Flow Production Tracking Panel
このドキュメントは、Toolkit の設定を管理するユーザのみが使用可能な機能について説明します。詳細については、『Flow Production Tracking 統合ユーザ ガイド』を参照してください。
 コンテンツ
コンテンツ
Flow Production Tracking Panel を設定する
Flow Production Tracking Panel で広範囲に設定できる主な領域は 2 つあります。UI の文字の表示と、データに関連付けるアクションです。次のセクションでは、2 つのシステムの設定を制御する方法について説明します。
表示内容を設定する
詳細領域の値とリストは両方とも Flow Production Tracking_fields フックから設定可能です。正確な値を表示するために、このフックをサブクラス化して実装を変更できます。
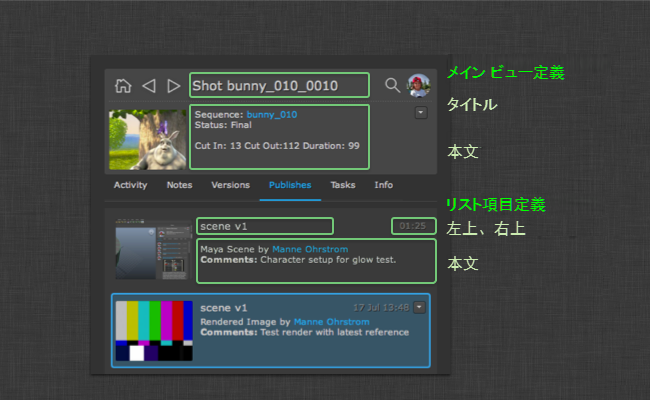
システムをテンプレート化する
フックはシンプルなテンプレート言語をサポートしているため、優れた柔軟性が得られます。また、Qt でサポートされている HTML サブセットもサポートしているため、表示される値の色、フォント サイズ、ウェイトなどをコントロールできますテンプレート言語は次のように機能します。
Flow Production Tracking の値は、
{brackets}のように<b>Description:</b> {description}で囲まれています。このテンプレートをレンダリングすると、{description}の部分が説明フィールドの値で置き換えられます。値が空以外の場合にのみ表示される値にオプションの接頭辞または接尾辞を指定する場合、
{[Prefix]sg_field[suffix]}構文を使用できます。両方の値が追加されている場合、テンプレート{[Start: ]start_date} {[End: ]end_date}はStart: 12 July 2009 End: 14 July 2012をレンダリングします。ただし、終了日を設定していない場合はStart: 12 July 2009をレンダリングします。一部の値が設定されていない場合はフォールバックを定義することができます。Flow Production Tracking のバージョンについては、プロデューサがアーティストの代わりにバージョンを送信するというワークフローをサポートするため、
created_byフィールドがartistフィールドよりも優先されます。この場合、バージョンはプロデューサによって作成されますが、artistフィールドはアーティストに設定されます。ただし、いつもそういうわけではありません。アーティストが自分の作業を送信するパイプラインでは、アーティスト欄は空欄になります。バージョンを表示する場合、最初にartistフィールドを確認できるようにしておくと役立ちます。今回このフィールドは設定されていないため、created_byフィールドにフォールバックします。このようにするには、Created By: {artist|created_by}のように構文{field1|field2}を使用します。{[Created By: ]artist|created_by}のようにオプション フィールドを組み合わせることができます。
このフックには次のメソッドが含まれます。
リストに表示される項目を制御する
get_list_item_definition() メソッドは、Flow Production Tracking のエンティティ タイプを考慮して、さまざまなリストの項目の外観を制御するディクショナリを返します。たとえば、top_left、top_right、および body といったキーを持つディクショナリを返します。
{
"top_left": "<big>{code}</big>",
"top_right": "{updated_at}",
"body": "By: {created_by}<br>Description: {description}"
} 上部の細部領域を制御する
get_main_view_definition() メソッドは、Flow Production Tracking のエンティティ タイプを考慮して、title キーと body キーを含むディクショナリを返します。これらの値は、詳細領域のオブジェクトの外観を次のように制御します。
{
"title": "{type} {code}",
"body": "By: {created_by}<br>Description: {description}"
} [情報] (Info)タブに表示されるフィールドを制御する
get_all_fields() メソッドは、[情報] (Info)タブで任意のエンティティがレンダリングされる場合に表示するフィールドのリストを返します。
タスク並べ替えフィールドを設定する
[タスク] (Task)タブを表示すると、タスク エンティティを特定のフィールドで並べ替える[並べ替え] (Sort)ボタンが配置されています。フィールドの一覧を設定するには、アプリ設定に sort_fields の設定を追加します。これにより、ユーザが使用できる並べ替えオプションをカスタマイズできます。
以下に、アセット名で並べ替えるためのフィールドを追加し、既定の並べ替えオプションを含める設定の例を示します。
sort_fields:
tasks:
- { field_code: "due_date", display_name: "Due Date", default: True }
- { field_code: "start_date", display_name: "Start Date" }
- { field_code: "sg_status_list", display_name: "Status" }
- { field_code: "step", display_name: "Step"}
- { field_code: "entity.Asset.code", display_name: "Asset Name"}field_code値には、Flow Production Tracking で有効なフィールド コードを指定する必要があります。field_codeを指定するときにドット表記を使用すると、リンクされたエンティティのフィールドにアクセスできます。- オプションの
defaultキー値を指定すると、オプションを指定できます。指定したオプションは、既定でオンになります。
