This section contains a general overview of the fundamental concepts, terms, and operations associated with file referencing.
Loaded and unloaded references
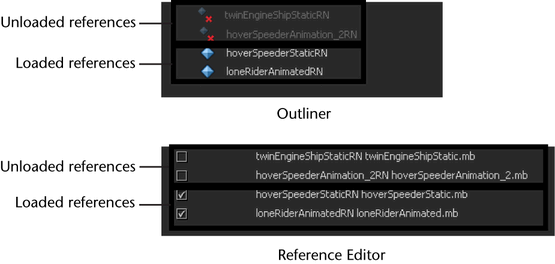
After a child scene has been referenced into an open parent scene, the contents of the child scene are placed in memory and displayed in the scene. This initial state for a referenced file is referred to as being loaded. Other child scenes can be loaded in the open parent scene simultaneously. When a referenced scene is unloaded, the connection between the referenced child scene and the parent scene is suspended and the contents of the referenced scene file is no longer loaded in memory. You can load, unload, or re-load referenced child scenes from within the open parent scene file.
You can load and unload references from the Outliner or Reference Editor. See Load and unload file references.
Reference edits
You can apply edits to referenced objects in the open parent scene without modifying the original referenced child scenes. Any edits applied to the referenced objects while working in the parent scene remain stored in a node a called a reference node. A reference node is created for each child scene when it is referenced into a parent scene. The reference node keeps track of how the parent scene uses and modifies objects contained within a child scene. You choose to keep edits to references isolated to the parent scene or apply them to the reference source files.
See Reference edits.
Reference hierarchies
Parent scenes can reference other parent scenes to create a hierarchy of nested references. A parent scene can both reference other files and be a referenced child of another parent scene based on its relative position within the file referencing hierarchy. When this occurs, the child scene files are referred to as grandchild scene files. This hierarchical referencing of a parent scene, child scenes, and other grandchild files is referred to as multi-level referencing.
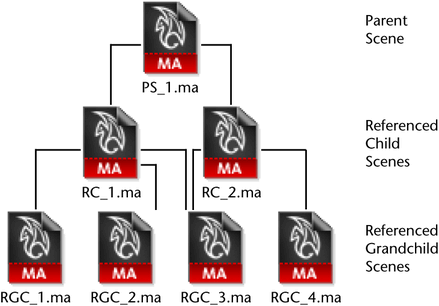
A hierarchy of multi-level references is one method for segmenting various components and levels of display complexity within a large scene. See File hierarchy assembly.
A referenced file cannot reference its parent scene or any other file that resides above it in the reference hierarchy.
Foster parent nodes
Foster parents are created any time a node from the referencing scene is parented to a referenced node. For example, if you reference geometry and then parent an object under it, a foster parent node is created when you unload your reference.
The foster parent node ensures that parenting is properly reapplied when you reload a reference. Since files are saved with references unloaded, both export and save automatically generates foster parent nodes.
To export the file without foster parent nodes, you can export with Preserve References turned off. However, this bakes all referenced nodes into the exported scene file. See Exporting file references.
Foster parent nodes only exist for the duration the reference is unloaded; they do not persist after the reference has been reloaded.