Access
Ribbon:
Sketch tab
 Draw panel
Draw panel
 Equation Curve
Equation Curve
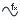
Equations can be parametric, where X and Y vary as a function of a variable t, or explicit, where Y varies as a function of X.
- x(t) or r(t)
- Parametric Specify x or r as a function of t. For example x(t): t^2.
- y(t) or θ(t)
- Parametric Specify y or θ as a function of t. For example, y(t): t^2.
- y(x) or r(a)
- Explicit Specify an equation for y or r as a function or x or a. For example, y(x): x^2.
- tmin, xmin, or amin
- Specify the minimum value to evaluate. The t, x, or a displays, depending on the Parametric/Explicit and Cartesian/Polar settings.
- tmax, xmax, or amax
- Specify the maximum value to evaluate. The t, x, or a displays, depending on the Parametric/Explicit and Polar/Cartesian settings.
- Parametric or Explicit
- Parametric equations use two equations to evaluate x and y or r and θ. Explicit equations use one equation to evaluate y or r and you specify a range for x or a.
- Cartesian or Polar
- Determine whether to specify equations using a Cartesian (x,y) coordinate system or polar (r, θ) coordinate system.
- Show units
- When not selected, the equation displays as it is entered. When selected, the equation displays with all units parsed.
- Show transform
- Available when editing an equation curve. Displays the values for X, Y, and Rotation for the transform. These values are zero until the curve is moved by dragging, constraints, or dimensions.