- Performance curve
-
- For a fan or pump, it represents the pressure rise (head) that the device can produce as a function of flow rate.
- For a valve or damper, it represents the pressure drop as a function of flow rate.
You can select the performance curve method for fans, pumps, valves, and dampers.
- Constant Flow
- Constant flow equipment produces the same, specified flow rate, irrespective of pressure (within a range). Enter a value of constant flow for the equipment.
You can select the Constant Flow method for fans and pumps.
- K Factor
- K factor represents minor losses, which means the pressure losses attributed to the flow flowing through fittings, valves, bends, elbows, tees, inlets, exits, enlargements, and contractions.
React Fluids handles the K factor in the three ways:
- For valves and dampers, you can select whether to use a K factor or other method
- For 2-way couplings and elbows, you can specify a K factor or use the K factor value computed by the solver
- For 3-way couplings (T couplings), you can only use the value computed by the solver because it is not possible to associate the k factor with each outlet or inlet.
You can select the K Factor method for valves and dampers.
- Cv
- Cv, referred to as Flow Coefficient, is used to specify the capacity of a control valve in imperial units.
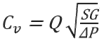
where:
Cv - flow coefficient of a valve
Q - rate of flow (US gallons per minute)
SG - specific gravity of fluid (for water, it is 1)
ΔP - pressure drop across valve (psi)
You can select the Cv method for valves.
- Kv
- Kv, referred to Flow Factor, is a metric equivalent of Cv.
You can select the Kv method for valves.