shapes to their material properties; this includes parameters defined in the material such as rotation, flip, and so on.
Deselect Bind if you want to enable the controls that follow it in the dialog.
Pre-Kit: Allow two instances of a part to be placed alongside each other at opposing angles as a “kit,” if it saves space. The kit is considered to be one part in the nest. A kit is not created if no space is saved.
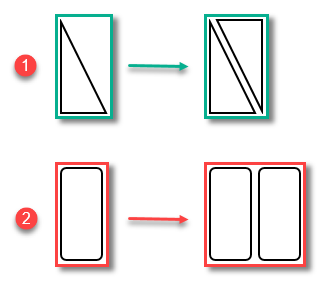
- Two instances are smaller than twice one, so space is saved.
- Two instances are not smaller than twice one, so no space is saved. No kitting takes place.
Rotate 90: Allow the shape to be rotated by 90 degrees.
Rotate 180: Allow the shape to be rotated by 180 degrees.
Rotate 270: Allow the shape to be rotated by 270 degrees.
- Preview: Scroll through different views of the part
 .
. Deviation: Allowable orientation deviation; for example, if you enter 10, a 90-degree orientation is allowed to deviate between 80 and 100.
Increment: Allowable deviation increments. For example, if you enter 2, a 10-degree deviation can occur in increments of 2; that is, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10.