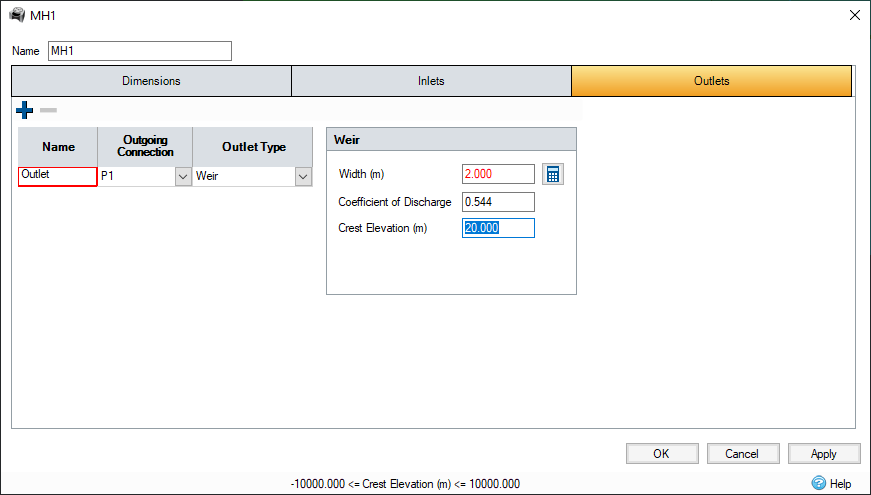
Weir Outlet allows a rectangular weir control to be modelled.
Specification
Width - Enter the width of the weir. If you are working to a maximum allowable discharge then a Calculator is provided to help size the control. This gives two additional parameters:
- Design Depth - Enter the maximum depth of water that you are designing to. This should be entered as a depth above the invert elevation of the control and will vary depending on the depth of the stormwater control and the desired freeboard.
- Design Flow - Enter the required flow when the water elevation reaches the design depth. This should be the maximum desired discharge through this control. Be aware that if the water elevation is lower than the design depth, the flow may be lower than the design flow and if the water elevation exceeds the design depth the design flow may be exceeded.
Coefficient of Discharge - The discharge coefficient depends on the type of weir or flume chosen. A default value of .544 is given and is generally suitable for flow over a flood bank, round nose horizontal - crested weirs and rectangular flumes. Other values may be used and as with the other controls, values for discharge coefficients may be found in any good reference on hydraulic control structures.
A selection of the more common coefficients is given below.
|
Description |
Coefficient |
Reference |
|
|
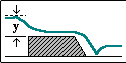
A round nose horizontal-created weir (or flow over a floodbank) |
0.544 |
British Standards Instn (1969) |

|
A rectangular profile weir |
0.46 |
Ackers, White, Perkins, Harrision (1978) British Standards Instn (1969) Crabbe (1974) |
|
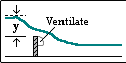
Rectangular thin-plate weir full width b with no side contractions |
0.59 |
Ackers, White, Perkins, Harrision (1978) British Standards Instn (1965) |
|
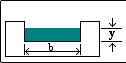
Rectangular thin-plate weir with side contractions. |
0.56(b +.003) |
Ackers, White, Perkins, Harrision (1978) British Standards Instn (1965) |
Crest Elevation - The crest elevation of the weir.
Calculations
Weir flow is calculated using the following formula in free flow conditions:
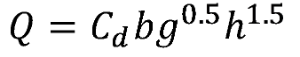
where
Q = Discharge
Cd = Discharge coefficient
b = Weir width
g = acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m²/s)
h = Water depth
When the downstream elevation is above the crest elevation the software will use the Villemonte equation to simulate the submerged nature of the flow:
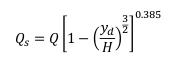
where:
Qs = Submerged Flow Rate
Q = Free-flow rate at H
Yd = Depth downstream
H = Water Depth at point of measurement
More details can be found in the SWMM Reference Manual Volume II - Hydraulics which is available Here.