Areas of the mold which cannot be cooled effectively by normal cooling channels may require the use of bubblers. Bubblers divert the coolant flow into areas that would normally lack cooling.
Bubblers are created by fitting a tube in the center of a drilled hole, forming an annular channel. The coolant flows into the bottom of the tube and bubbles out of the top, like a fountain. The coolant continues down around the outside of the tube and continues through the cooling channels. The following diagram illustrates the coolant flow through a bubbler.
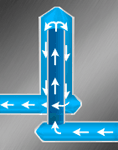
Bubblers provide the most effective cooling of parts with slender cores. The diameter of both sections of the bubbler must ensure that the flow resistance in both sections is equal. The condition for this is-inner diameter / outer diameter = 0.707
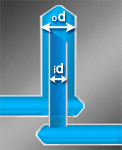
Bubblers are commercially available and are usually screwed into the core. The tubing should be beveled at the end to enlarge the cross section of the outlet for diameters up to 4mm. Bubblers can be used for core cooling and for cooling flat mold sections where drilled or milled channels can not be used.