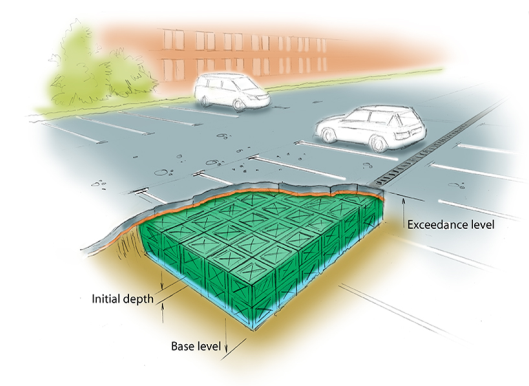
Cellular Storage stormwater controls may be used to model cellular crate-based structures, such as Stormcell.
Total Volume
The Total Volume value shown in the bottom-right corner of the data form shows the volume available in the system up to the Freeboard elevation.
Dimensions
The Dimensions tab has the following fields:
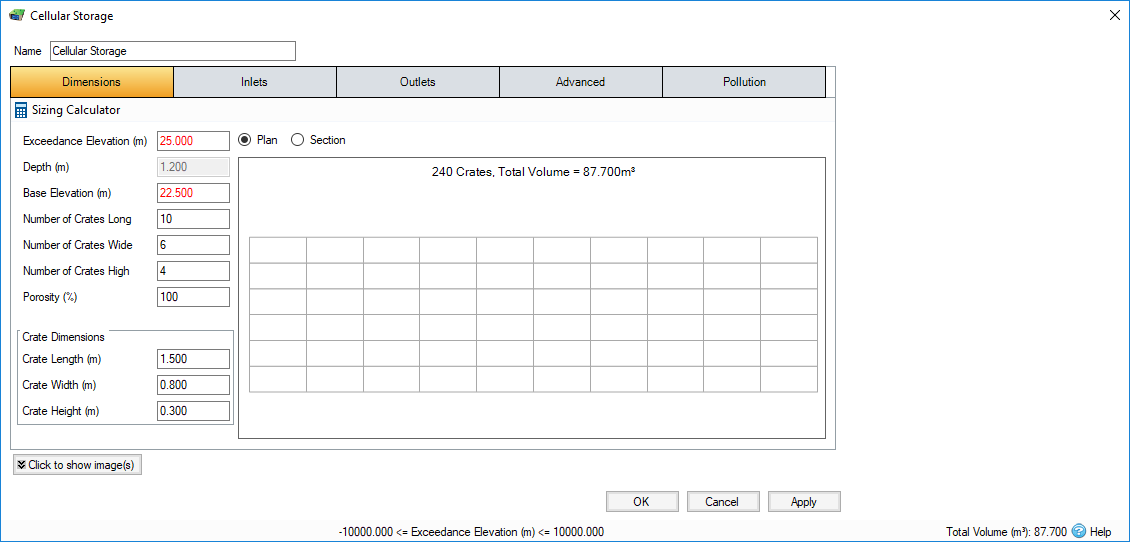
Exceedance Elevation - Represents the elevation (above datum) of the stormwater control above which flooding is reported. This may be the elevation that interacts with the ground surface or the top of an embankment, whichever is higher. An overflow or spillway crest elevation may be specified at a lower elevation as part of the outlet control details. If a Surface Data is present, the Exceedance Elevation will automatically be picked up from the center of the icon or from the lowest point on the perimeter if an area has been drawn. This, combined with the Freeboard setting, allows a Status of Flood Risk to be assigned to the system on the Summary. For stormwater controls on a slope, the Exceedance Elevation applies to the downstream (lowest) end. Above the Exceedance Elevation, water will be stored above the ground and then allowed to drain back into the network. The ponding area used for the flooded volume is the area the Cellular Storage occupies on the plan.
Depth - Represents the depth of the stormwater control. This field is automatically calculated from the crate dimensions and is not editable.
Base Elevation - Represents the elevation (above datum) of the base of the stormwater control.
No. of Crates Long - The number of crates along the length of the structure. You can design up to 1000 crates.
No. of Crates Wide - The number of crates across the width of the structure. You can design up to 1000 crates.
No. of Crates High - The number of crates deep in the structure. You can design up to 1000 crates.
Porosity - Defines the percentage of the Cellular Storage that is available for storage. This is dictated by the type of fill material that is used, i.e. 100% if empty or typically 30% for rubble.
