Writing a CgFX shader
Maya supports Cg version 3.0.015.
CgFX examples are shipped with Maya Creative. You can find these examples at:
- (Windows) <drive>:\Program Files\Autodesk\<version>\presets\CgFX\examples
- (Mac OS X) /Applications/Autodesk/<version>/Maya/Contents/presets
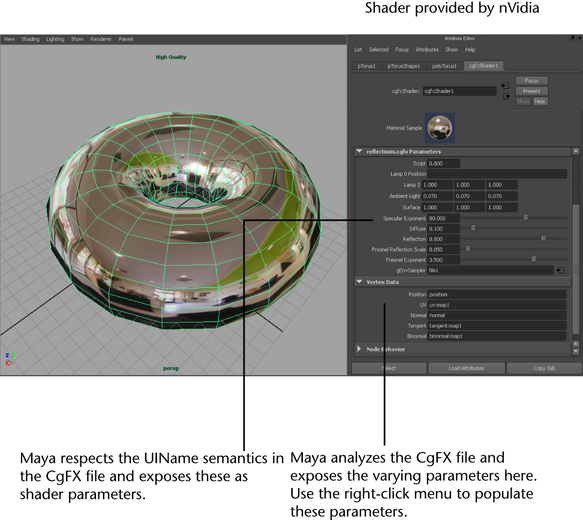
Varying parameter packing
You can pack multiple mesh inputs into a single varying parameter register. For example, you can pack two sets of UV coordinates into a single float4 register.
The following is a sample workflow:
- The following vertex shader input structure shows a packed
float4 that needs to contain 2 UV sets in a single varying parameter:
struct appdata { float3 Position: POSITION; float4 UVs: TEXCOORD0; }; - Create a second structure that describes the elements that should be packed into this input. To enable Maya to locate this second structure, its name must match the name of the original varying parameter (in this case,
UVs).
In this example, this auxiliary structure informs Maya that the original float4 parameter should be assembled on the fly from two float2 inputs: one named UV1, and one named UV2. This structure is not used by the shader itself - it simply tells Maya how to assemble the data for this input.
struct UVs { float2 UV1; float2 UV2; }; - Because Maya knows that this is a packed input, it presents the artist with an interface to the underlying data (UV1 and
UV2) rather than the final packed structure (UVs). You can now optimize and reorganize the varying parameter register assignment without breaking any existing shader bindings in scenes using the shader.
For more information, see UVPacking.cgfx as an example.
Note:Where the data assigned to a structure element is too large for the Cg data type specified (for example, a position with (x, y, z) coordinates is passed into a float2 value), the first n values will be used to populate the value, and any subsequent elements will be ignored (for example, x and y will be passed in, and z will be ignored).
Other CgFX shader features
- Time semantic
-
Maya supports parameters that vary by time. See MrWiggle.cgfx for an example of a shader that moves with time.
- Matrix semantic
-
You can specify matrices in your CgFX shader. Maya supports all matrix semantics keywords.
- Transparent CgFX shaders
-
Maya supports rendering of transparent CgFX shaders. Maya detects whether the blending state is enabled in the first pass. If blending is enabled, Maya uses the Object Transparency Sorting or Polygon Transparency Sorting options in the scene view to correctly render the transparent shader.
- Maya shader files
-
Maya provides shader files that developers can incorporate into their own CgFX shader, in the following directory:
- (Windows) <install_dir>\bin\cg
- (Mac OS X) <install_dir>/Maya.app/Contents/bin/cg
where <install_dir> is the directory where you installed Maya Creative.
Select a Maya_*.cgh code example; for example, maya_blends.cgh, the code that Maya uses for blending of the layered texture:
- Orientation for the texture co-ordinate system
- When the CgFx plug-in compiles a CgFx shader, it sets the compilation macro MAYA_TEXCOORD_ORIENTATION to either OpenGL or DirectX to specify the orientation used for the texture co-ordinate system. For more information, see Orientation of the texture co-ordinate system for CgFX shaders.
Customizing the CgFX shader
You can use the MAYA_CGFX macro to customize your CgFX shaders to include Maya specific attribute annotations without breaking the compatibility with other applications that might also use the same CgFX shader.
For example, you can use the following code to declare the directional light attribute in both Maya and another application without causing any compatibility issues:
#if defined(MAYA_CGFX) || defined(XSI)
// Declares the « dirlight0 » with attribute annotations for Maya or XSI
float4 dirlight0 : Direction <
string UIName = "Distant Light 0 Direction";
string Object = "DirectionalLight";
string Space = "World";
> = {-1.0f, -1.0f, 0.3f, 0.0f};
#else
// Declares the « dirlight0 » with attribute annotations for another application:
....
#endif
The lines between #if defined(MAYA_CGFX) || defined(XSI) and #else are only parsed when loaded by Maya/XSI.