Parameters in Fusion
The Change Parameters tool lets you create parametric equations that drive key dimensions, quantities, and other aspects of your Fusion design.
Design > Modify > Change Parameters ![]()
Fusion is a parametric modeling program and the Change Parameters tool can help you manage many aspects of your design in one place.
Parameter types
There are two types of parameters:
User Parameters
 : Parameters that you create in the Parameters dialog and then reference in features and other parameter expressions.
: Parameters that you create in the Parameters dialog and then reference in features and other parameter expressions.Model Parameters
 : Parameters that drive the dimensions and values for features in the timeline. There are a few ways to create them:
: Parameters that drive the dimensions and values for features in the timeline. There are a few ways to create them:- Model parameters are automatically created when you create timeline features or define dimensions in your design. For example, when you create an Extrude feature, a model parameter is generated for the distance value that you entered.
- You can create named model parameters in context as you create different sketch and modeling features.
Favorite parameters
You can favorite user and model parameters to make them easily accessible. Favorites ![]() display in a list at the top of the parameters table.
display in a list at the top of the parameters table.
When you create and name a model parameter during a modeling workflow, Fusion automatically adds it to your Favorites ![]() , so that it is easy to find in the Parameters dialog.
, so that it is easy to find in the Parameters dialog.
Filter parameters
You can click a filter at the top of the Parameters dialog to filter the list of parameters:
- Favorites

- User Parameters

Sort parameters
You can sort the list of parameters in a variety of ways:
Click a column header to sort by that aspect of the parameter:
- Name: Sorts by parameter name alphabetically.
- Unit: Sorts by unit type alphabetically.
- Expression: Sorts by expression alphabetically and then numerically.
- Value: Sorts by value in numerical order.
- Comment: Sorts by comment alphabetically and then numerically.
At the top of the dialog, click Sort in Timeline Order ![]() to reorder the list of parameters in the order they were created in the timeline.
to reorder the list of parameters in the order they were created in the timeline.
Edit parameters
When you edit a parameter, the edit automatically updates anywhere it is referenced in the design. For example, if you update a parameter name, it will update in any expressions that reference it.
Import and export user parameters
You can use Export Parameters ![]() to save User Parameters
to save User Parameters ![]() as a CSV file, edit them in an external table editor, then use Import Parameters
as a CSV file, edit them in an external table editor, then use Import Parameters ![]() to import them back into a Fusion design.
to import them back into a Fusion design.
When you edit a parameters CSV file, verify the following:
- Each parameter has a unique name.
- The unit type that results from a parameter expression matches the parameter's assigned unit type.
- The parameter's unit syntax is entered correctly.
- The table header is formatted correctly.
Example table:
| Name | Unit | Expression | Value | Comments | Favorite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter_1_name | in | .75 | .75 in | Plywood thickness | true |
| Parameter_2_name | in | 10 | 10 in | Cabinet width | false |
| Parameter_3_name | in | Parameter_2_name*2 | 20 in | Cabinet height | false |
| Parameter_4_name | in | 12 | 12 in | Cabinet depth | false |
Automatic update
Automatic Update is on by default and automatically updates the design in the background as you edit parameters. This lets you see how the changes affect your design in real time as you edit them.
You can disable Automatic Update to pause updates and reduce compute time.
Reference parameters
As you specify values in different modeling tools, Fusion automatically suggests parameters when you click inside a compatible value field and start typing.
In the dialog:
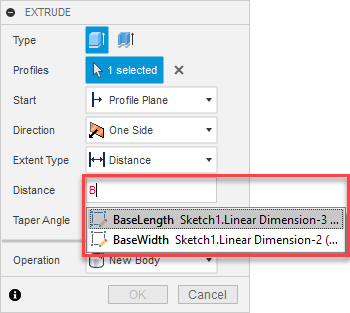
In the canvas:

Equations
You can write formulas to calculate the value of a parameter. In an expression you can:
- Reference other parameters
- Reference mathematical constants
- Use algebraic operators, such as
+and*. - Use logical operators, such as
if,>, or=. - Use math and trigonometry functions
Logical operators
You can use logical operators in expressions used by the if function to control setting of values.
| Operation | Syntax | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| greater than | > |
Height > Width |
The height is greater than the width. |
| less than | < |
Height < Width |
The height less than the width. |
| greater than or equal to | >= |
Height >= Width |
The height is greater than or equal to the width. |
| less than or equal to | <= |
Height <= Width |
The height is less than or equal to the width. |
| equal to | == |
Height == Width |
The height equal to the width. |
| not equal to | <> |
Height <> Width |
The height is not equal to the width. |
The if function requires 3 arguments:
- A logical expression
- The expression if the result is true
- The expression if the result is false
The result is either true or false. If functions can be nested so the second or third arguments of an if function can be another if function. You can use this to create an and if/else or an if/else structure.
For example, you could specify an expression for the number of shelves on a bookshelf:
`if(BookShelfHeight <= 500 mm; 2; (if(BookShelfHeight >= 1200 mm; 4; 3)))`Result: If the bookshelf height is less than or equal to 500 mm, it will have 2 shelves. If the bookshelf height is between 500 mm and 1200 mm, it will have 3 shelves. If the bookshelf height is greater than 1200 mm, it will have 4 shelves.
Parametric Text
You can reference Text as a parameter in sketches, features, and configurations.
To create them:
- Add text to a Sketch to create a new model parameter automatically.
- In the Parameters dialog, create a new user parameter with Text unit type, then reference it in a sketch or add it to the Configuration Table.
How it works:
- Wrap plain text in single quotes
" - To reference an existing text parameter, type the parameter name and select it to add it to the expression.
- To connect existing text parameters together, add a
+between each parameter.
Example 1: 'Example text'
Example 2: 'Example text' + ExistingTextParameter1
Example 3: ExistingTextParameter1 + ExistingTextParameter2