For Chinese conduit design, the regulation recommends the rational method, so every city has a rainfall intensity formula with same form :

Keifer & Chu (1957) design rainfall (also called as Chicago Rainfall) describes how to generate a design rainfall using that intensity formula.
Parameters
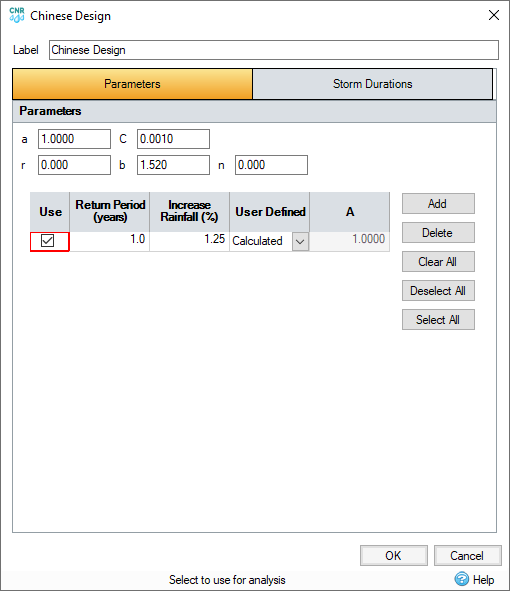
a
Equation constant, used in calculation of A when calculation of A is set to Calculated
C
Equation constant, used in calculation of A when calculation of A is set to Calculated
r
The portion of the duration of the event occurring before the peak
r value examples:
|
place |
r(times) |
area |
r(times) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Chicago |
0.375(83) |
Beijing |
0.355(57) |
|
Soviet |
0.35(—) |
Shanghai |
0.367(80) |
|
Japan |
0.50(1050) |
North china |
0.3-0.4(483) |
|
Most Chinese city |
0.3-0.4(—) |
Wuhan |
0.3-0.4(—) |
b
User defined equation constant.
n
User defined equation constant.
Return Period
Period, in years, between events of the same intensity or of a greater intensity than this storm.
Increase Rainfall
This will scale all rainfall by the amount specified. This can be used to take climate change, or other factors, into account.
Calculation of A
Select method of specifying value of A:
- Calculated - A is calculated from a, C and return period values.
- User - A is user defined.
A (Calculated)
A is calculated as:
a(1 + Clog10P)
Where P is return period.
A (User)
User defined equation constant.
Intensity and Rainfall Calculation
The duration for the design rainfall is ![]()
Instantaneous intensity before peak is ![]() , corresponding duration is
, corresponding duration is ![]() , and cumulative depth is
, and cumulative depth is ![]() .
.
Instantaneous Intensity after peak is ![]() , corresponding duration is
, corresponding duration is ![]() , and cumulative depth is
, and cumulative depth is ![]() .
.
Total rainfall depth ![]()
Set ![]() , the peak time ratio is r (which has a range of 0-1), then
, the peak time ratio is r (which has a range of 0-1), then ![]() .
.
Assume the density formula is ![]()
In China, A = a(1 + log10 P) where P is the return period and a is a constant.
the instantaneous intensity before ![]() and after peak
and after peak ![]() are:
are:
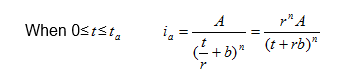
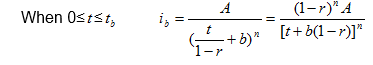
So ![]() and
and ![]() are calculated as follows:
are calculated as follows:
![]()
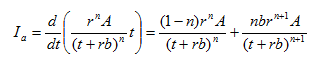
![]()
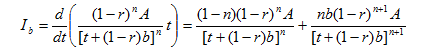
From the above two equations, the cumulative rainfall depth is produced ad shown below:
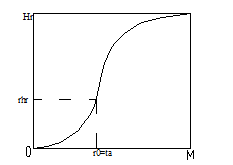
The cumulative rainfall is calculated by following equations:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
where
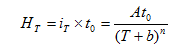
Reference on Chicago rainfall
C.J. Keifer, H.H. Chu, synthetic storm pattern for drainage design, proc paper 1332. ASCE. Aug. 1957.
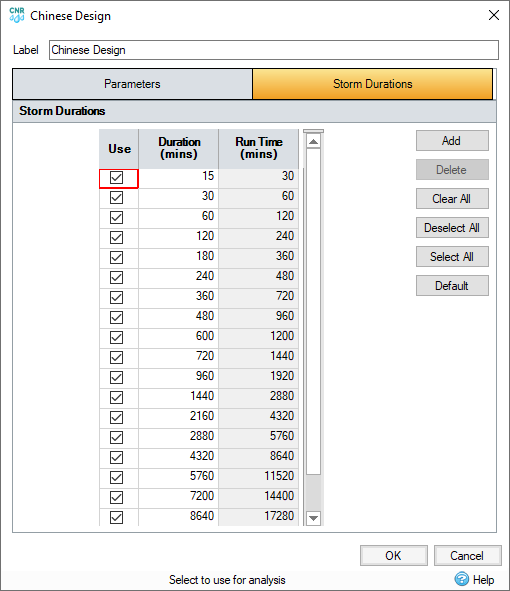
Storm Durations
A set of Storm Durations and run times must be specified for the analysis to run back to back. All duration values can be edited, and new rows can be added for additional durations.