フィルタを設定する
[フィルタ] (Filter)ボタン メニューのオプションを使用して、Flow Production Tracking パネルの特定のタブに表示される項目をフィルタできます。このメニューには、プリセット フィルタとフィールド フィルタが一覧表示されます。
メニューに表示されるフィールドを直接設定することはできませんが、shotgun_fields.py フックを使用してメニュー項目に表示されるフィールドを設定することはできます。メニュー項目に表示するように設定されたすべてのフィールドが、フィルタ メニューに表示されます。
プリセット フィルタは、フィルタ メニューの[プリセット] (Presets)セクションの下に表示されます。このセクションが表示されない場合、設定されたプリセット フィルタはありません。プリセット フィルタとは、Web UI で作成できる保存済みフィルタと同様にオンとオフを切り替えることができる、事前設定された一連のフィルタのことです。これらは、パネル アプリの UI では設定できません。定義するには shotgun_filters.py フックを使用してください。プリセット フィルタを使用すると、単純なフィールド値フィルタよりも複雑なフィルタを作成できます。
プリセット フィルタを設定するには、shotgun_filters.py フックを引き継いて、get_preset_filters() メソッドにロジックを実装する必要があります。このメソッドは、ディクショナリを返す必要があります。ディクショナリでは、キーがプリセット フィルタ名として、値が Flow Production Tracking API と同じ形式に準拠しているフィルタのリストとして指定されています。
アクションを設定する
アクションは Flow Production Tracking のデータを操作するコードの小さなスニペットです。例を次に示します。
- 任意の Flow Production Tracking バージョンの RV を起動するアクション
- 任意のタスクに自分に割り当てることができるアクション
- Maya リファレンスとして Maya に Flow Production Tracking パブリッシュをロードするアクション
アクションの実際のペイロードは アクション フック で定義されます。アクションのロジックを定義したら、アプリ設定の Flow Production Tracking オブジェクトにこのアクションをマップすることができます。次に、このアクション マッピングの例を示します。
action_mappings:
PublishedFile:
- actions: [reference, import]
filters: {published_file_type: Maya Scene}
- actions: [texture_node]
filters: {published_file_type: Rendered Image}
Task:
- actions: [assign_task]
filters: {}
Version:
- actions: [play_in_rv]
filters: {}上記の例では、reference、import、texture_node、assign_task、および play_in_rv といったアクションを使用します。次に、さまざまな Flow Production Tracking のオブジェクトと条件にこのアクションをマップします。たとえば import アクションは、タイプが「Maya Scene」であるすべてのパブリッシュに表示されるよう要求しています。
オブジェクトがパネルにロードされると、上記のアクション設定が読み込まれ、分析されます。現在のオブジェクトに適したアクションのリストが決定され、generate_actions() フック メソッドが実行されます。この特定の Flow Production Tracking オブジェクトに対してアクションを実行できるかどうかをフック コードが判断できるように、この時点で指定したエンティティの Flow Production Tracking データがフックに渡されます。この方法により、各フックで表示前にチェックを実行できます。たとえば、play_in_rv フックはメディアをローカルで利用できる場合にのみ意味を持ちます。設定でセットアップされたアクション マッピングは指定した Flow Production Tracking エンティティで有効にするアクションをパネルに通知しますが、指定したオブジェクトに適していないと generate_actions() メソッドによって判断された場合は、すべてのアクションが表示されない可能性があります。
generate_actions() メソッドから返されるアクションはアクション メニューに表示されます。ユーザがクリックすると、execute_action() フック メソッドが呼び出されてアクションが実行されます。
パネルがサポートするアプリケーションごとに、適切なアクションを実装するアクション フックがあります。たとえば Maya などの場合、既定のフックは reference、import、texture_node の各アクションを実装し、それぞれが特定の Maya コマンドを実行して現在の Maya シーンにパブリッシュを取り込みます。すべてのフックと同様に、アクションを完全にオーバーライドおよび変更できます。また、埋め込まれたフックに基づいたフックも作成できるため、たくさんのコードを複製しなくても、組み込みのフックに他のアクションを簡単に追加できます。
パネルは Toolkit の第 2 世代のフック インタフェースを使用するため、柔軟性に優れています。このフックの形式は改善された構文を使用します。これは既定の構成設定で次のように表示されます。
actions_hook: '{self}/tk-maya_actions.py'キーワード {self} は、フックのアプリの hooks フォルダを確認するように Toolkit に指示します。このフックをユーザが設定した実装でオーバーライドする場合は、値を {config}/panel/maya_actions.py に変更します。これにより、設定フォルダ内の hooks/panel/maya_actions.py と呼ばれるフックを使用するように Toolkit に指示します。
詳細については、アプリに付属するフック ファイルを参照してください。フックは継承も活用します。つまり、フック内のすべての項目をオーバーライドすることなく、さまざまな方法で既定のフックを簡単に拡張または強化して簡単にフックを管理できます。