Crate Dimensions
Crate Length - The length of an individual crate.
Crate Width - The width of an individual crate.
Crate Height - The height of an individual crate.
Sizing Calculator
The Sizing Calculator allows you to re-size the Cellular Storage by specifying a volume and a parameter to modify to achieve that volume. The Sizing Calculator is discussed in more detail in the Stormwater Control Sizing Calculator .
Inlets
Refer to the Inlets page for more details on the different types of Inlets that can be specified.
Outlets
Refer to the Outlets page for more details on the different types of Outlets that can be specified.
Advanced
The Advanced tab has the following fields:
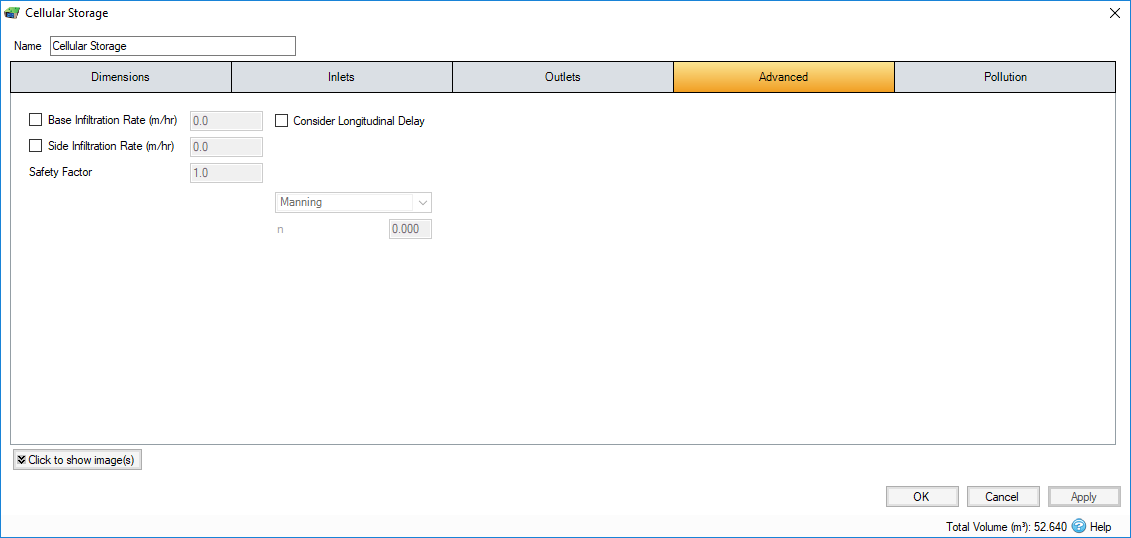
Base Infiltration Rate - Defines the rate of infiltration through the base of the filter area. This should be determined from a performance site test.
Side Infiltration Rate - Defines the rate of infiltration through the sides of the filter area. This should be determined from a performance site test.
Safety Factor - Reduces the infiltration rate during the analysis to account for silting up or poor maintenance. This is required for the UK.
Consider Longitudinal Delay - Determines if a time of travel needs to be considered across the structure. This may not be required as they are laid flat and can be considered as filling instantaneously. If the travel time is to be considered a roughness method and value should be selected.
Friction Scheme - Specifies the formula used to calculate velocity and time of travel. Select from: Manning's, and Colebrook-White. The variable below the combo box depends on the option selected.
n - Manning’s n roughness value. Used by the Manning Formula equation to calculate the velocity and therefore time of travel when using the Manning's option.
Roughness - Colebrook-White roughness value. Used by the Colebrook-White Formula equation to calculate the velocity and therefore time of travel when using the Colebrook-White option.
Pollution
The Pollution tab has the following fields:

Name - Name of pollutants. This is populated based on the Pollutants set up as part of the Site Data.
Background Concentration - Value below which the pollution concentration cannot fall during analysis. When concentration reaches this elevation, no further removal occurs.
Method - Percentage Removal or First Order Decay method can be selected. Click the links for more information about each method.
Percentage Removal - Available if Percentage Removal entered. The value entered will be deducted from the Inflow into the system.
τ - The decay time constant or (mean) lifetime of the pollutant. It can be entered manually or calculated from the decay constant or decay half-life. See Pollutant Removal Method - First Order Decay for more details.