Double-sided shading lets you shade a surface with one material on one side and a different material on the other side. This is the only way you can apply more than one material to a NURBS surface. You use both the Condition and Sampler info utility to create this effect.
To create a double-sided shaded surface
- In the
Hypershade, create one of each of the following:
- Material (this procedure uses a Phong material).
- A Sampler Info utility. The Sampler Info utility provides access to camera and surface information that you can pipe into your shading networks during rendering.
- A Condition utility. The Condition utility lets you specify which texture is mapped to each side of the surface.
- Checker texture.
- Crater texture.
- Assign the Phong material to the surface.
- In the Hypershade, connect the Checker’s Out Color attribute to the Conditions Color If True attribute .
- Connect the Crater’s Out Color attribute to the Condition’s Color if False attribute.
- Connect the SamplerInfo Flipped Normal attribute to the the Condition’s First Term or Second Term attribute.
- Connect the Condition OutColor attribute to the Phong Color attribute.
- Perform a test render.
Maya shades each side of the surface with a different texture.
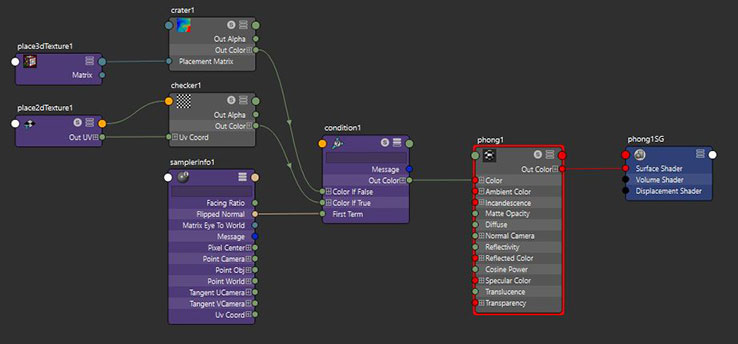
Image of resulting connections in the Hypershade.
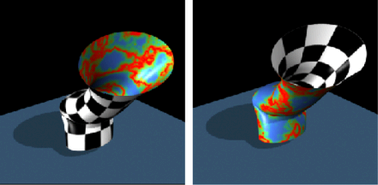
Swapping the textures on the surfaces
You can use the Condition utility to specify which texture is applied to the front and back sides of the surface.
To swap texture mapping for double-sided shading
- Select the Condition node. In the Property Editor, Condition Attributes section, change the Operation attribute to Not Equal (or if it is set to Not Equal, change it to Equal).
- Perform a test render. The following shows the result.
 Note:
Note:You can apply more than one material to polygonal models at the face level.