第 2 世代のフック形式については、こちらで確認してください。
フックの継承を使用すると、次のように既定のフックに他のアクションを追加できるようになります。
import sgtk
import os
# toolkit will automatically resolve the base class for you
# this means that you will derive from the default hook that comes with the app
HookBaseClass = sgtk.get_hook_baseclass()
class MyActions(HookBaseClass):
def generate_actions(self, sg_data, actions, ui_area):
"""
Returns a list of action instances for a particular object.
The data returned from this hook will be used to populate the
actions menu.
The mapping between Flow Production Tracking objects and actions are kept in a different place
(in the configuration) so at the point when this hook is called, the app
has already established *which* actions are appropriate for this object.
This method needs to return detailed data for those actions, in the form of a list
of dictionaries, each with name, params, caption and description keys.
Because you are operating on a particular object, you may tailor the output
(caption, tooltip etc) to contain custom information suitable for this publish.
The ui_area parameter is a string and indicates where the publish is to be shown.
- If it will be shown in the main browsing area, "main" is passed.
- If it will be shown in the details area, "details" is passed.
:param sg_data: Flow Production Tracking data dictionary with all the standard publish fields.
:param actions: List of action strings which have been defined in the app configuration.
:param ui_area: String denoting the UI Area (see above).
:returns List of dictionaries, each with keys name, params, caption, group and description
"""
# get the actions from the base class first
action_instances = super(MyActions, self).generate_actions(sg_data, actions, ui_area)
if "my_new_action" in actions:
action_instances.append( {"name": "my_new_action",
"params": None,
"group": "Pipeline Utils",
"caption": "My New Action",
"description": "My New Action."} )
return action_instances
def execute_action(self, name, params, sg_data):
"""
Execute a given action. The data sent to this be method will
represent one of the actions enumerated by the generate_actions method.
:param name: Action name string representing one of the items returned by generate_actions.
:param params: Params data, as specified by generate_actions.
:param sg_data: Flow Production Tracking data dictionary with all the standard publish fields.
:returns: No return value expected.
"""
if name == "my_new_action":
# do some stuff here!
else:
# call base class implementation
super(MyActions, self).execute_action(name, params, sg_data)
これで、この新しいアクションを設定内のパブリッシュ タイプのセットにバインドできます。
action_mappings:
PublishedFile:
- actions: [reference, import, my_new_action]
filters: {published_file_type: Maya Scene}
Version:
- actions: [play_in_rv]
filters: {}上記のようにフックの派生を利用すれば、カスタム フック コードには、管理と更新を簡単にするために実際追加するビジネス ロジックを含めるだけで構いません。