The following section provides examples of how you can use constraints in your Scene Assembly workflows.
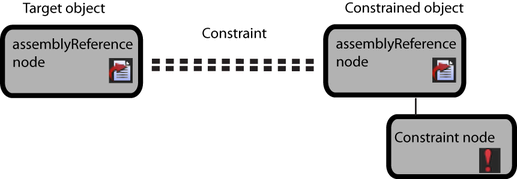
Example 1: Target and constrained objects are assemblyReference nodes
Use-case
In this example, the target object is a hierarchical assembly reference ( assemblyReference node with Scene representations containing other assemblyReference nodes) of a cruise ship model. The assembly reference contains several representations of the cruise ship, each of varying levels of detail. The constrained object is an assembly reference of a character located on the deck of the ship. When the ship model is animated to simulate its motion on the water, the character follows the same motion. This setup lets the different representations of each assembly reference (ship and character) to be quickly switched to suite the needs of the required shot.
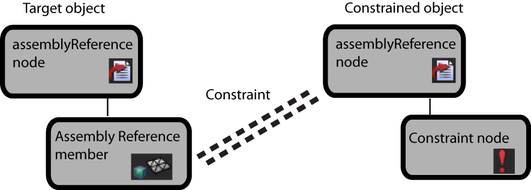
Example 2: Target object is an assembly reference member and constrained object an assemblyReference node
Use-case
An assembly reference of a prop object, such as a flashlight or crowbar, is constrained to the member of another assembly reference. When the character is animated, the prop remains in the character's hand.
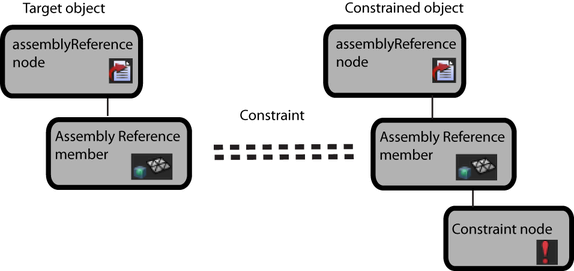
Example 3: Target and constrained objects are assembly reference members
Use-case
An assembly reference member, the hand control of a character rig, is constrained to an assembly reference member of another assembly reference, which is the steering wheel of a car model. When the wheel is turned, the character's hand remains attached to the wheel.
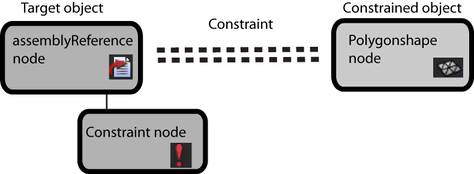
Example 4: Target is an assemblyReference node or an assembly reference member and constrained object is a main scene Maya object
Use-case
A main scene object, such as a user-defined camera, is a target object that constrains an assembly reference member, such as a part of a cruise ship model. When the ship model moves or rocks back and forth, the camera remains fixed and tracks the ship's motion.