The resulting time of concentration is determined as the sum of the travel times from each of the calculations (Sheet Flow, Shallow Flow, Channel Flow).
Tt = Tsheet flow + Tsheet concentrated flow + Tchannel flow
Sheet Flow
Parameters
Manning's roughness coefficient - Manning’s n Roughness value.
Flow Length - The length of the Sheet flow path.
Two-year 24-hour rainfall - The depth of rainfall for the 2 year return period 24 hour event.
Land Slope - The slope of the hydraulic grade line.
Calculation
For sheet flow of less than 300 feet, use Manning's kinematic solution (Overtop and Meadows 1976) to compute Tt:
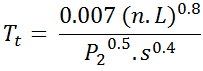
where:
Tt = travel time (hrs)
n = Manning's roughness coefficient
L = Flow length (ft)
P2 = 2-year, 24-hour rainfall (in)
s = slope of hydraulic grade line (land slope, ft/ft)
t c = time of concentration (hrs)
This simplified form of the Manning's kinematic solution is based on the following: (1) shallow steady uniform flow, (2) constant intensity of rainfall excess (that part of a rain available for runoff), (3) rainfall duration of 24 hours, and (4) minor effect of infiltration on travel time.
Shallow Concentrated Flow
Parameters
Flow Length - The length of the Shallow flow path.
Watercourse Slope - The slope of the hydraulic grade line.
Average Velocity - The average velocity.
Calculation
Travel time (Tt) is the ratio of flow length to flow velocity:

where:
Tt = travel time (hrs)
L = Flow length (ft)
V = average velocity (ft/s)
Channel Flow
Parameters
Cross sectional flow area - The Cross Sectional Flow Area.
Wetted Perimeter - The Wetted Perimeter for Flow Area.
Manning's roughness coefficient - Manning’s n Roughness value.
Flow Length - The length of the Channel flow path.
Calculation
Manning's equation is:

where:
V = average velocity (ft/s)
r = hydraulic radius (ft) and is equal to a/pw
a = cross sectional flow area (ft2)
pw = wetted perimeter (ft)
s = slope of hydraulic grade line (land slope, ft/ft)
n = Manning's roughness coefficient for open channel
Manning's n values for open channel flow can be obtained from standard textbooks such as Chow (1959) or Linsley et al. (1982). After average velocity is computed using equation 3, T t for the channel segment can be estimated using the equation 2.