Instead of LoF and CoF scores being weighted and scaled down, you can instead choose to use 100% of both LoF and CoF in your risk scores.
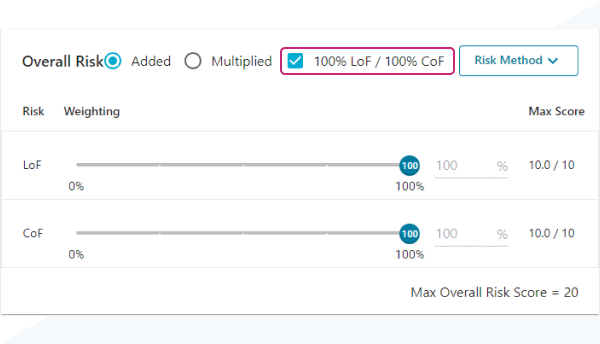
Example scores for 100% LoF and 100% CoF
When LoF and CoF scores are calculated, both the LoF Weight and the CoF Weight will be 100%.
Let's compare the scores we would get when marking '100% LoF / 100% CoF' to the scores from the example given in Risk Calculations (LoF 80% + CoF 20%).
| LoF (100%) + CoF (100%) | LoF (80%) + CoF (20%) | |
|---|---|---|
|
Weighted LoF component scores (Component Score * Component Weight * Category Weight * LoF Weight) |
|
|
| Total LoF Score
(Sum of all weighted LoF component scores) |
|
|
|
Weighted CoF component scores (Component Score * Component Weight * Category Weight * CoF Weight) |
|
|
| Total CoF Score
(Sum of all weighted CoF component scores) |
|
|
| Risk Score
(Total LoF Score + Total CoF Score) |
|
|
For a full example and explanation of risk score calculations, see Risk Calculations.